Capillary array analyzer by rotating scanning
A capillary array and capillary technology, applied in the field of biological analysis, can solve the problems of limited instrument detection sensitivity, small fluorescence collection angle, and large working distance of the lens, and achieve the effect of low working distance requirements, small scanning inertia, and compact results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
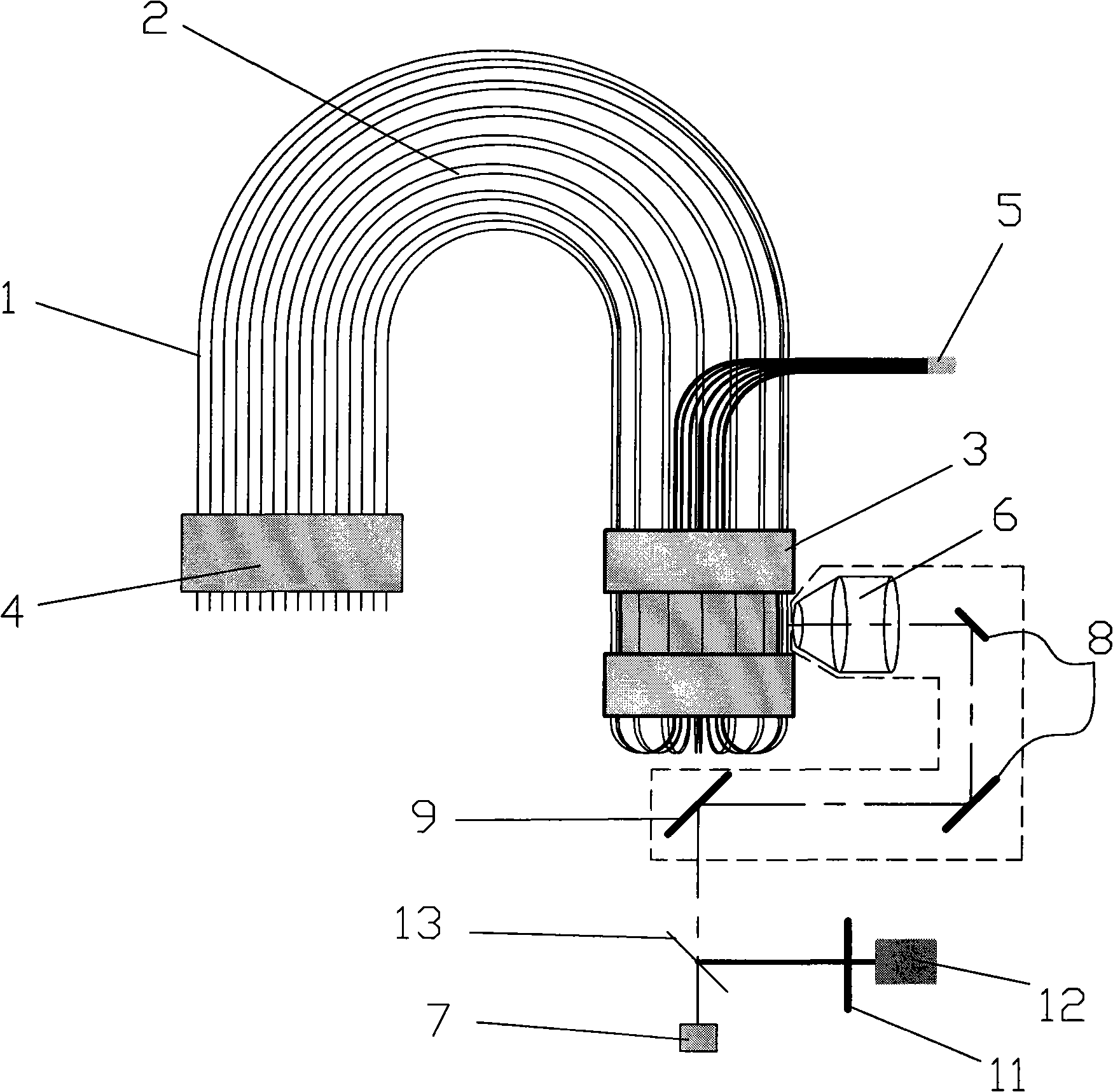
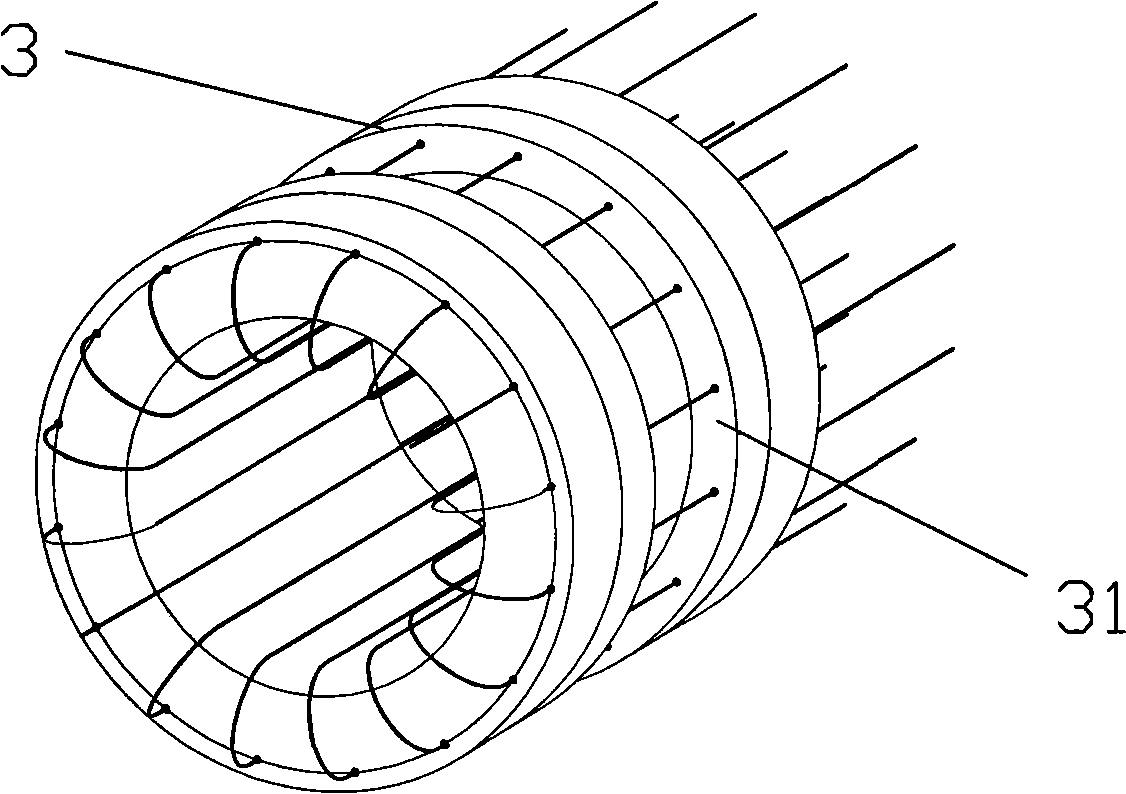
[0025] Embodiment one: if figure 1 , 2 As shown, the rotating scanning capillary array analyzer includes a capillary detection window fixing device 3, a capillary sampling end 4, a capillary waste liquid end 5, a scanning objective lens 6, a laser light source 7, a beam turning system 8, a scanning mirror 9, and a fluorescence beam splitter 10. Fluorescent color filter 11, photodetector 12, and scanning central axis 13. A plurality of capillary tubes 1 are arranged in a cylindrical array around the scanning central axis 13 to form a capillary array 2, which is fixed on the capillary detection window fixing device 3. The scanning objective lens 6 , the beam deflection system 8 and the scanning mirror 9 are mounted on the same scanning platform and rotate around the scanning central axis 13 to scan the detection window 31 on each capillary in the detection capillary array 2 . The fluorescence beam splitter 10 adopts a dichroic mirror or a mirror with a hole in the center.
[0...
