Bi-or multi-modal particle size distribution to improve dragreduction polymer dissolution
A particle size distribution, polymer technology for lubricating compositions, drilling compositions, gas/liquid distribution and storage, which can solve problems that are not fully satisfactory
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0018] Preparation of Slurries Containing Multimodal Particle Distributions
[0019] There are many different methods that can be used to prepare drag reducing polyolefin slurries. The multimodal particle size distribution compositions of the present invention are not necessarily limited to those discussed herein, but may include others. It should be understood that within the context of the present invention "multimodal" includes "bimodal". Some of the main methods and average particle size distributions for the preparation of DRA that will be discussed are given in Table I.
[0020] Table I
[0021] Average particle size distribution (microns) of some DRA prepared by different methods
[0022] A-precipitation / slurry B-Body / Ambient Grinding C-Body / homogenization D-Body / Cryogenic Grinding E-encapsulation 100-150
350-550
250-350
100-200
Microcapsules
150-5000
large capsule
>5000-15,000
[002...
Embodiment 1
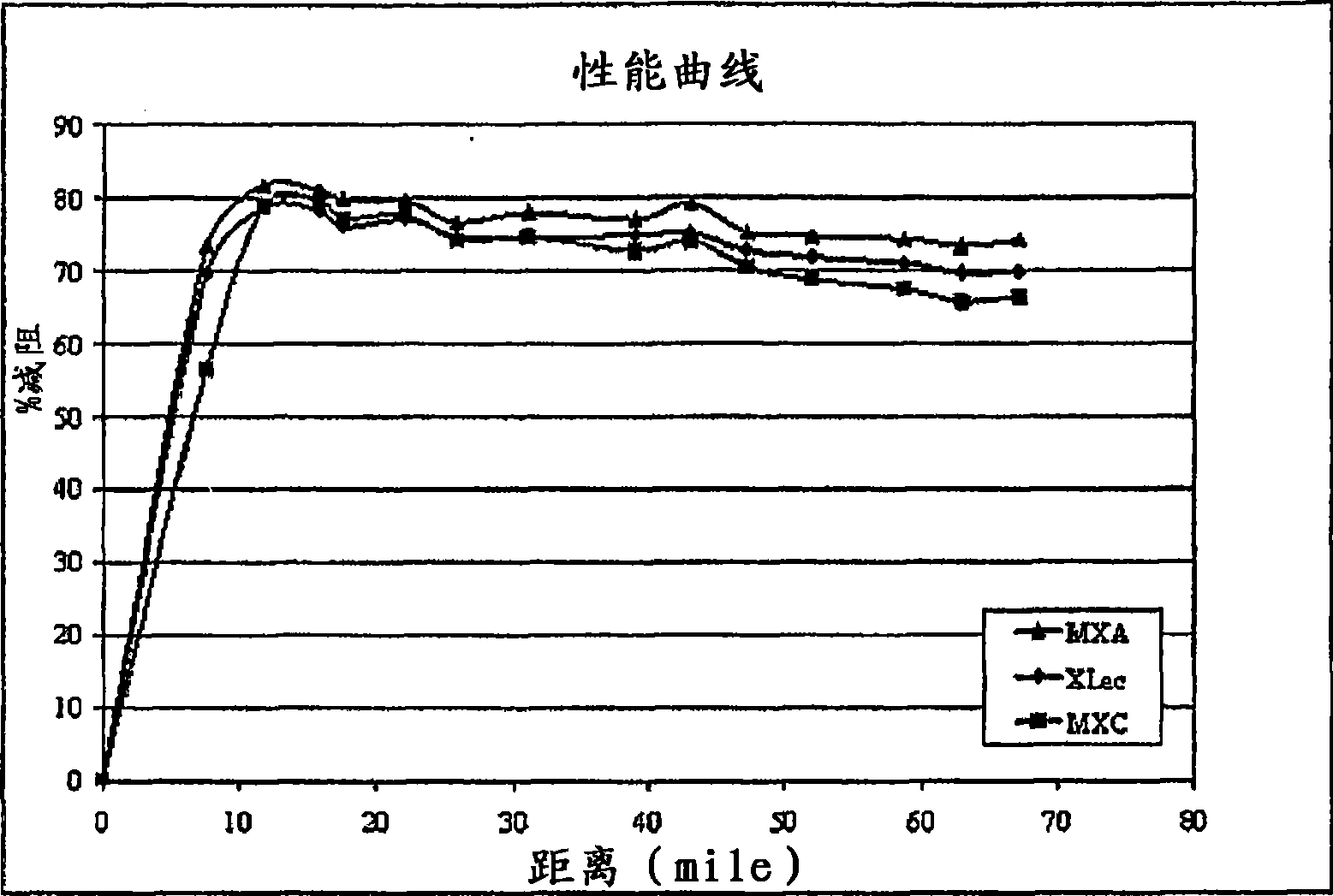
[0059] Field trials were carried out on three different drag reducing formulations with different particle sizes. One product was a commercial sample prepared by the method of the precipitation technique described above (available from Baker Petrolite XLec drag reducing additive). The particle size or distribution of the product is 100-150 microns. The second commercial product tested was MXC drag reducing additive (available from Baker Petrolite), which is prepared by bulk polymerization followed by grinding technique on a Ross Mega-Shear homogenizer. The particle size of MXC products is 250-300 microns. The third formulation tested was XLec and A mixture of MXC products, combined at a polymer weight ratio of 2:3 (40wt% XLec Polymer: 60wt% MXC polymer), hereinafter referred to as MXA drag reducing additive. The resistance properties of the three products were tested in a 60 mile (97 km) long, 20" (51 cm) diameter pipeline carrying a specific gravity of ...
