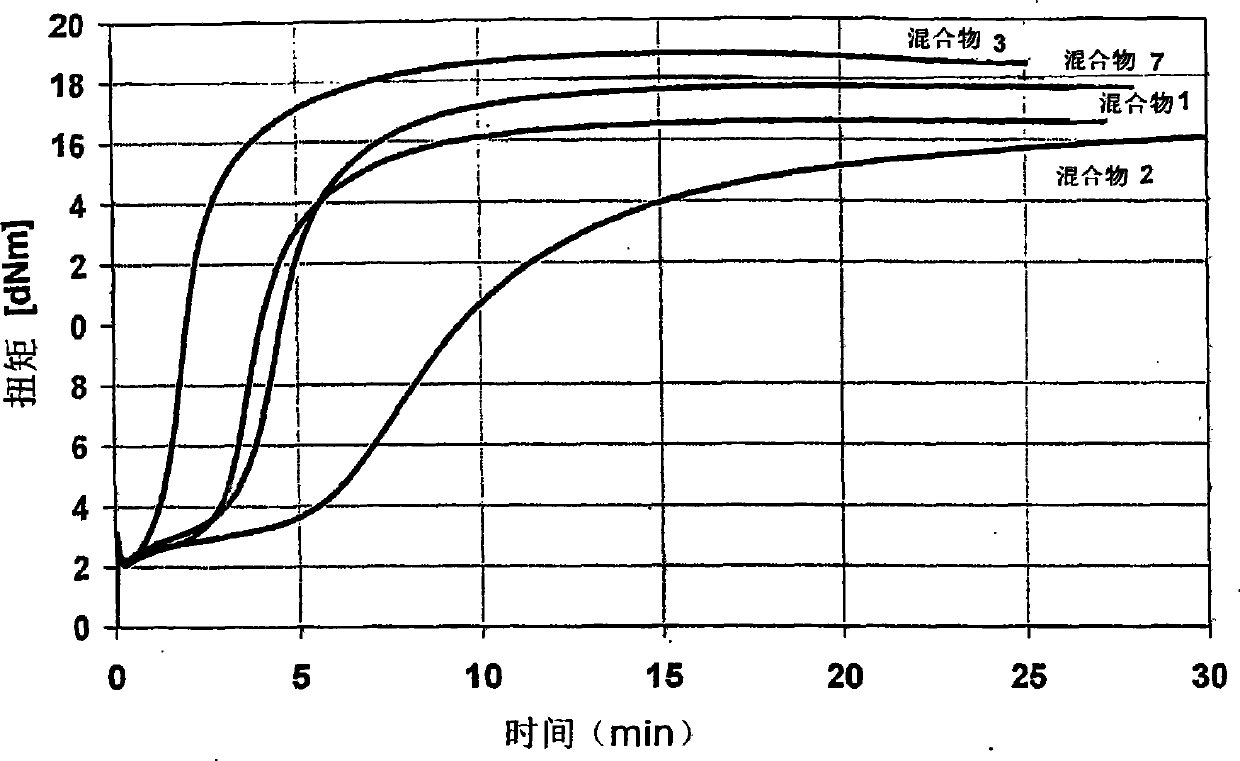
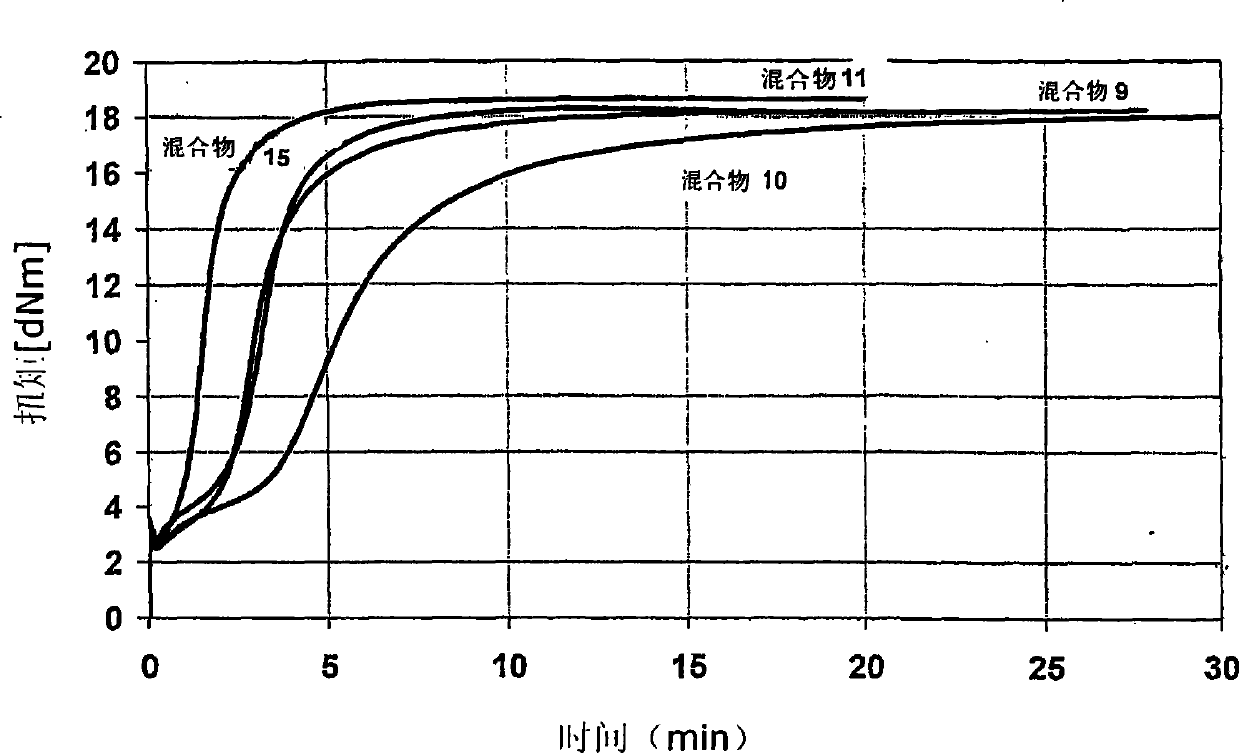
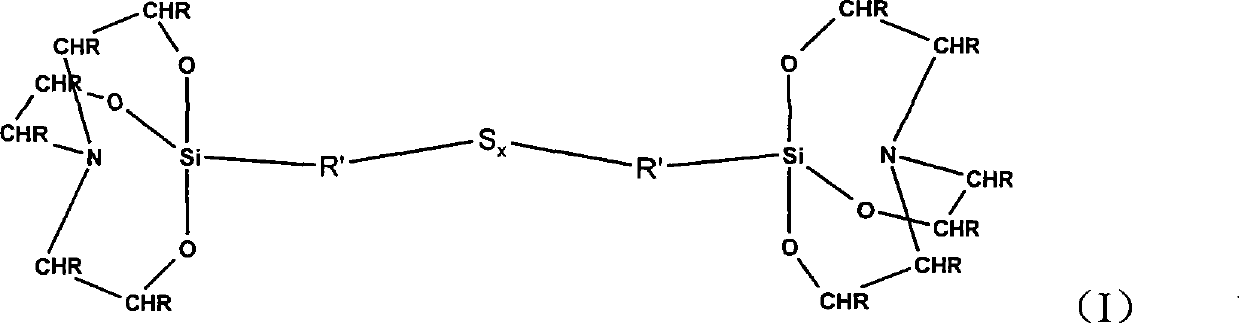
Rubber mixtures
A kind of rubber mixture, rubber technology, applied in the compound of elements of Group 4/14 of the periodic table, organic chemistry, chemical instruments and methods, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0229] At room temperature, 400g of bis(triethoxysilylpropyl) polysulfide Si 69 obtained from Degussa AG and 224.2g of triethanolamine, 2g of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4- Ionol CP is mixed with 0.6g titanium tetrabutoxide. The heating oil bath is heated to 100°C and the ethanol produced is removed by distillation at 200 mbar. After about 150 ml of ethanol was removed by distillation, the temperature of the oil bath rose to 160°C and the pressure dropped to 100 mbar. When ethanol is no longer distilled, the mixture is heated at 160° C. and 50 mbar for another 120 min. Then 2 g of 3-glycidyloxypropyl (triethoxysilane) (Dynasylan GLYEO, available from Degussa AG) was added, and the mixture was stirred for another 30 min at 160° C. in vacuum. The black product was poured into the coated mold under argon and cured. The product obtained is 403.5 g, a black solid.
[0230] according to 1 H NMR analysis showed that the product contained 29.8% by weight of bis(silatranylpropyl) disulfide, 34.1% by...
Embodiment 2
[0233] At room temperature, 400 g of bis(triethoxysilylpropyl) polysulfide Si 261 was mixed with 247.7 g of triethanolamine and 1 g of tetrabutyl titanate in a distillation apparatus. The heating oil bath is heated to 150°C, and the ethanol produced is