Degradation method for polychlorinated biphenyl with staphylococcus epidermidis
A technology of Staphylococcus epidermidis and polychlorinated biphenyls, which is applied in the field of pollution microorganism degradation, and can solve problems such as high price and secondary pollution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
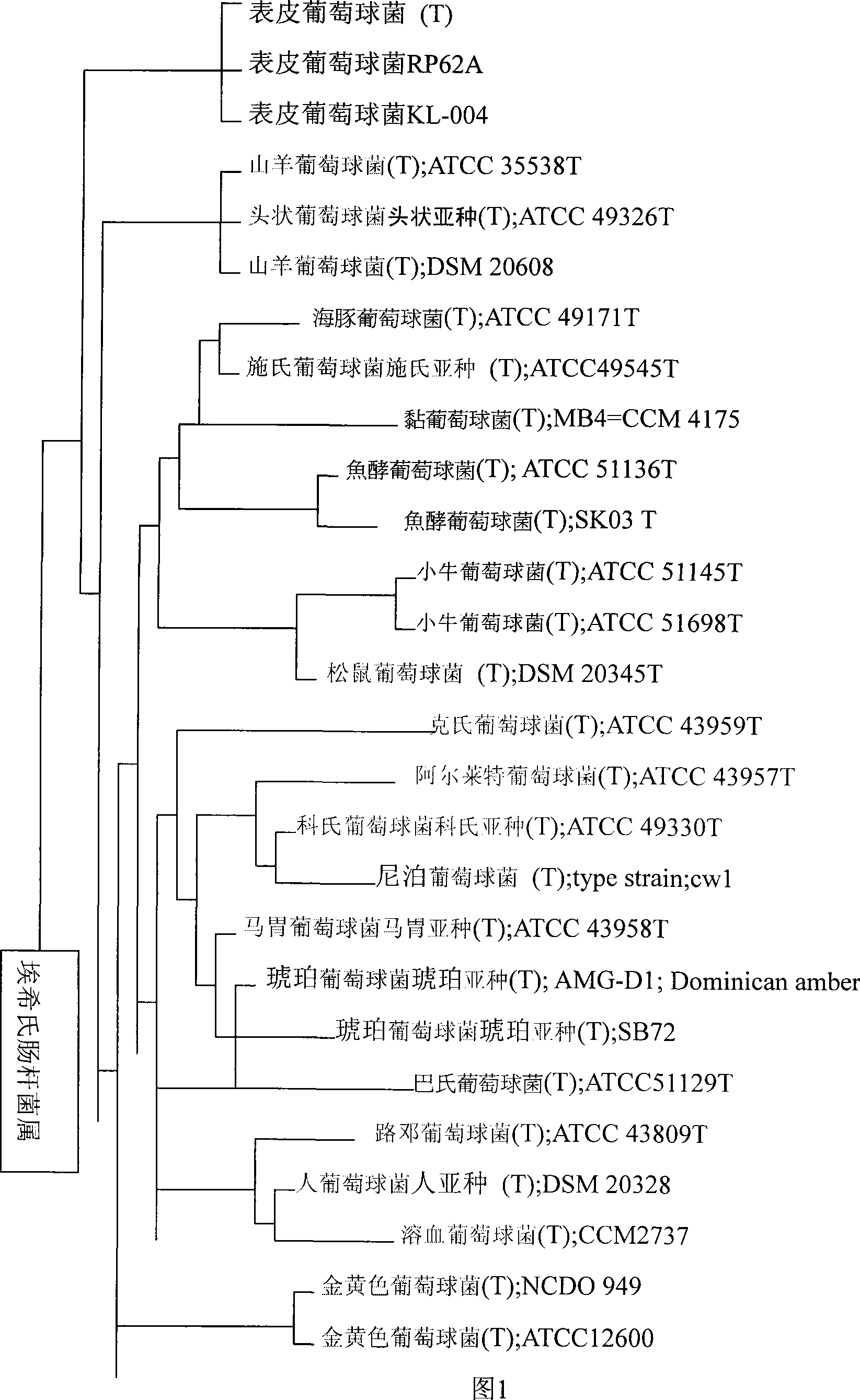
[0021] Example 1 Isolation and Identification of PCB Degrading Bacteria
[0022] 1. Isolation of strains
[0023] (1) Collect activated sludge from Shanghai Songjiang Sewage Treatment Plant, place it in a 60cm long, 40cm wide, and 50cm high glass domestication device, and use an air compressor to aerate without adding nutrients and without water inflow and outflow exchange After 3 days, change the water, drain about 10L of mud-water mixture in the device, add nutrient solution and carry out uninterrupted aeration. After 10 days of cultivation, the waste liquid of PCBs was added to carry out acclimatization and cultivation while adding nutrient solution, and the acclimatization was cultivated for two months. Preparation of culture medium: 5 grams of glucose, 2 grams of urea, and 1 gram of potassium dihydrogen phosphate. Prepare a nutrient solution of about 10 liters.
[0024] (2) Precipitate the acclimatized water sample for 30 minutes, take the supernatant night, and then f...
