Low mass transfer resistance infiltration flow type electrochemical method and reaction apparatus thereof
A technology of mass transfer resistance and electrochemistry, applied in the field of electrochemistry, can solve problems such as slow mass transfer, and achieve the effects of simple operation, improved reaction surface area and activity, and improved electrochemical efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Embodiment 1 handles reactive brilliant red X-3B simulation dye wastewater
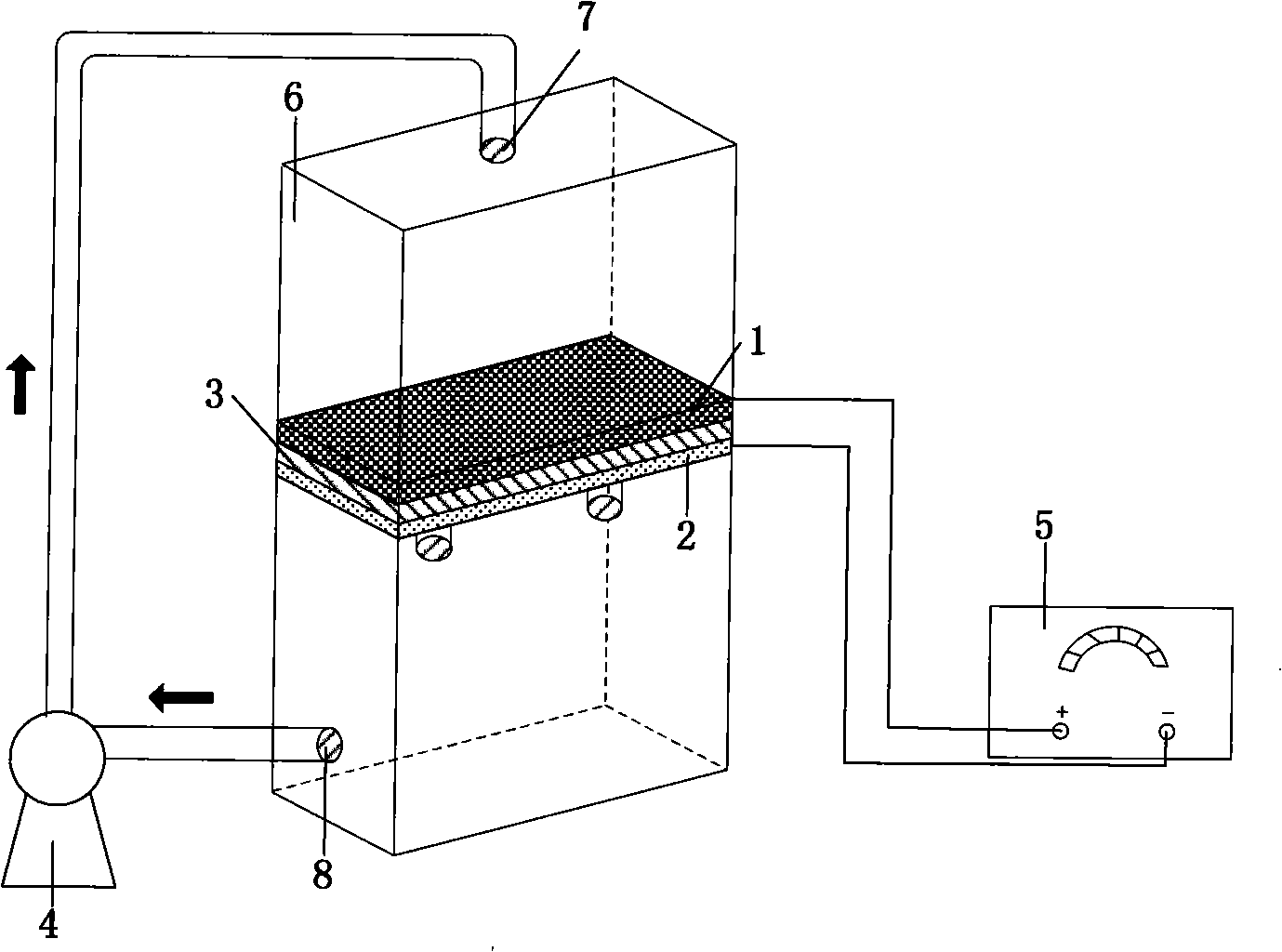
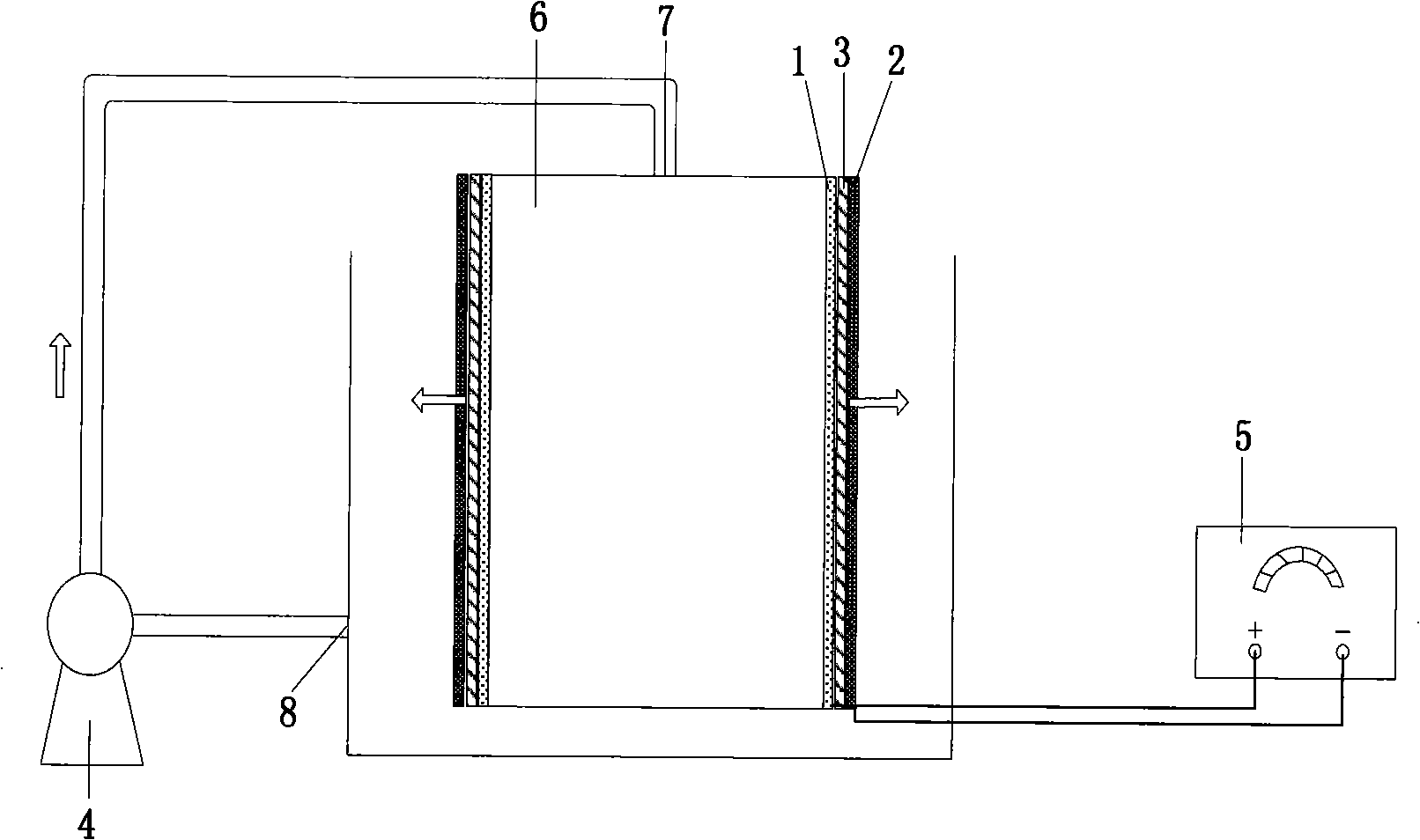
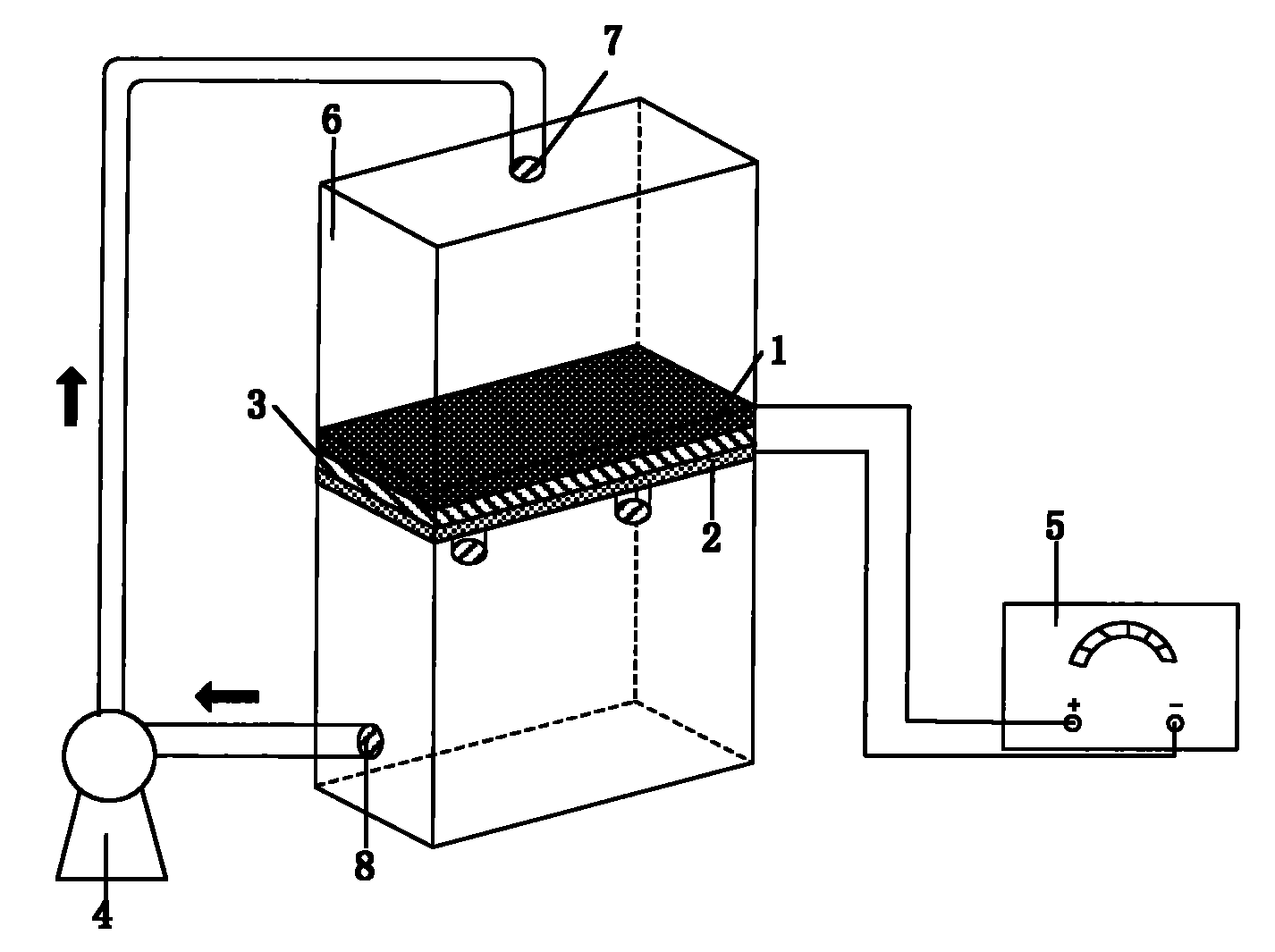
[0021] Such as figure 1 As shown, the reaction device adopted in this embodiment includes a reaction vessel 6, the reaction vessel 6 is divided into upper and lower parts, the middle is separated by an anode 1, a cathode 2 and an insulating layer 3, and the solution is continuously flowed in the upper and lower parts of the reaction vessel 6 by a peristaltic pump 4. During the solution cycle, the anode 1 and the cathode 2 are continuously permeated, and the mass transfer resistance is reduced through the interaction with