Method of extracting crude enzyme preparation for degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
An extraction method and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon technology, applied in the field of environmental restoration, can solve the problem of high cost, and achieve the effect of low cost, quick effect and great application value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] Embodiment 1: the extraction of crude enzyme liquid
[0015] 1.1 Mushroom dregs tested
[0016] Mushroom residues of Agaricus bisporus and Pleurotus eryngii were cultivated in our laboratory, and samples of mushroom residues of Pleurotus ostreatus and Coprinus comatus were purchased from Henan Academy of Agricultural Sciences. The samples were stored at 4°C after acquisition until use.
[0017] 1.2 Extraction of crude enzyme solution
[0018] The extraction step is: adding an acidic buffer solution with a pH of 4 to 6 in Agaricus bisporus, Pleurotus eryngii, Pleurotus eryngii or Coprinus comatus slag, the acidic buffer is acetic acid, phosphoric acid or citric acid (preferably pH 5, 50mM acetic acid buffer solution), shake at 20-40°C for 2 hours at a speed of 100-200 rpm, centrifuge at 11,000 g for 10 minutes at a high speed, and the obtained supernatant is the crude enzyme solution.
[0019] Or, take 50g of fresh mushroom dregs into a 500mL conical flask, add 250mL ...
Embodiment 2
[0020] Embodiment 2: Crude enzyme liquid is to the degradation kind of 15 kinds of PAHs
