Rh-epo nasal formulations with low sialic acid concentration for the treatment of diseases of the central nervous system
A technology of erythropoietin and sialic acid, which is applied in the field of biopharmaceutical industry, can solve the problem of not being able to promote the proliferation, differentiation and maturation of red blood cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
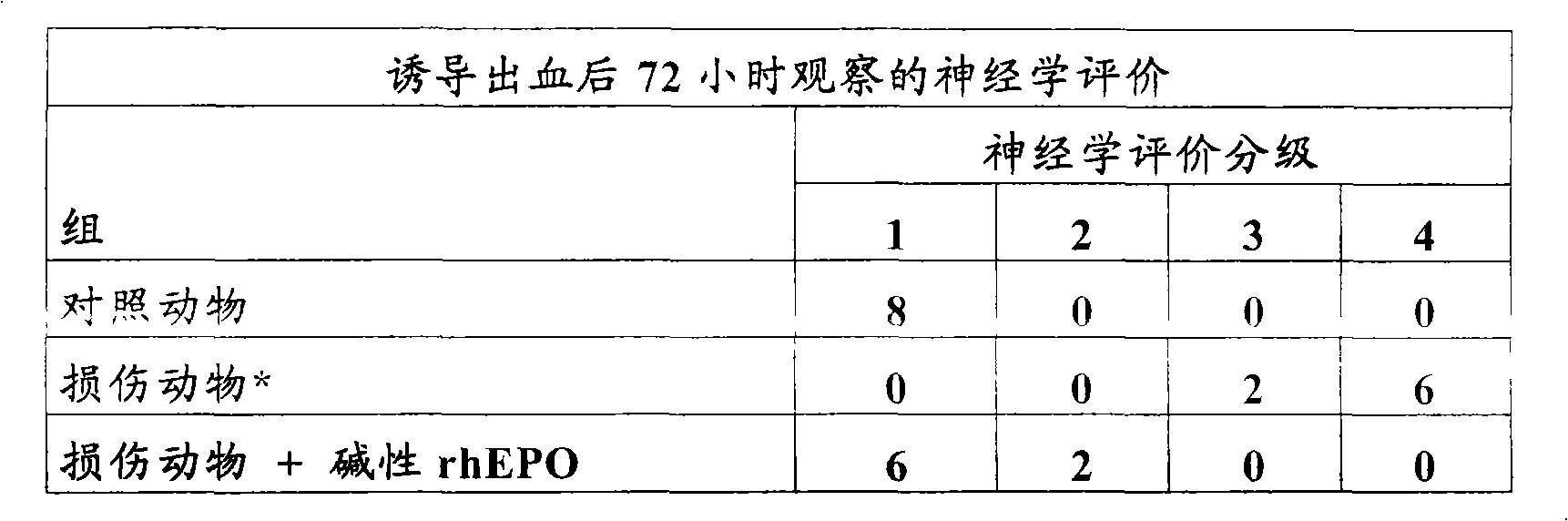
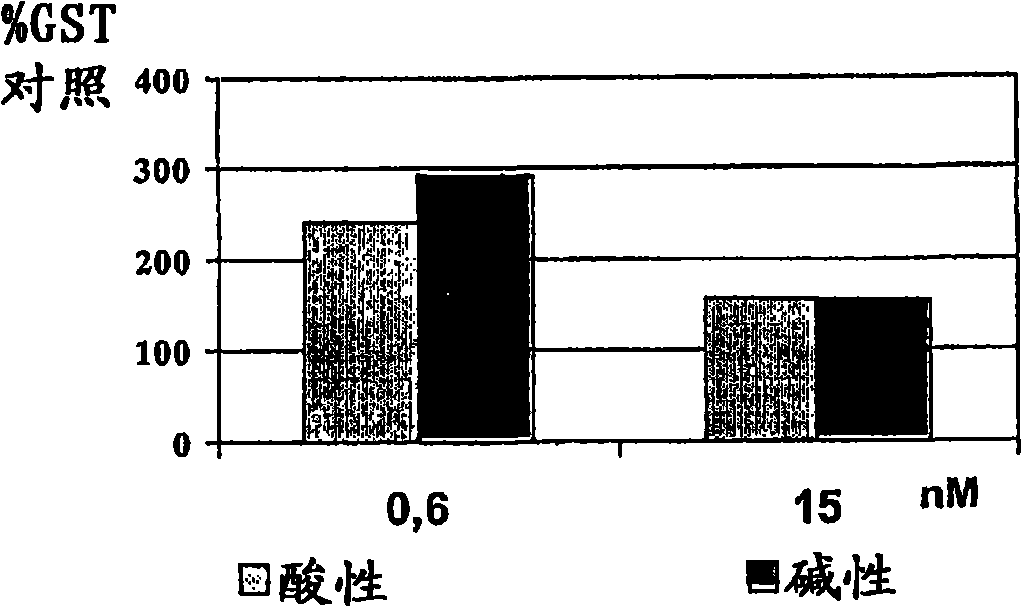
Examples
Embodiment 1
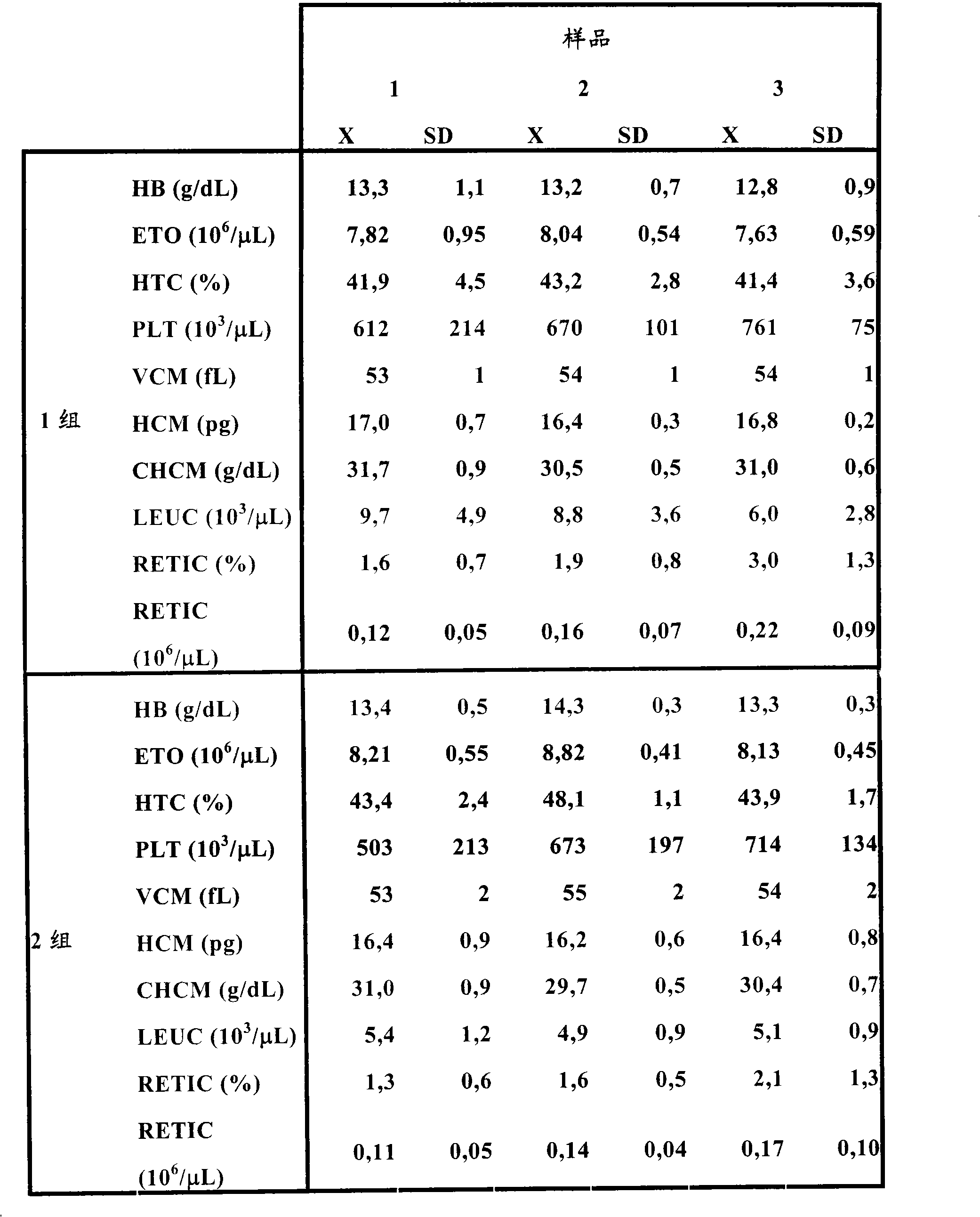
[0046] Purification of rhEPO with low content of sialic acid
[0047] In order to obtain basic erythropoietin with less than 40% sialic acid, three basic chromatographic steps were performed, starting from a material that was very complex and had a lot of contaminating proteins, since this material contained 5% fetal bovine serum. Additional steps are then performed to obtain the target isoform.
