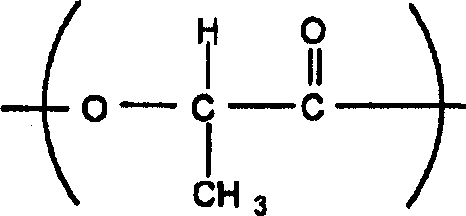
Polylactic acid and method for producing the same
A technology of polylactic acid and lactic acid, which is applied in the field of polylactic acid and its preparation, can solve the problems of large molecular weight, easy residue, and high crystal melting point
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0093] Step (1): Preparation of the first polylactic acid
[0094]Under nitrogen flow, 100 parts by weight of L-lactide (Musashino Chemical L-lactide, optical purity 99% or more) and 0.15 parts by weight of stearin were added from the feed port of a polymerization reaction vessel equipped with a condensation distillation tube. alcohol. Next, the inside of the reaction container was replaced with nitrogen five times to melt L-lactide at 190°C. When L-lactide was completely melted, 0.05 parts by weight of tin 2-ethylhexanoate and 500 μL of toluene were simultaneously added from the feed port, and polymerized at 190° C. for 1 hour to obtain the first polylactic acid.
[0095] Step (2): Removal of Lactide
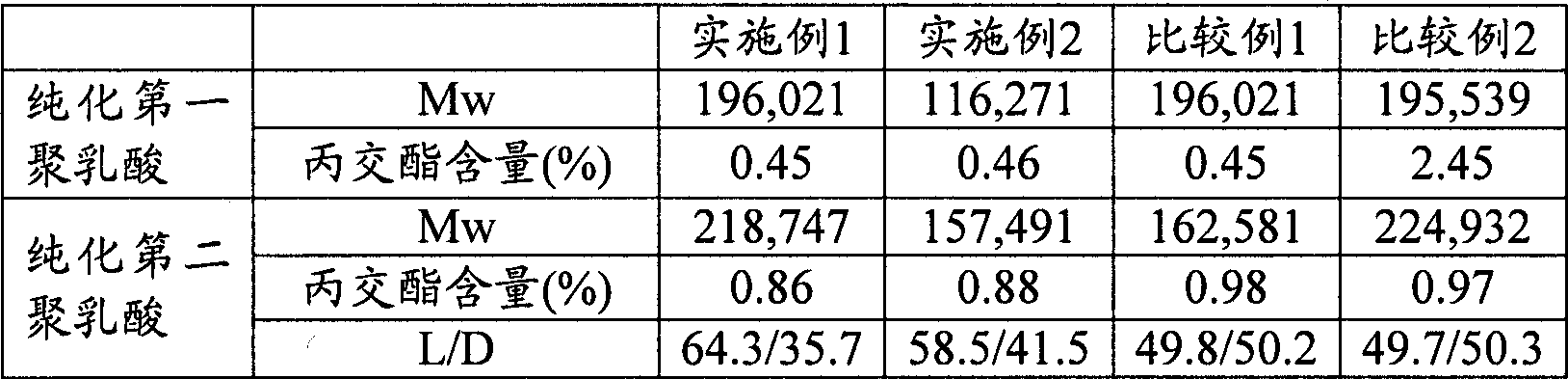
[0096] Next, the inside of the reaction vessel was depressurized to 1.33 kPa to remove excess lactide to obtain purified first polylactic acid. The Mw and lactide content of the obtained purified first polylactic acid are shown in Table 1.
[0097] Step (3): Preparati...
Embodiment 2
[0102] Steps (1) and (2)
[0103] Except having changed 0.15 weight part of stearyl alcohols into 0.2 weight part, the same operation as the step (1) of Example 1 was performed, and the purified 1st polylactic acid was obtained. The Mw and lactide content of the purified first polylactic acid are shown in Table 1.
