Method for producing high efficiency multi-element compounded fertilizer
A production method and multi-element technology, applied in urea compound fertilizer, nitrogen fertilizer, potash fertilizer, etc., can solve the problems of limited ability to solve pollution sources, high production cost, and no scale production, so as to prolong the service life and work space, shorten The effect of reducing production cycle and energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0029] (1) Chemical composition adjustment in boron mud
[0030] Take a certain amount of naturally air-dried boron mud with a water content below 5%, and at room temperature, add 92% concentrated sulfuric acid evenly under constant stirring. At this time, the insoluble magnesium, calcium, boron, iron and free SO 4 2- The ionic reaction makes the pH value of the boron mud finally reach neutral, and the pH value is 6-7. After drying and crushing, it becomes a boron mud-based fertilizer for use;
[0031] Its main chemical reaction formula is:
[0032] CaCO 3 +H 2 SO 4 →CaSO 4 ↓+CO 2 ↑+H 2 o
[0033] MgCO 3 +H 2 SO 4 → MgSO 4 +CO 2 ↑+H 2 o
[0034] (2) Boron adjustment fertilization and granulation
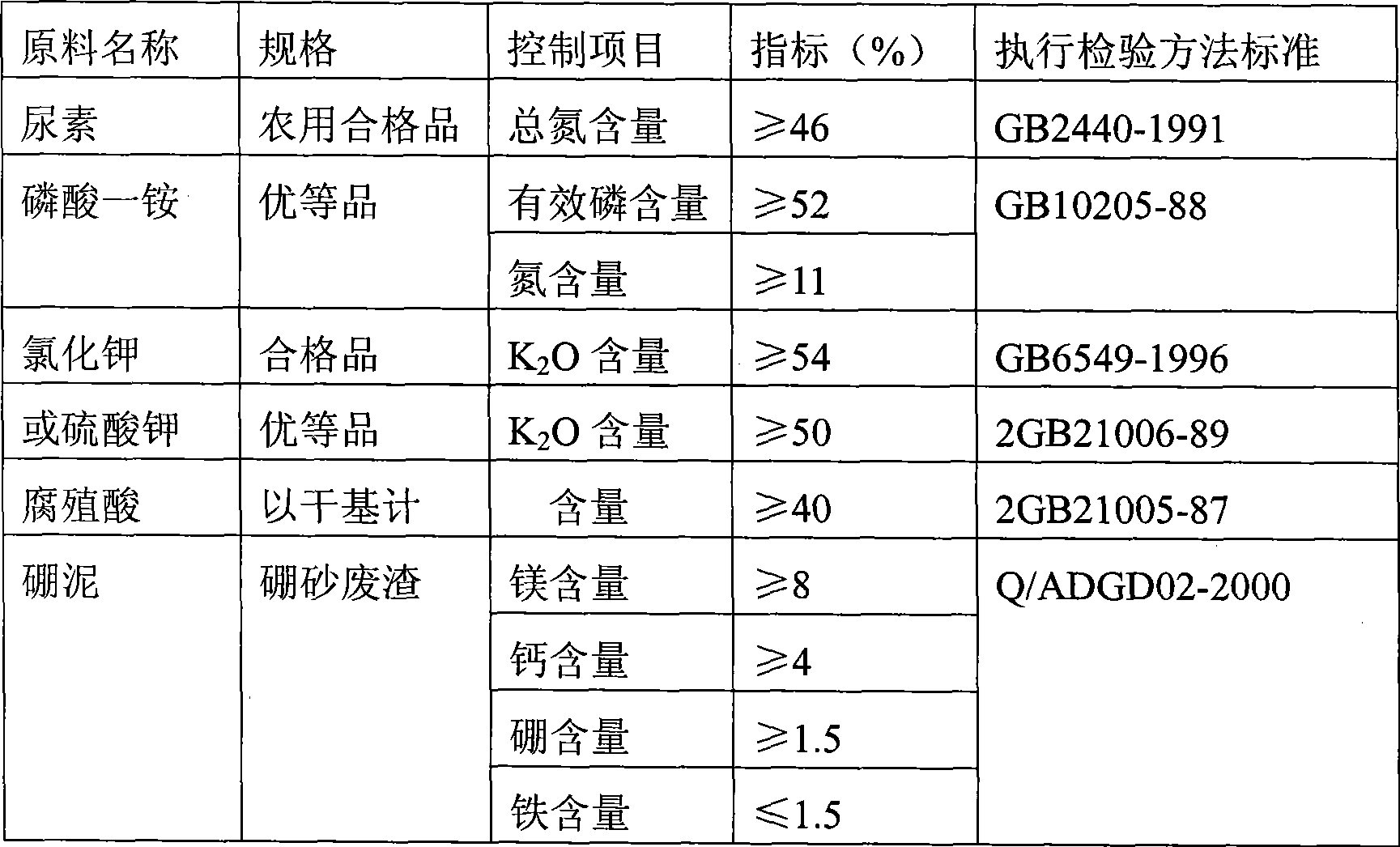
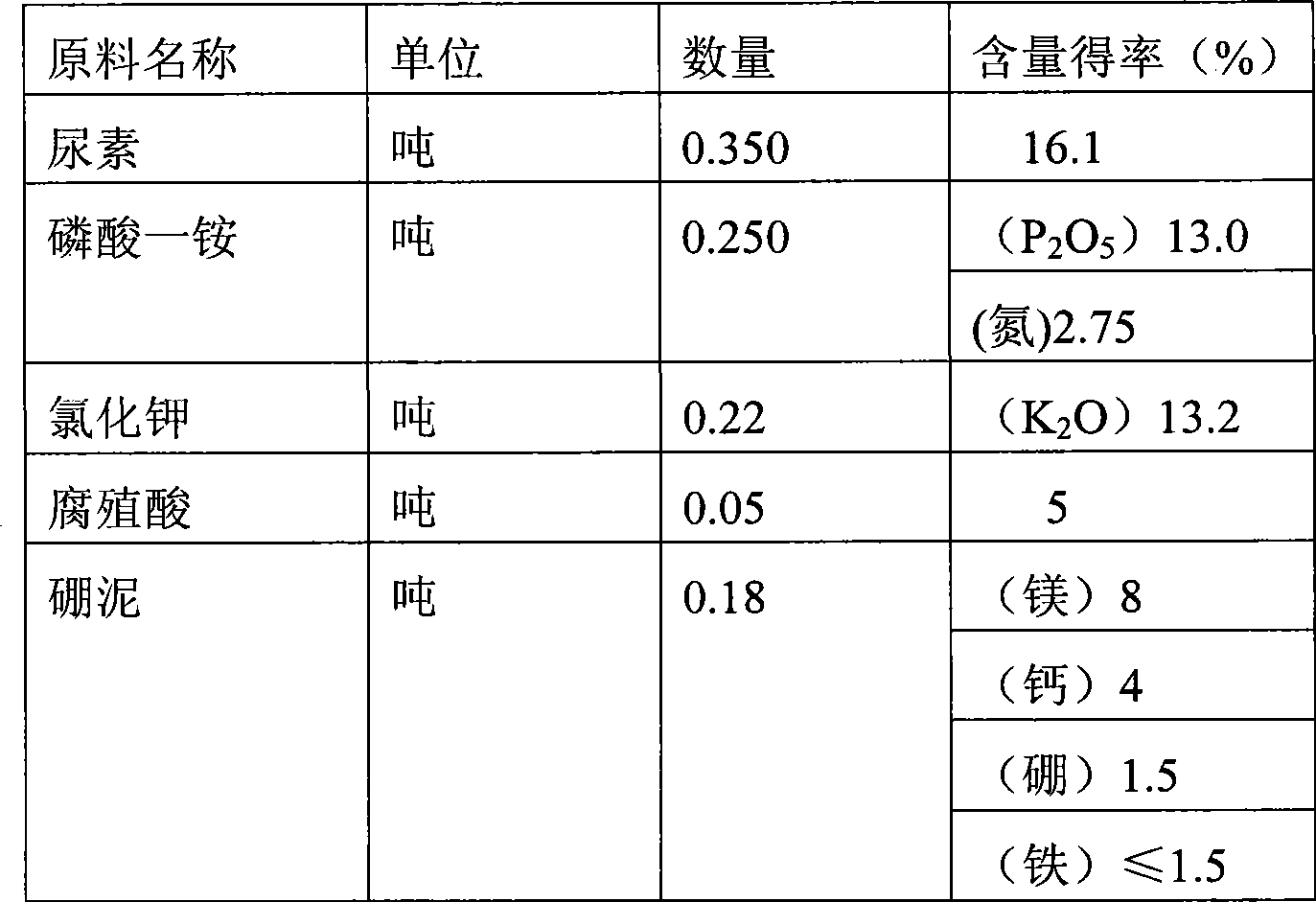
[0035] Take 180 kg of the above-mentioned boron mud base fertilizer, then add 350 kg of urea, 250 kg of monoammonium phosphate, 220 kg of potassium chloride, and 50 kg of humic acid in sequence, mix and granulate, the particle size is 2.00-6.00 mm, and then carry out ...
example 2
[0041] Boron mud base fertilizer in this example is identical with example 1;
[0042] Take 340 kg of the above-mentioned boron mud-based fertilizer, then add 250 kg of urea, 180 kg of monoammonium phosphate, 180 kg of potassium chloride, and 100 kg of humic acid in sequence, mix and granulate, the particle size is 2.00-6.00 mm, and then carry out Drying, sieving, cooling to below 40°C when the water content is less than 4%, and packaging, it is the finished product of multi-element compound fertilizer. The total amount of N, P, K, boron, magnesium, calcium, iron, and humic acid in the finished product Content: 58.82%, of which N, P, and K contents are 33.82% (see Table 3 for details). The selected raw materials are listed in Table 1.