[0021] 2.1 Test method
[0022] Take 4.5 mL of the crude enzyme solution obtained in step 1.2 and place it in a 15 mL brown reagent bottle with a stopper, add 0.5 mL of acetonitrile solution containing 15 kinds of PAHs (see Table 1 for the initial concentration of PAHs in the reaction system), tighten the stopper, shake well, and place Incubate in a dark room for 48 hours (25° C.), and add 5 mL of acetonitrile to terminate the reaction. Shake well, let stand for 1h (25°C, 150rpm), centrifuge at high speed (11,000g), pass through a 0.22μm filter membrane, and perform HPLC determination. As a control, the crude enzyme solution was added in the form of inactivation (boiling for 30 min), and each treatment was repeated three times.
[0023] 2.2 Sample analysis
[0024]The samples were analyzed by Shimadzu UFLC-20 ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography. The analytical column is a macrop...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Example 3: Degradation of high concentration anthracene and benzo[a]pyrene by crude enzyme solution
[0028] 3.1 Test method
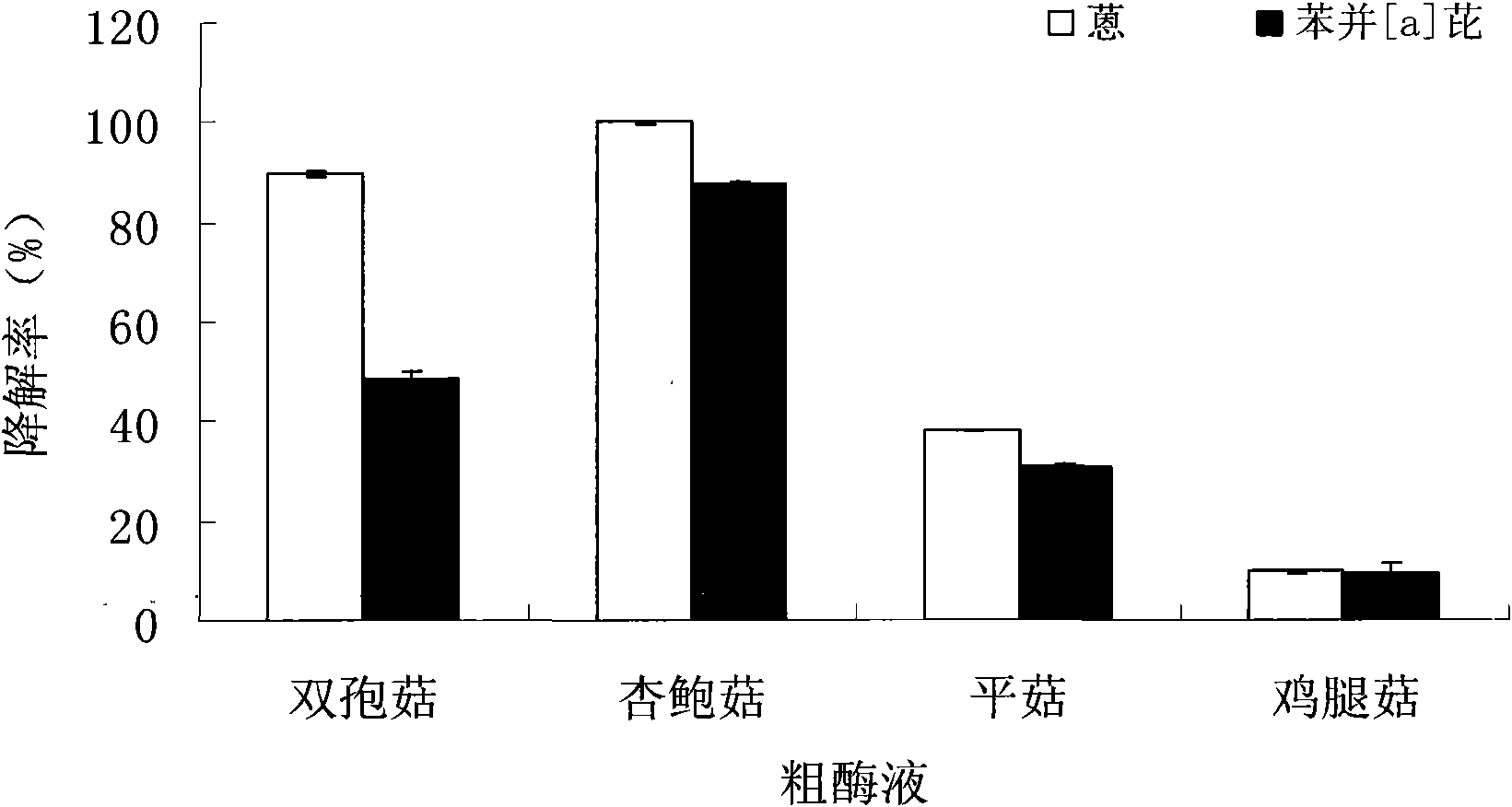
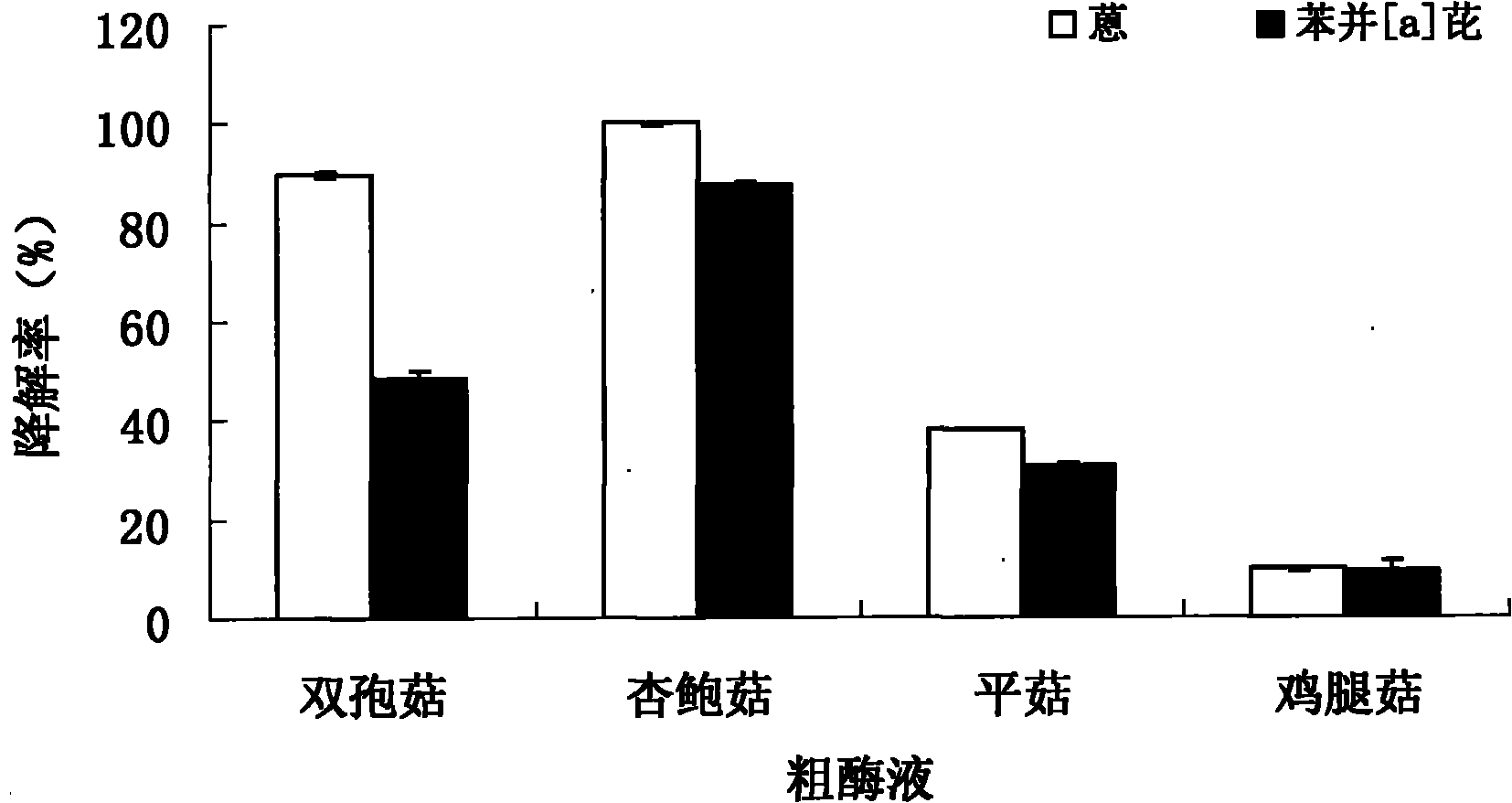
[0029] Put 4.5 mL of the crude enzyme solution obtained in step 1.2 into a 15 mL brown reagent bottle with a stopper, add 0.5 mL of acetonitrile solution containing anthracene and benzo[a]pyrene, and make the anthracene and benzo[a]pyrene in the reaction system reach 1000 μgl -1 , other steps are the same as 2.1.