Embodiment 2
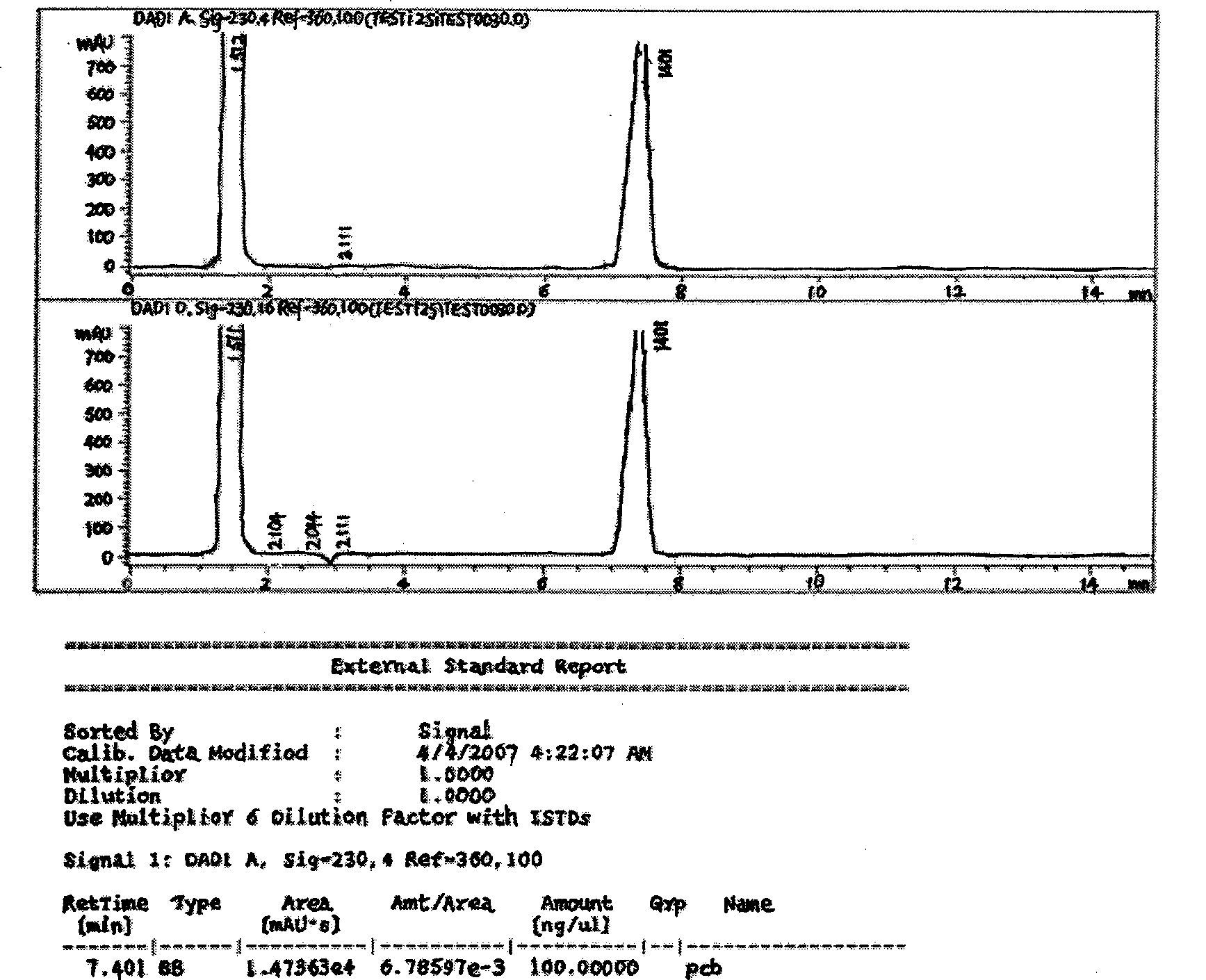
[0031] Example 2 Degradation Analysis of Polychlorinated Biphenyls by Staphylococcus Epidermidis
[0032] Inoculate Staphylococcus epidermidis into sterilized acclimation medium (0.5g / L KH 2 PO 4 , 0.5g / L K 2 HPO 4 , 0.2g / L MgSO 4 , 0.1g / LCaCl 2 , 0.2g / LNaCl, 1.0g / L (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , 1g / L biphenyl), placed in a constant temperature shaker, 30°C, 150rpm, cultured for 14 days. Then inoculated in PCBs degradation medium (Degradation Medium) (0.5g / L KH 2 PO 4 , 0.5g / L K 2 HPO 4 , 0.2g / L MgSO 4 , 0.1g / L CaCl 2 , 0.2g / LNaCl, 1.0g / L(NH4) 2 SO 4 , 100mg / L 2,3',4', 5-tetrachlorobiphenyl-acetone solution, pH7.0), the sample was determined by high-performance liquid chromatography, and the degradation effect of the bacteria on PCBs was analyzed.
[0033] Liquid chromatography conditions:
[0034] ①Single-column single-detection system, 250mm long, 5mm inner diameter activated carbon column.