Embodiment 2
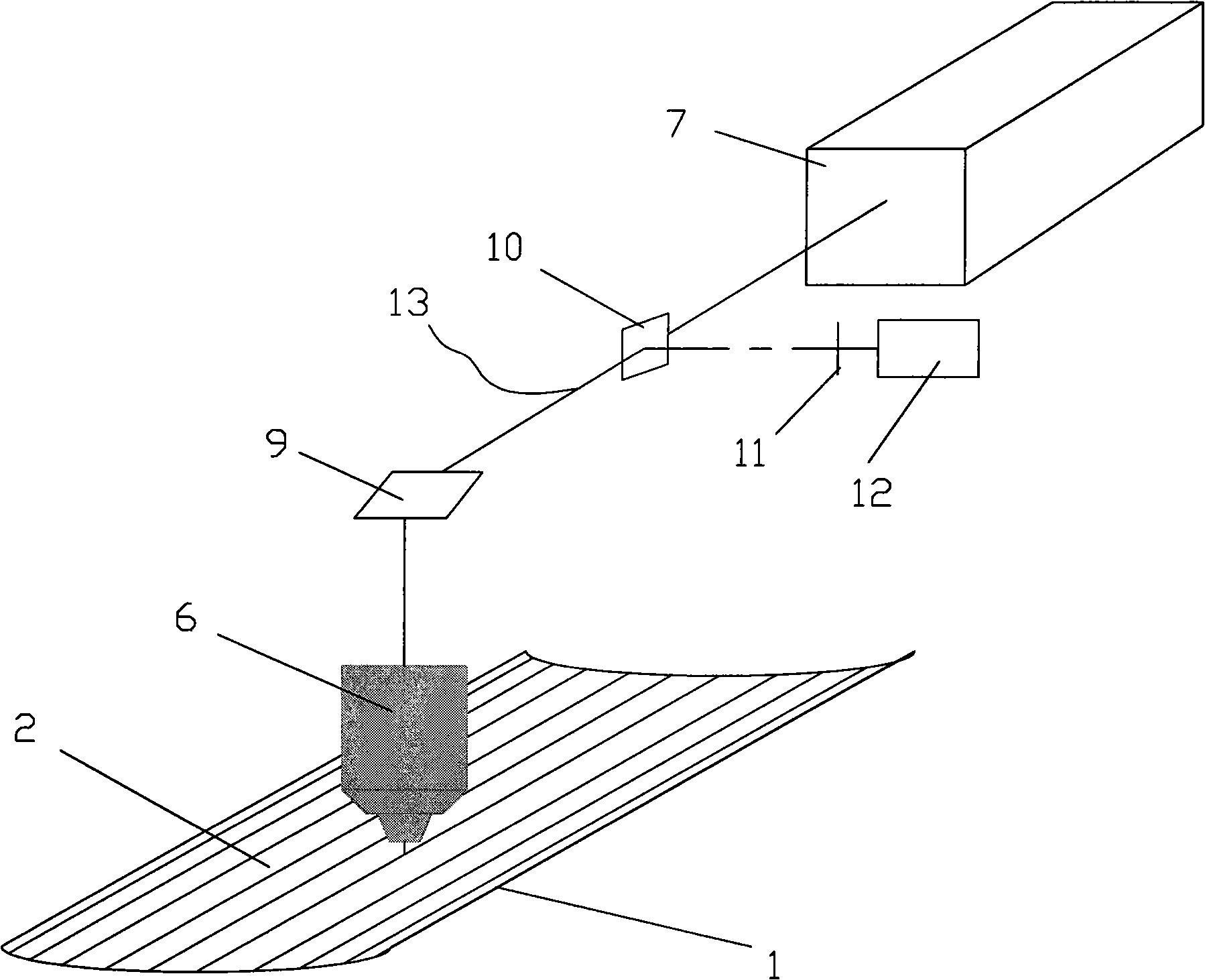
[0030] Embodiment two: if image 3 As shown, the capillary array 2 of this embodiment is an array formed by a plurality of capillaries 1 arranged on an arc surface around the scanning central axis 13 , and the scanning objective lens 6 and the scanning central axis 13 are located on the same side of the capillary array 2 .
[0031] The scanning objective lens 6 and the scanning mirror 9 are used to reciprocate and scan around the scanning central axis 13, and the capillary array 2 is fixed. During the scanning process, the central axis of the excitation beam coincident with the scanning central axis 13 is reflected by the mirror and meets the scanning objective lens 6. The optical axes coincide, and the signal fluorescence collected by the scanning objective lens 6 is reflected by the mirror and parallel to the scanning central axis 13, so as to avoid the movement of other optical devices of the detection system.
[0032] Other content of this embodiment is the same as that of...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment three: as Figure 4 As shown, the scanning objective lens 6 and the scanning central axis 13 are located on both sides of the capillary array 2, and the capillary array 2 is rotated to scan, and only the capillary array 2 needs to scan and detect around the scanning central axis 13, while other components do not move.
[0035] Other contents of this embodiment are the same as those of Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com