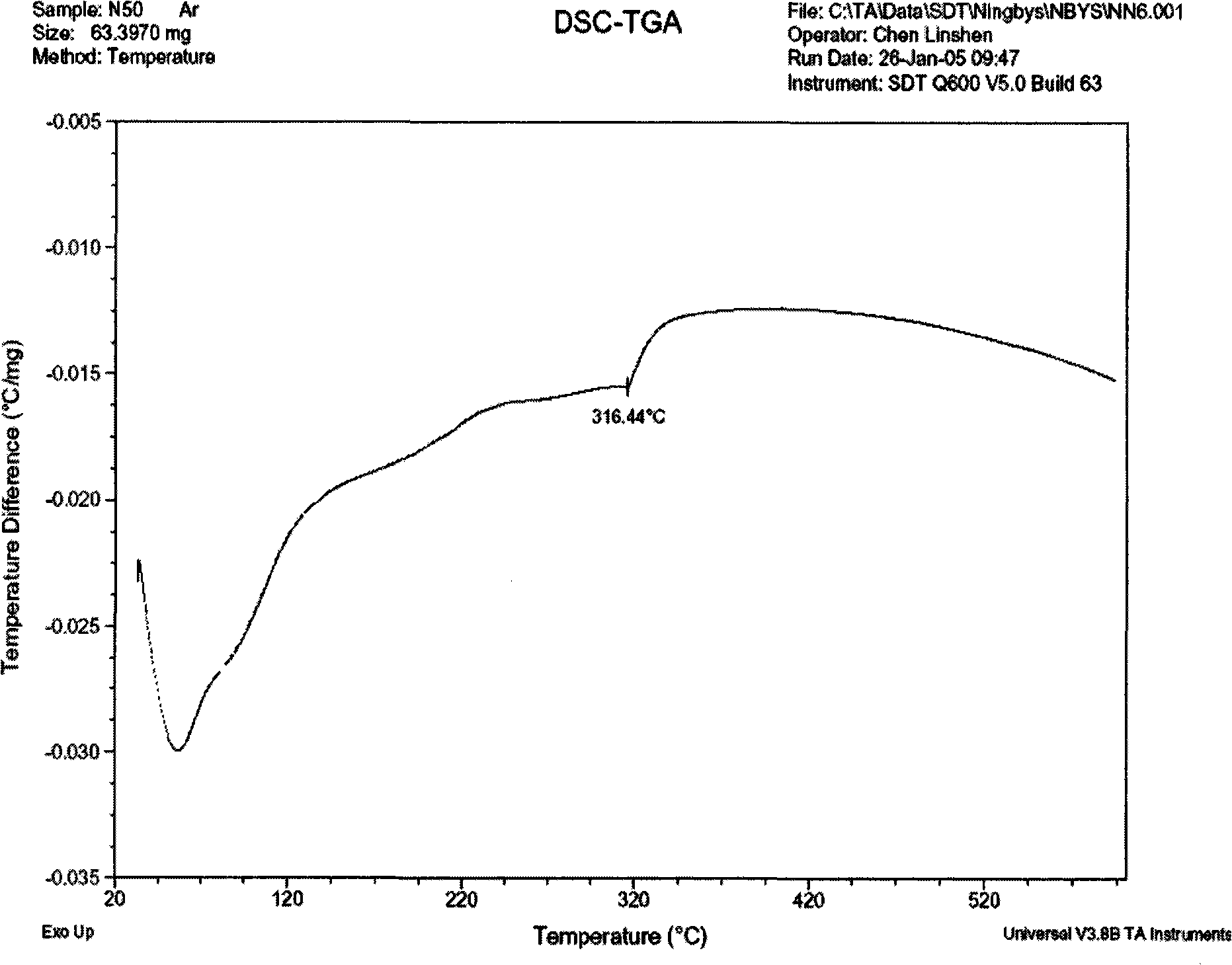
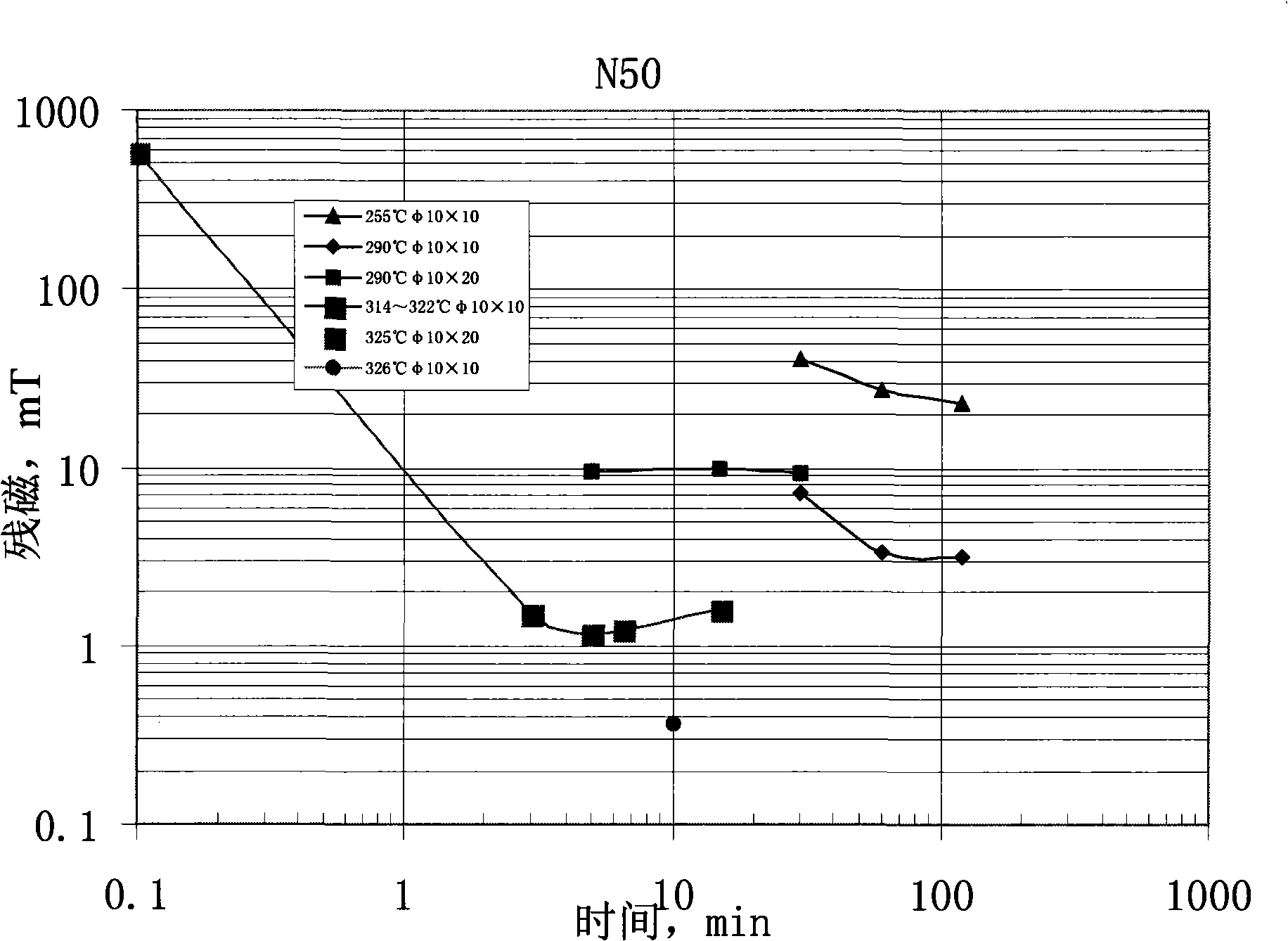
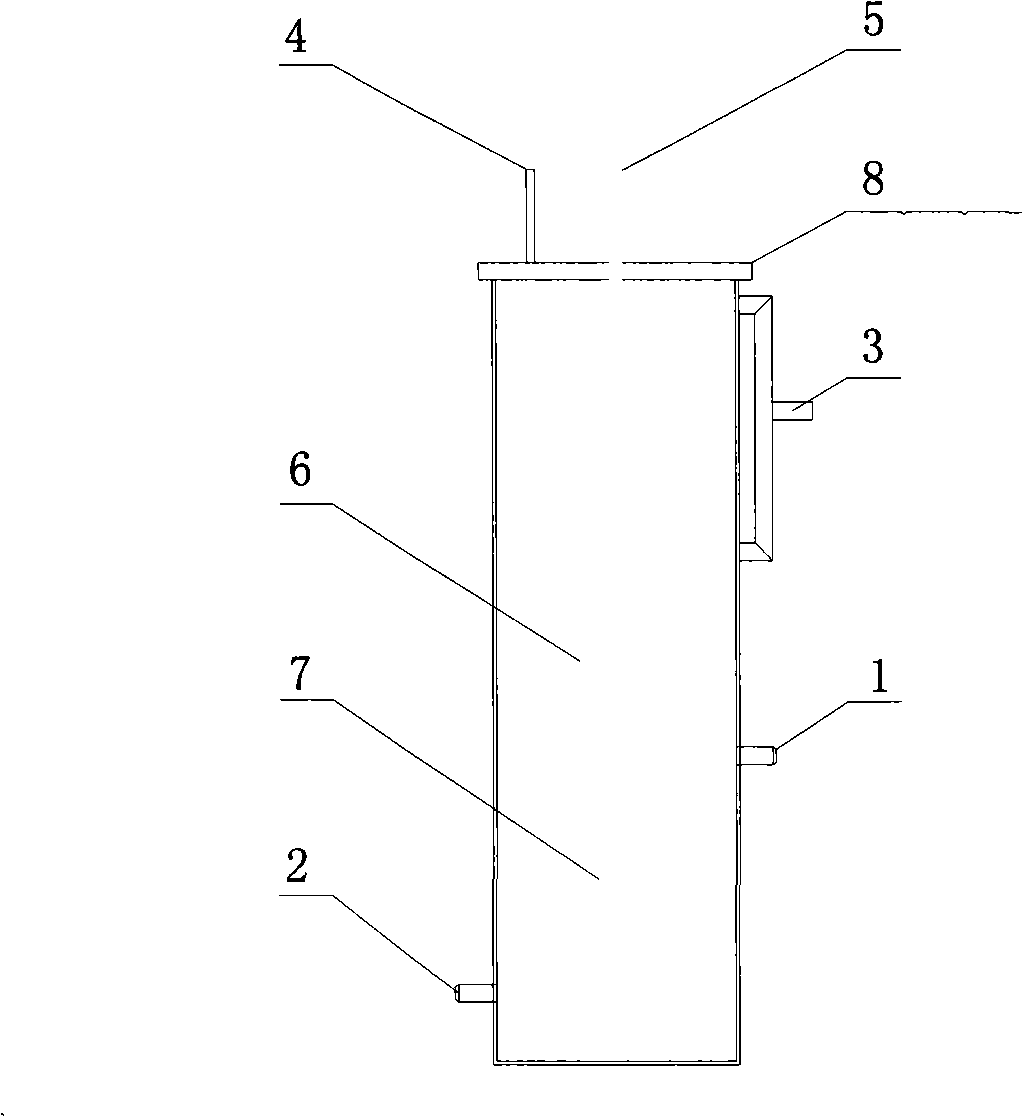
Method and apparatus for stew demagnetizing sintered Nd iron boron permanent magnet
A permanent magnet and neodymium-iron-boron technology, which is applied in the direction of magnetic objects, magnetic materials, inorganic materials, etc., can solve the problems of high heating temperature, difficult heat dissipation of permanent magnets, and large energy consumption, and achieve the effect of wide applicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Four 42SH sintered NdFeB permanent magnet φ10×11 samples were magnetically measured at 80°C, and then dried in an oven. Then put the sample into the workpiece basket 6, put the high-temperature gasket, the flange 8, the lifting rod 5 and the hook of the workpiece basket, and seal the furnace body by tightening the bolts. The gas inlet 3 is fed with inert gas, the gas replaces the air in the furnace body, and then the gas outlet 4 