[0030] 3.2 Sample analysis
[0031] Same as 2.2.
[0032] 3.3 Statistics
[0033] Same as 2.3.
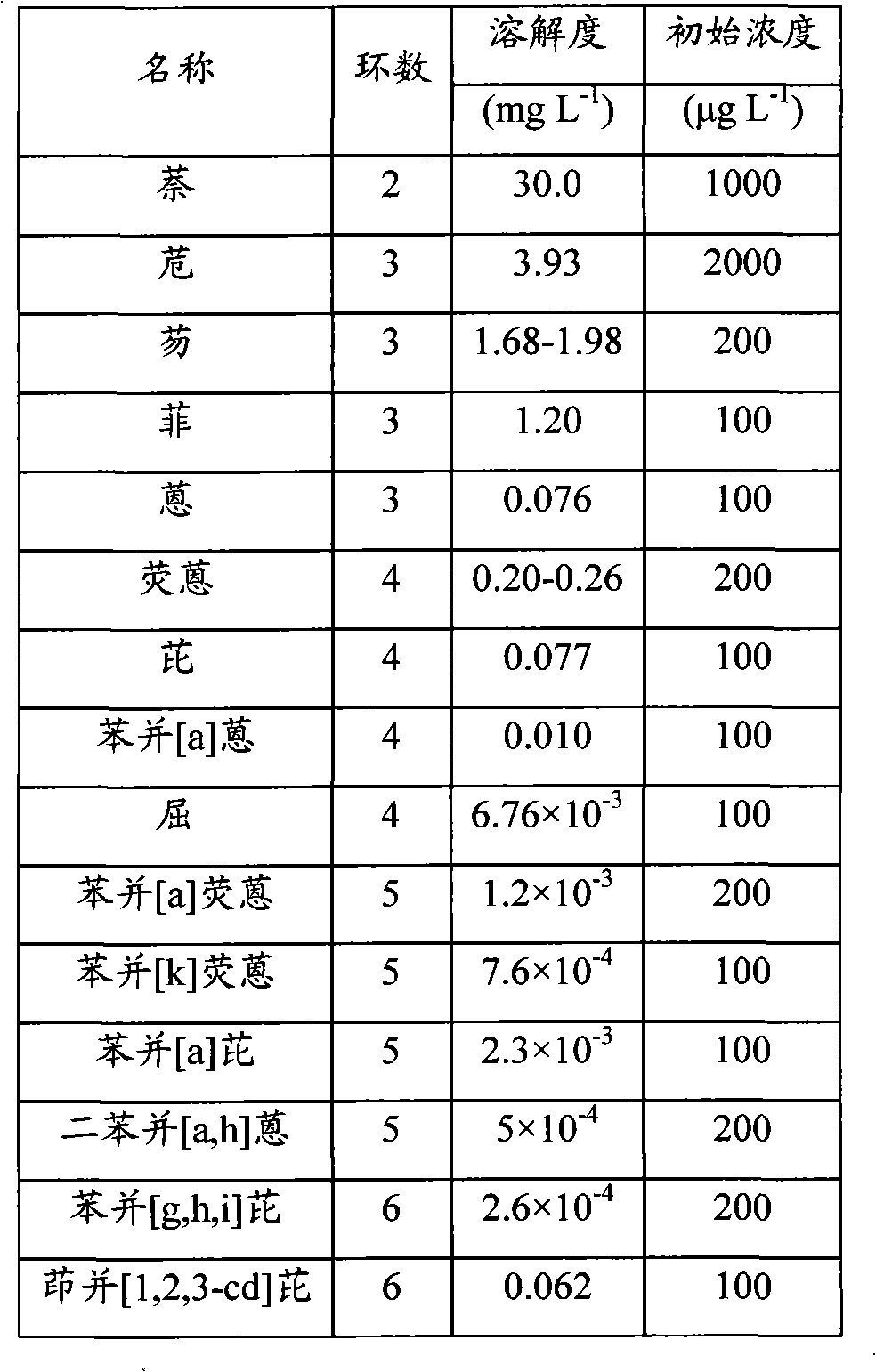
[0034] Table 1 is the Chinese name, ring number, solubility and initial concentration in the reaction system of the 15 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to be tested.
[0035] Table 1 Initial concentrations of 15 PAHs
[0036]
[0037] Table 2 shows the degradation rate of 15 kinds of PAHs by the extracted crude enzyme solution. The values in the table are: mean ± standard deviation, and those marked with the same l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com