Catalyst for producing gluconic acid sodium salt, method of preparing the same and applications
A sodium gluconate and catalyst technology, applied in the field of chemical building materials, can solve the problems of low product cost performance, difficult separation of products, large amount of catalyst, etc., and achieve the effects of less by-products, improved reaction selectivity, and good reactivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1: the preparation of composite catalyst
[0029] 1. Add 50ml of water to 45g of dry activated carbon (particle size 200 mesh) to suspend the activated carbon in water.
[0030] 2. 2.54g of nickel oxide (containing 2 grams of nickel) is dissolved in 9.9ml of 25% hydrochloric acid, and 7 grams of chloroplatinic acid solution (mass concentration is 30%, containing 1 gram of platinum) and 18.8 grams of Chloropaladic acid solution (mass concentration is 25%, containing 2 grams of palladium), stirred evenly.
[0031] 3. Mix the above suspensions and solutions, heat up to 75° C., add 30.7 grams of 15% NaOH solution (containing 4.6 grams of NaOH) to make the suspension alkaline and have a pH of 10.
[0032] 4. Stir at 75° C. for half an hour, add 10.19 ml of 37% formaldehyde solution to reduce platinum, palladium and nickel compounds.
[0033] 5, filter, wash, make the composite catalyst A of activated carbon supported platinum, palladium, nickel, wherein contain ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2: the preparation of other several catalysts
[0035] Catalysts were prepared under the same conditions as in Example 1, except that the types and weight percentages of the catalyst components were changed to prepare catalysts B, C, D, E, F, and G respectively. The catalyst composition is shown in Table 1.
[0036] Table 1 Catalyst Composition
[0037] catalyst
Embodiment 3
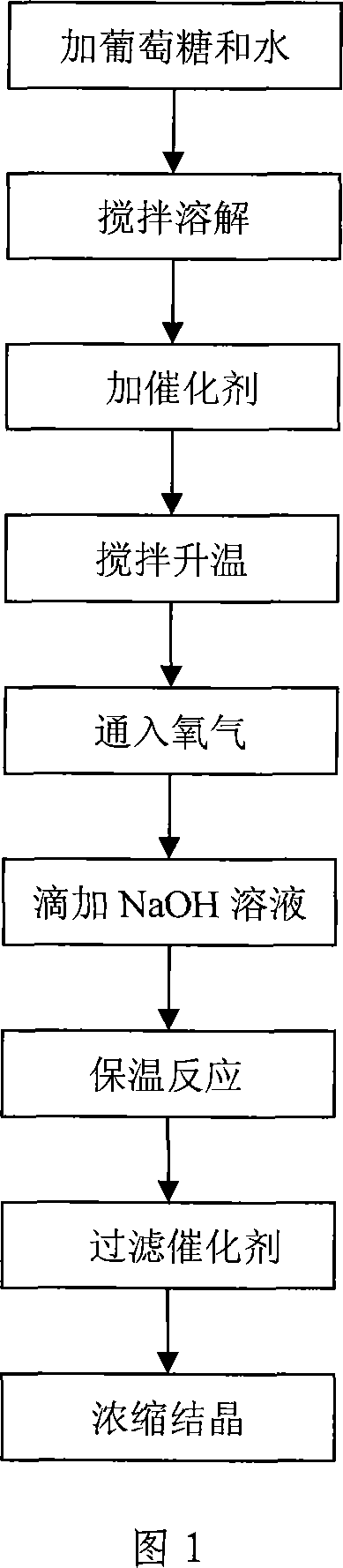
[0038] Embodiment 3: Glucose oxidation synthesis sodium gluconate
[0039] Add 18 grams of glucose in a 250ml four-necked flask, then add 12ml of water, stir and dissolve to obtain a glucose solution with a concentration of 60%, to which 0.36 grams of catalyst A prepared in Example 1 and Example 2 are added (catalyst and glucose mass ratio is 2:100), the reaction solution was stirred and heated to 50°C, at this time, oxygen was introduced, and NaOH solution (concentration was 15%) was added dropwise during the reaction to keep the reaction solution alkaline (pH was 8-10) , heat preservation reaction for 3 hours. After the reaction, filter the catalyst, concentrate and crystallize to obtain sodium gluconate. Repeat the above operation, just change catalyst A to catalyst B, C, D, E, F, G respectively. The catalyst reaction evaluation results are shown in Table 2.
[0040] The yield is determined by measuring the residual sugar content in the reaction system by high-pressure l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com