the electrodes during the process. The DC stabilized power supply 5 applies the voltage to the anode 1 and the cathode 2, and can be adjusted according to the reaction conditions.
[0022] During implementation, the anode 1, the cathode 2 and the insulating layer 3 are respectively fixed on the reaction vessel 6, the anode 1 and the cathode 2 are connected to the DC stabilized...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Embodiment 2 The influence of different voltages on the decolorization rate of reactive brilliant red X-3B
[0038] The reaction device and implementation process used in this embodiment are the same as in Example 1.
[0039] The specific implementation conditions and results of this embodiment are as follows:
[0040] Reaction target solution volume: 300mL
[0041] Reaction target solution concentration: Reactive Brilliant Red X-3B 50mg / L
[0042] Ambient temperature: 25°C
[0043] Initial pH: 7
[0044] Electrolyte concentration: 2g / L
[0045] Electrode area: 28cm 2
[0046] Anode: activated carbon fiber carbon nanotube electrode
[0047] Cathode: activated carbon fiber carbon nanotube electrode
[0048] Volume flow: 80.2mL / min.
[0049] The decolorization rates of different voltage treatments are shown in Table 2.
[0050] Table 2 Example 2 The dye decolorization rate (%) of different voltage treatment
[0051]
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3 Treatment of Reactive Brilliant Blue X-BR Simulation Dye Wastewater
[0053] The reaction device and implementation process used in this embodiment are the same as in Example 1.
[0054] The specific implementation conditions and results of this embodiment are as follows:
[0055] Reaction target solution volume: 300mL
[0056] Reaction target solution concentration: Reactive Brilliant Blue X-BR 100mg / L
[0057] Ambient temperature: 25°C
[0058] Initial pH: 2
[0059] Electrolyte concentration: 1g / L
[0060] Electrode area: 28cm 2
[0061] Voltage: 8V
[0062] Anode: activated carbon fiber carbon nanotube electrode
[0064] Volume flow: 122.5mL / min.
[0065] The decolorization rate and COD removal rate of dyes after treatment are shown in Table 3.
[0066] The decolorization rate and COD removal rate of dyestuff after table 3 embodiment 3 processes
[0067] time (min)
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com