[0104] Steps (3) and (4)
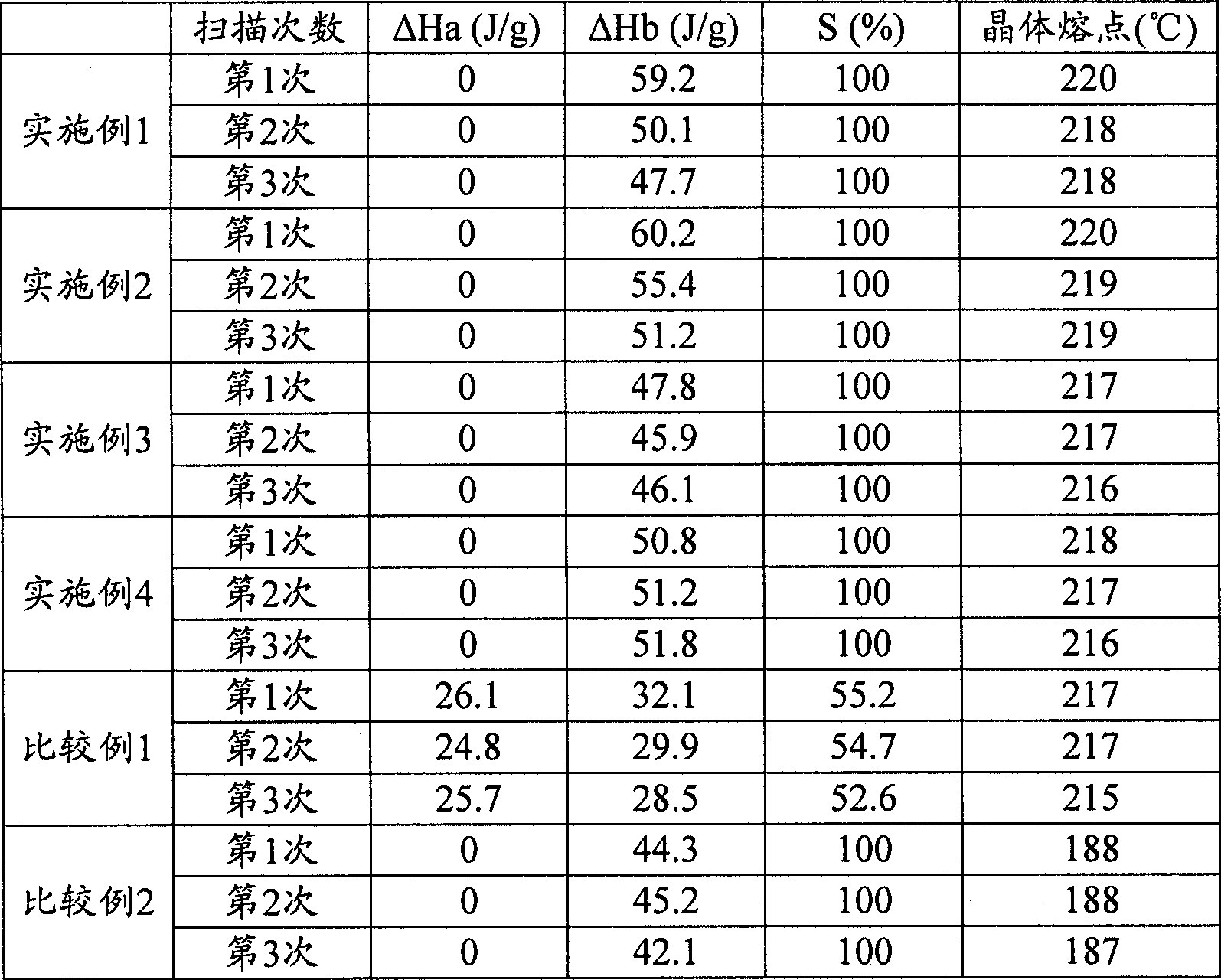
[0105] The same operation as in Example 1 was carried out to obtain the purified second polylactic acid. The Mw, lactide content and L / D of the purified second polylactic acid are shown in Table 1. The crystal melting enthalpy, stereocomplex crystal content (S) and crystal melting point are shown in Table 2.
Synthetic example 1
[0107] (Synthesis of PDLA)
[0108] Under a nitrogen stream, 100 parts by weight of D-lactide (manufactured by Musashino Chemical Research Laboratories) and 0.15 parts by weight of stearyl alcohol were added from the feed port of a polymerization reaction vessel equipped with a condensing distillation tube. Next, the inside of the reaction vessel was replaced with nitrogen five times to melt D-lactide at 190°C. When D-lactide was completely melted, 0.05 parts by weight of tin 2-ethylhexanoate and 500 μL of toluene were simultaneously added from the feed port, and polymerized at 190° C. for 1 hour. Next, the pressure in the reaction container was reduced to 1.33 kPa to remove excess lactide. The Mw of the obtained PDLA was 198,422.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| optical purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com