[0043] table 3
[0044]
example 3
[0046] Boron mud base fertilizer in this example is identical with example 1;
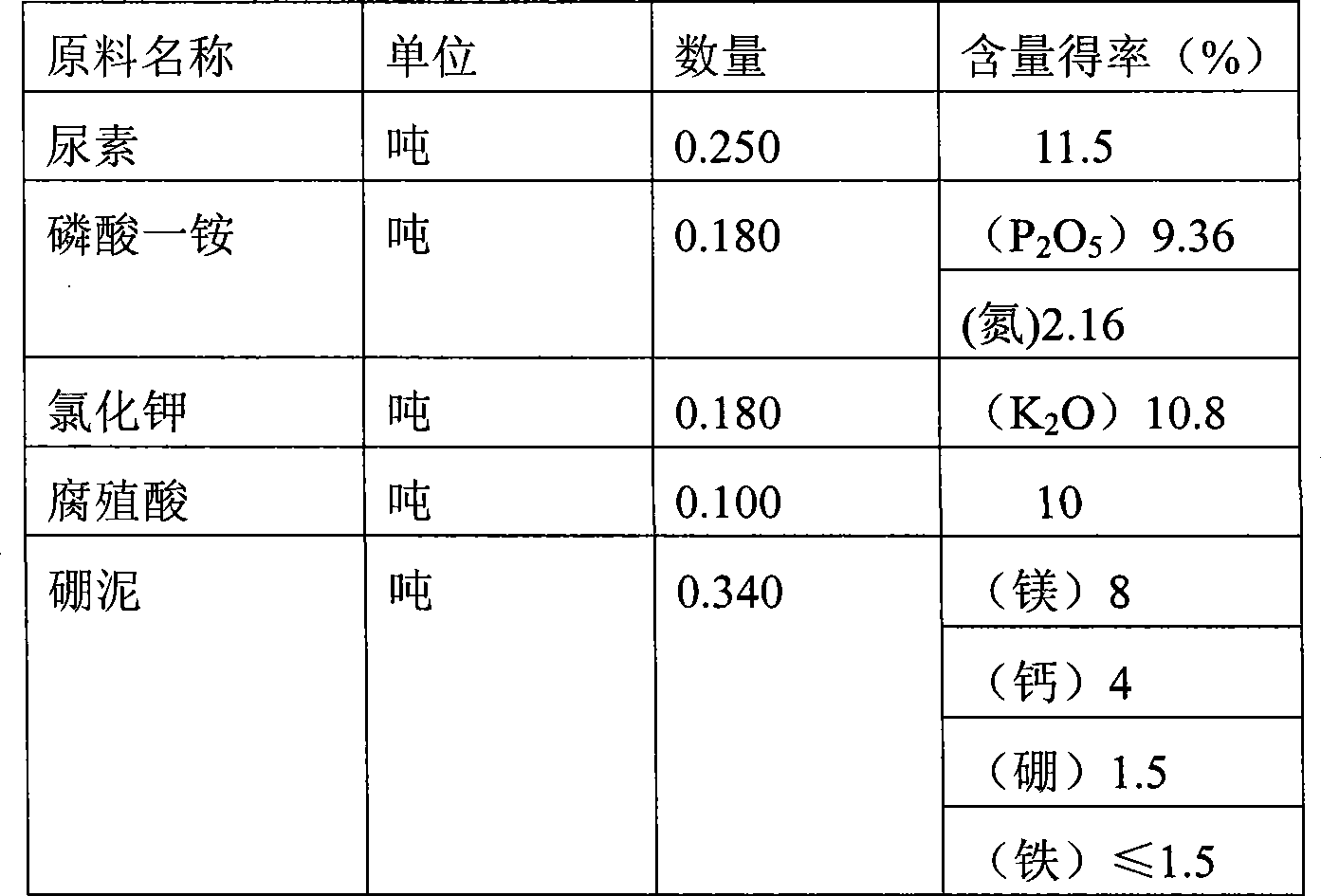
[0047] Take 400 kg of the above-mentioned boron mud-based fertilizer, then add 200 kg of urea, 150 kg of monoammonium phosphate, 180 kg of potassium sulfate, and 150 kg of humic acid in sequence, mix and granulate, the particle size is 2.00-6.00 mm, and then dry , sieve, cool to below 40°C when the water content is less than 4%, and pack it, which is the finished product of multi-element compound fertilizer. The total content of N, P, K, boron, magnesium, calcium, iron, and humic acid in the finished product : 58.8%, wherein N, P, K content 27.8% (see Table 4 for details). The selected raw materials are listed in Table 1.
[0048] Table 4
[0049]
[0050] The concrete fertilization method of above-mentioned example 1-3 multi-element compound fertilizer is as follows:
[0051] When used for wheat crops, generally 30-40 kg per mu as base fertilizer, 60% evenly applied when plowing and land pre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com