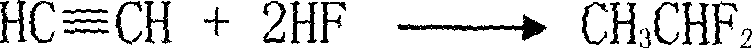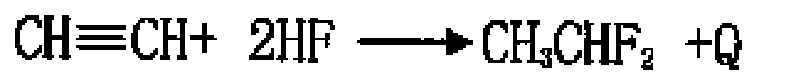Preparation of 1,1-difluoroethane and fluorating catalyst
A technology based on fluorination catalyst and difluoroethane, applied in 1 field, can solve problems such as difficulty in disposal, affecting product yield and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
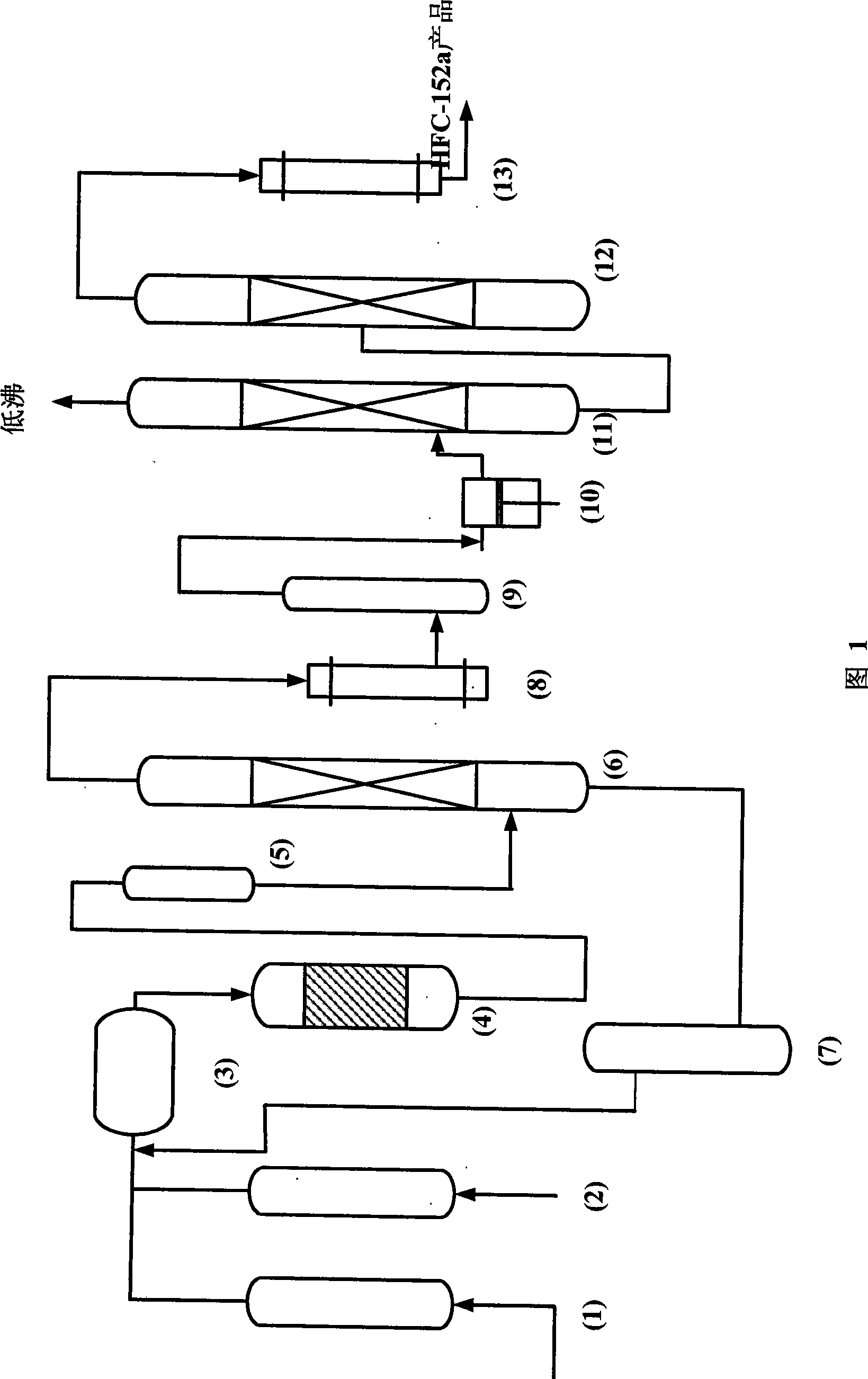
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] After vaporizing anhydrous hydrofluoric acid and acetylene, they are mixed into a 180ml carbon steel fixed-bed reactor with receiving conditions, and the fluorination reaction is carried out under the action of a chromium-based catalyst to control the ratio of anhydrous hydrofluoric acid and acetylene materials 8 : 1, the reaction temperature is 230℃, the pressure is 1.0Mpa, (under the standard condition) the space velocity of the reactor is 800h -1 , the outlet material of the reactor was sampled and analyzed, and the conversion rate of acetylene was 78.55%, and the selectivity of HFC-152a was 95.40%.
preparation Embodiment 1
[0051] Put 0.5gIn (NO 3 ) 3 ·9H 2 O, 4g CoCl 2 ·6H 2 O and 50g Cr (NO 3 ) 3 ·9H 2 O was dissolved in 800 g of pure water to obtain an aqueous solution containing indium, cobalt and chromium. In this solution, ammonia water was added for precipitation reaction, so that the pH value of the reaction solution was in the range of 6.5 to 10, filtered, and washed with distilled water. dry for 12 hours. The obtained solid is ground finely, mixed with graphite, pressed into a tablet shape with a tablet machine, loaded into a roasting furnace, and heated in N 2 The catalyst precursor was obtained by calcining at 400°C for 4 hours in a gas stream. The obtained precursor was charged into a reaction tube, using N 2 The catalyst was prepared by activation at 350° C. in a diluted AHF gas stream, and its physical properties are shown in Table 4.
[0052] Table 4 Physical properties of fluorination catalysts
[0053] catalyst 01 02 Bulk density (g / ml) 0.88 0.90 ...
preparation Embodiment 2
[0056] Cr(NO 3 ) 3 ·9H 2 The O solution was mixed with ammonia water under full stirring to obtain a slurry of chromium hydroxide. The slurry was filtered, and the filter cake was thoroughly washed with distilled water, and then dried at 110° C. for 12 hours. The obtained solid was ground, and In(NO) was slowly added dropwise to 50 g of the thus obtained ground. 3 ) 3 ·nH 2 O and CoCl 2 ·6H 2 Aqueous solution of O. This powder was dried at 110°C for a further 12 hours, then mixed with graphite and subsequently granulated with a granulator. Then, molding, calcination and fluorination treatment were carried out in the same manner as in Catalyst Preparation Example 1. The physical properties of the catalyst are shown in Table 5.
[0057] Table 5 Physical properties of fluorination catalysts
[0058] catalyst 03 04 Bulk density (g / ml) 0.91 0.92 Specific surface area (m 2 ·g -1 ) 112.8 115.6 Pore volume (ml g -1 ) 0.35 0.34
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com