[0048] For diafiltration and concentration of basic rhEPO a laboratory scale ultrafiltration system (SARTOFLOW SLICE 200) connected to a peristaltic pump (IP55 Watson-Marlow) was used. A 10 kDa Hydrosart membrane was used. The work was performed at a flow rate of 1.9 ± 0.25 mL / min, a push pressure (P1) of 2.9 ± 0.25 bar, a retained fraction pressure (P2) of 0.65 ± 0.1 bar and a transmembrane (TM) pressure of 1.8 ± 0.2 bar. For the determination of protein concentration, an Ultrospec™ 3100 spectrophotometer was used at λ = 280 nm. For the diafiltration process, use NaH with a pH ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] A nasal formulation of rhEPO containing low sialic acid using HPMC as a bioadhesive polymer, histidine hydrochloride as a stabilizer, Tween 80 as a nonionic surfactant and benzalkonium chloride as a preservative.
[0053] Preparation:
[0054] The preparation of this solution starts with 30% by volume of water for injection in the total volume of the formulation. This volume is used to dissolve preservatives, buffers and isotonic agents. In addition, in a container of appropriate capacity, put water for injection with a volume equal to 15% of the total volume of the preparation, and heat to a temperature of 85 to 95° C., and disperse the polymer under vigorous and constant stirring. Once the polymer is wetted, the previously prepared solution is incorporated into it while shaking vigorously until all is homogenized. Shaking was then reduced for incorporation of corresponding amounts of basic rhEPO, non-ionic surfactant and protein stabilizer. Finally, the volume was ...
Embodiment 3
[0068] RhEPO nasal formulation with low sialic acid content similar to the previous example but using methylcellulose as the bioadhesive polymer
[0069] Preparation method: similar to Example 2.
[0070] The composition of the prepared preparation is as follows:
[0071] Component Ratio
[0072] Basic rhEPO 0.8mg / mL
[0073] Methylcellulose 3.0mg / mL
[0074] Histidine hydrochloride 1.0mg / mL
[0075] Sodium dihydrogen phosphate 2mg / mL
[0076] Disodium hydrogen phosphate 0.7mg / mL
[0077] Tween 80 0.25mg / mL
[0078] Sodium chloride 7.4mg / mL
[0079] Disodium EDTA 0.1mg / mL
[0080] Benzalkonium Chloride 0.2mg / mL
[0081] Water for injection 1ml
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com