Embodiment 2
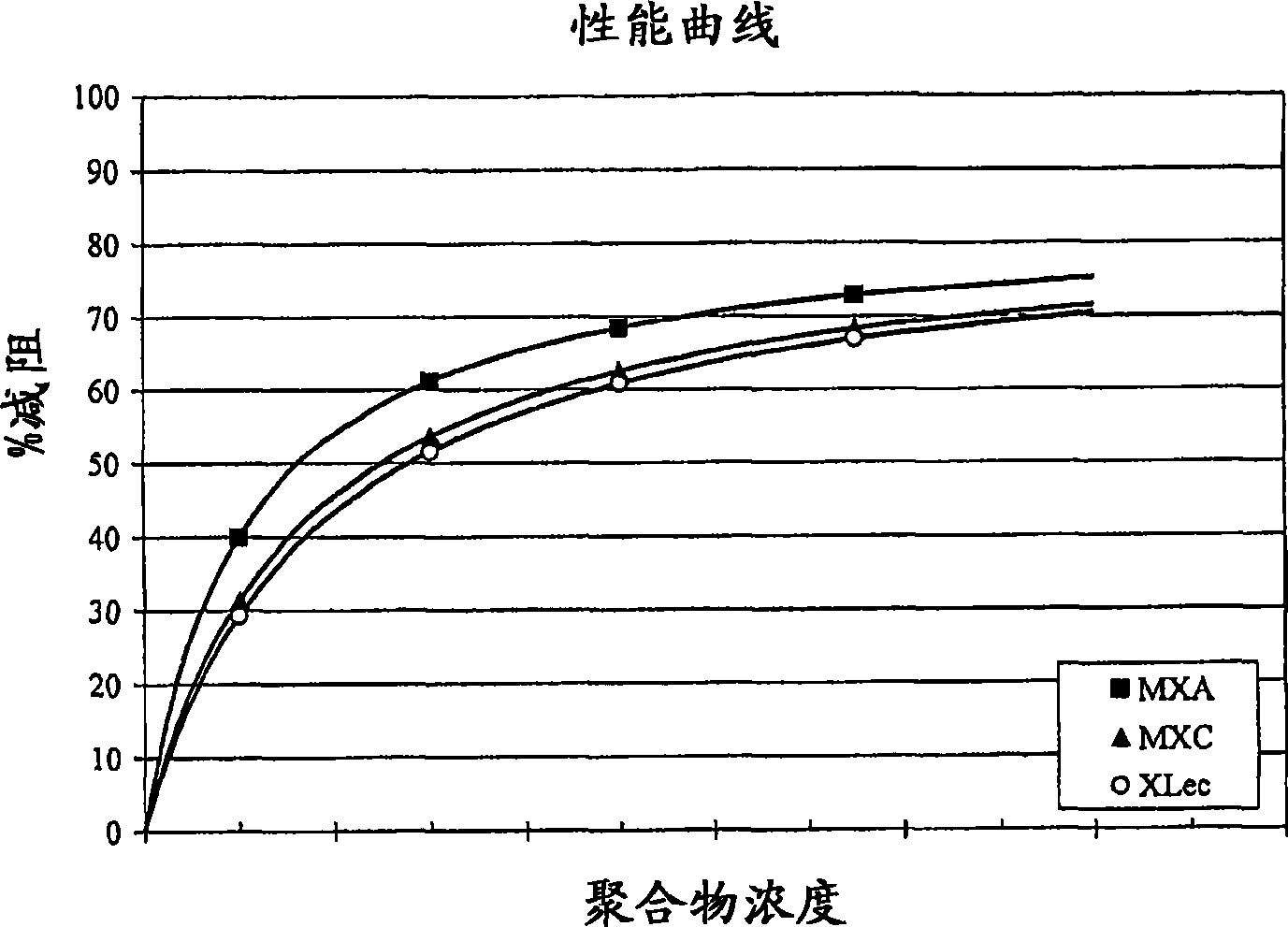
[0063] A second field trial was conducted using three of the above formulations in a 300 mile (482 km) long, 40" (102 cm) diameter pipeline carrying a specific gravity of 0.8 and a viscosity of 2.0 centistokes (2.0 x 10 -6 m 2 / s) crude oil. The temperature of crude oil is 75°F (24°C). The oil flow rate is 22,000 barrels per hour (about 3,500m 3per hour), corresponding to a Reynolds number of 570,000 and a line filling time of the pipeline of 5 days. The dose rates of the drag reducing composition injected into the pipeline are also qualitatively comparable. In the absence of frequent pressure sensors along the pipeline, the information gathered allows the generation of information related to overall performance relative to drag reducer content, rather than as figure 1 Performance with respect to distance as in . The actual performance in terms of drag reduction is: MXC is 43%, 46% for XLec, XA is 54%. XLec, MXC and The performance curves for MXA products ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com