Low-alloy high-strength steel laser composite weld hardness control method
A composite weld and hardness control technology, used in welding equipment, manufacturing tools, metal processing equipment, etc., can solve the problem of lack of improvement of weld formation, and achieve reduction of microhardness, reduction of martensitic structure ratio, and reduction of martensitic structure. The effect of the content of the tensite structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] This embodiment is used for welding low-alloy high-strength steel with dimensions of 250mm×100mm×10mm (length×width×thickness).
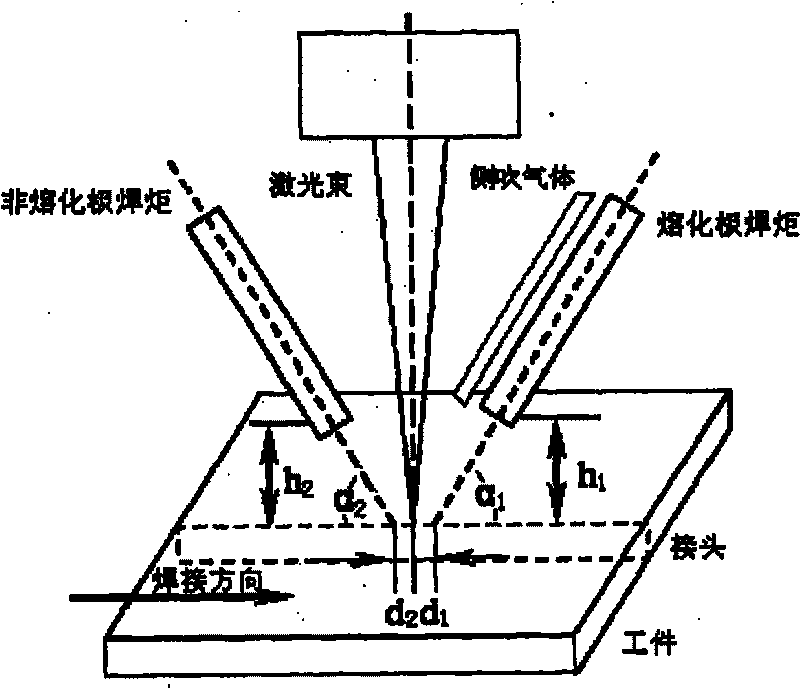
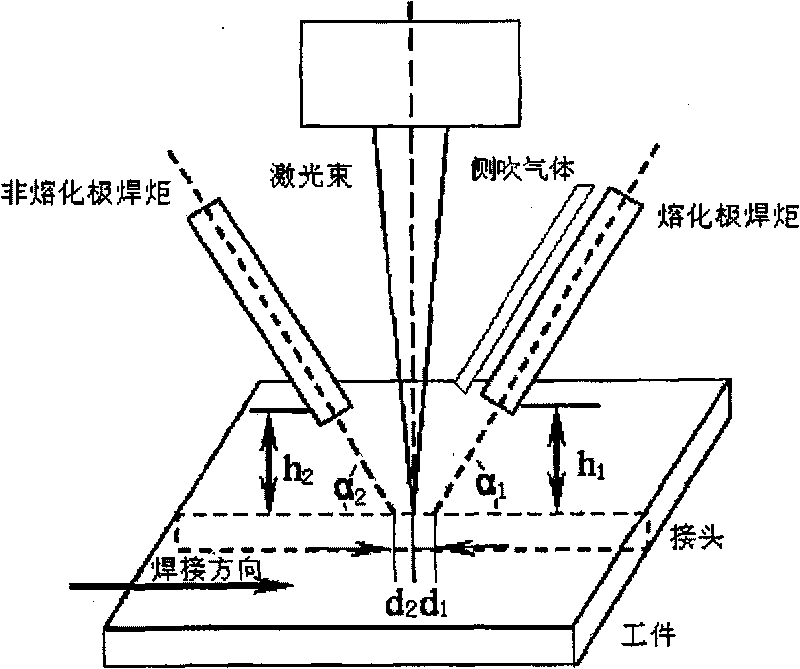
[0030] Such as figure 1 As shown, in this embodiment, the melting electrode arc heat source, laser heat source, and non-melting electrode arc heat source are arranged on a straight line along the welding direction in the order of acting on the workpiece, and the melting electrode arc is placed in front of the laser focus along the welding direction. By controlling the distance between the melting electrode arc and the laser focal point, the photoinduced plasma of the laser and the melting electrode arc plasma maintain interaction to form a molten pool together. The molten pool is shallow in the area covered by the melting electrode arc, while in the photoplasm The area is deep; the non-melting electrode arc is placed behind the laser focus along the welding direction, and the distance between the non-melting electrode arc and the laser focus ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] This embodiment is used for welding low-alloy high-strength steel with dimensions of 250mm×100mm×4mm (length×width×thickness).
[0036] The steps of this embodiment are the same as those of Embodiment 1, except that the welding parameters are adjusted, as follows:
[0037] Laser power:
8KW (laser output power)
Defocus amount:
-1mm (the laser focus is located 4mm below the upper surface of the sample)
Arc parameters:
280A, 21V (melting electrode arc)
[0038] Laser power:
8KW (laser output power)
150A, 17V (non-melting electrode arc)
Welding speed:
2.2m / min
Laser side blowing gas:
Pure helium, 20L / min
Arc shielding gas for melting electrode:
80% argon + 20% carbon dioxide, 15L / min
Non-melting electrode arc shielding gas:
Pure argon, 10L / min
Heat source spacing:
3mm (distance between melting electrode arc and laser)
5mm (distance between non-m...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com