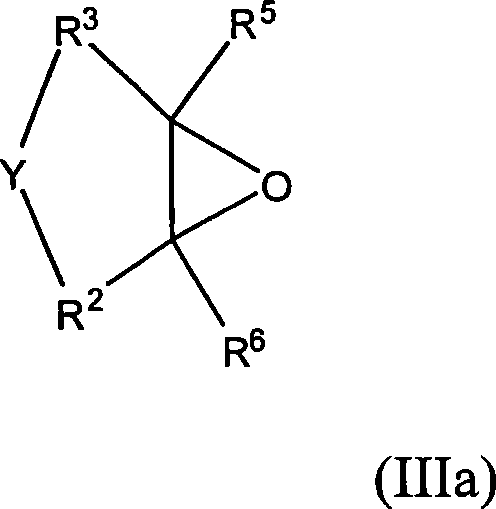
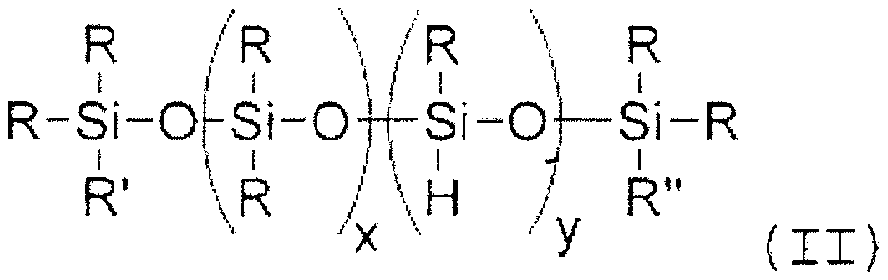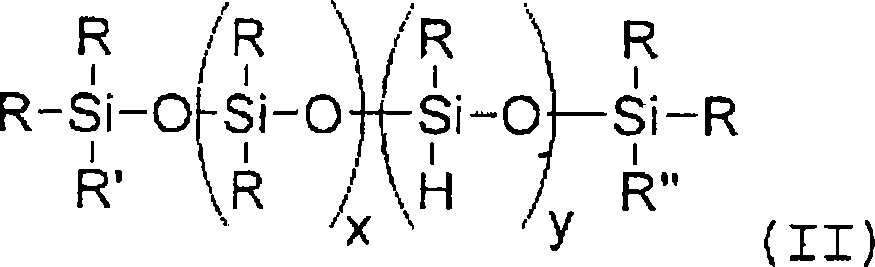Method for producing polyether alcohols with DMC catalysts using compounds containing SIH combinations as additives
A technology of polyether alcohol and catalyst, which is applied in the field of preparing polyether alcohol by using compounds with SiH groups as additives and using DMC catalysts, which can solve the problems of not being able to approach polydispersity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1a
[0103] At first under nitrogen, add 215.7g polypropylene glycol (weight average molecular weight M in the autoclave of 3 liters) w =2000g / mol), 0.03g of hexacyanocobaltate (III) zinc DMC catalyst and 5.9g of heptamethylhydrotrisiloxane (Rhodia) (CAS[1873-88-7] with a SiH content of 4.5eq / kg ), and heated to 130°C with stirring. The reactor was evacuated to an internal pressure of 30 mbar in order to remove by distillation any volatile constituents present. To activate the DMC catalyst, a 40.0 g portion of propylene oxide was added. After the reaction had started and the internal pressure had dropped, a further 944 g of propylene oxide were metered in continuously within 60 minutes with cooling to 130° C. and a maximum reactor internal pressure of 1.5 bar. The reaction was continued at 130° C. for 30 minutes, followed by a degassing step. This removes volatile components such as residual propylene oxide by distillation at 130°C under reduced pressure. The resulting polyethe...
Embodiment 1b
[0107] In other comparative experiments carried out similarly to Example 1a, no additives were added to the polypropylene glycol / DMC catalyst mixture at the start of the alkoxylation according to the current state of the art.
[0108] The resulting long-chain, low-viscosity polypropylene glycol has an OH value of 9.8 mg KOH / g, a viscosity (at 25°C) of 7100 mPas, and according to GPC, its polydispersity M w / M n 1.4 (relative to polypropylene glycol standard).
[0109]
[0110] Preparation of mixed ethylene oxide / propylene oxide-based polyethers with addition of additives by the process of the invention
Embodiment 2a
[0112] First add 180.0g polypropylene glycol monoallyl ether (weight average molecular weight M to 3 liters of autoclave under nitrogen) w =400g / mol), 0.08g of zinc hexacyanocobaltate DMC catalyst and 5.25g of heptamethylhydrotrisiloxane (CAS[1873-88-7]), and heated to 130°C with stirring. The reactor was evacuated to an internal pressure of 30 mbar in order to remove by distillation any volatile constituents present. To activate the DMC catalyst, a 36.0 g portion of propylene oxide was added. After the reaction had started and the internal pressure had dropped, a mixture of 396 g of ethylene oxide and 1269 g of propylene oxide was metered in continuously within 90 minutes while cooling to 130° C. and a maximum reactor internal pressure of 1.5 bar. The reaction was continued at 130°C for 30 minutes, followed by a degassing step. This removes volatile components such as residual propylene oxide by distillation at 130°C under reduced pressure. The resulting polyether is coole...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hydroxyl value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hydroxyl value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| dispersity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com