[0035] ②Carrier ratio: chromatography grade methanol 10%, purified water 90%
[...
Embodiment 3
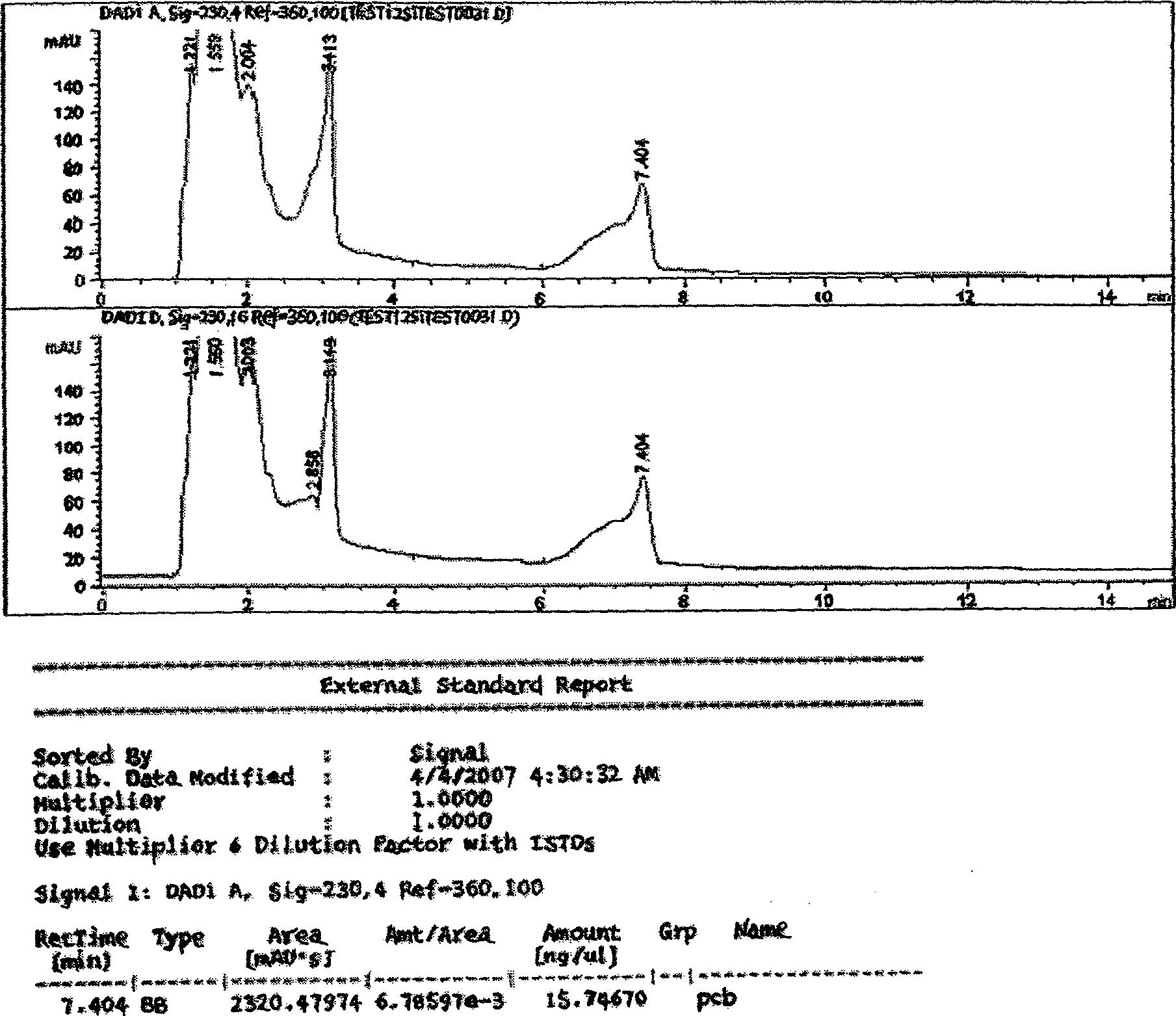
[0042] Example 3 Effect of external carbon source on the degradation efficiency of polychlorinated biphenyls
[0043] (1) Insert Staphylococcus epidermidis into enrichment medium EM, place in a shaker at 30° C., 150 rpm, and enrich for 5 days.
[0044] (2) Three 50ml degradation medium DM were prepared, one of which was added with 2g / L glucose as an external carbon source, and placed in a 150ml Erlenmeyer flask. One bottle was left blank without inoculation, and the other two bottles were inoculated with 100ul enriched bacterial solution. Cultivate on a shaker at 30°C, 150rpm.
[0045] (3) Under aseptic operation conditions, take out 5ml of bacterial solution on 1d, 2d, 3d, 4d, and 5d after inoculation respectively.
[0046] (4) Sample pretreatment
[0047] ①Put the bacterial solution in a separatory funnel, and add dichloromethane three times. Add 2ml for the first and second time, and 1ml for the third time. Shake well after each addition and let stand for a while. Aft...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com