removed by distillation at 200-600 mbar. The internal temperature rose from 135°C to 148°C within 180 minutes. After the distillation process is over, the brown product is poured into the coated mold under argon and cured. The product obtained is 420.1 g, a dark brown solid.
[0234] According to 29 Si NMR analysis, the product contained 8.7% by weight of bis(silazepine propyl) monosulfide, 77.2% by weight of bis(silazepine propyl) disulfide, and 12.6% by weight Bis(Siazatricyclylpropyl) trisulfide and 1.5% by weight of bis(Siazatricyclylpropyl) tetrasulfide. The measured average chain length of the polysulfide mixture was 2.1 (using the S1-S10 average value).
Embodiment 3
[0236] At room temperature, 400 g of bis(triethoxysilylpropyl) polysulfide Si 262 was mixed with 247.7 g of triethanolamine and 0.7 g of tetrabutyl titanate in a distillation apparatus. The heating oil bath is heated to 160°C, and the ethanol produced is removed by distillation at 50-400 mbar. The internal temperature rose to 159°C within 90 minutes. After the distillation process is over, the black product is poured into the coated mold under argon and cured. The product obtained is 413.7 g, a fragile black solid.
[0237] according to 29 Si NMR analysis showed that the product contained 70.2% by weight of bis(azatricyclylpropyl) disulfide, 22.0% by weight of bis(azatricyclylpropyl) trisulfide, and 3.1% by weight of bis( Siazatricyclyl propyl) tetrasulfide. The measured average chain length of the polysulfide mixture was 2.3 (using the S1-S10 average value).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molar mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com