forms a gas protection circuit. The sample is suspended in the furnace body 19 through the lifting rod 5 without contacting the oil. Open the high-temperature electromagnetic valve 11, open the high-temperature electromagnetic valve 17, open the manual valve 18, and start the hot oil pump 13 to form an "oil injection circuit ①". When the liquid level detector 12 gives a lower liquid level signal, the high temperature solenoid valve 11 is closed, the heater 14 is started, and the temperature sensors 15 and 20 control the temperature of the heat...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Cut out φ10×11 samples from the same sintered NdFeB permanent magnet 48H blank, take 3 samples for vacuum demagnetization, and then 3 samples for demagnetization with the same process as in Example 1, the same process for chamfering and electroplating NiCuNi for both, and test the magnetic properties at 80 °C can, but the magnetic survey is unified by φ10, and the data recorded are shown in Table 3, as can be seen, the demagnetization process H of the present invention cJ higher.
Embodiment 3
[0052] The magnetized 38H specification R2.9×10.4×5.8×1.3 is sintered with Zn-plated NdFeB permanent magnet, and demagnetized in an oil bath at 335°C×10min in the device mentioned in Example 1. 20pcs were randomly selected before and after demagnetization to test the magnetic flux, and the average change of the magnetic flux was less than 1%.
[0053] Table 1 Comparison of magnetic properties of sintered NdFeB permanent magnets with external heating furnace for vacuum demagnetization at 50°C
[0054]
[0055] Table 2 Comparison of magnetic properties of 42SH sintered NdFeB permanent magnets immersed in oil and thermally demagnetized at 80°C
[0056]
[0057] Table 3 Comparison of magnetic properties of 48H sintered NdFeB permanent magnets under vacuum demagnetization and oil bath thermal demagnetization at 80°C
[0058]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Curie point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com