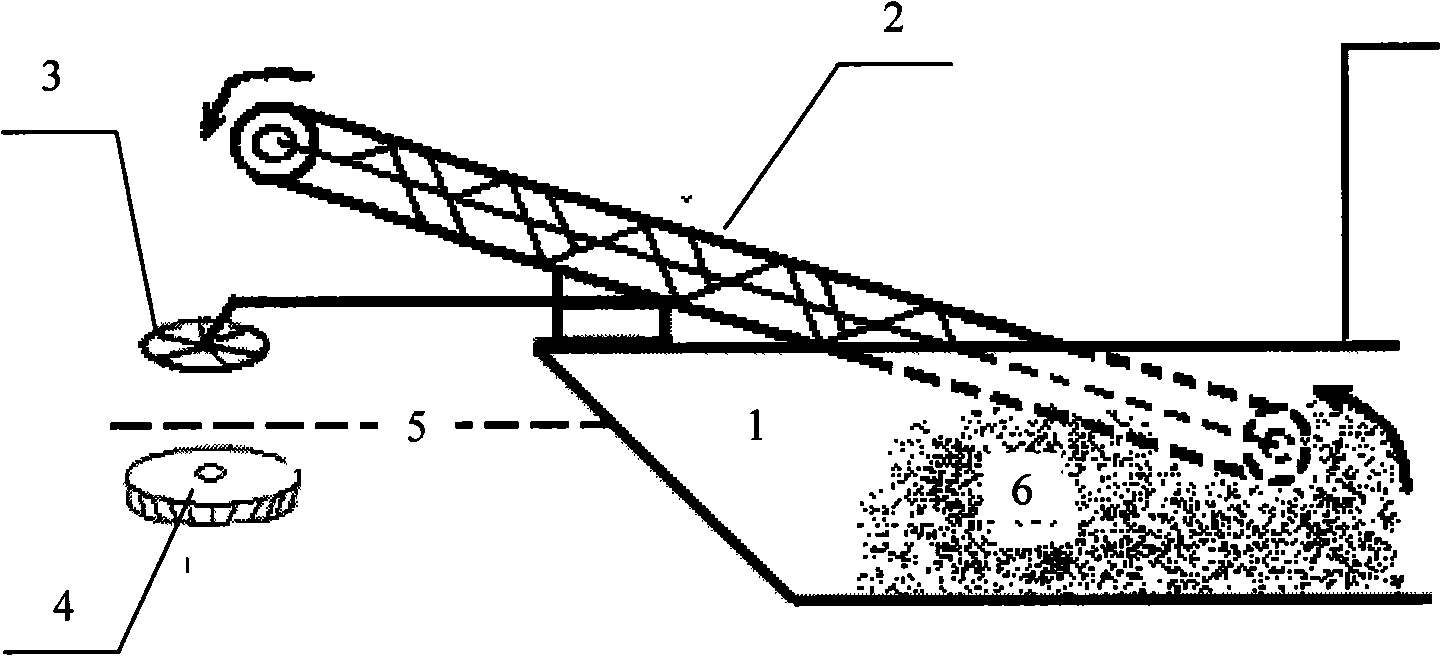
Method for treating water body with arsenic pollution
A technology for arsenic pollution and water body, applied in the field of environmental engineering, can solve problems such as difficulty in effect, difficulty in waste treatment, eutrophication of water body, etc., and achieves the effect of simple and easy method, obvious effect of arsenic removal, and easy access to soil
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1: Adsorption rate (adsorption kinetics).
[0027] After the soil is sprinkled into the water body, a dispersed mud layer is formed in the water. The space occupied by the mud layer during the sinking process is about 50cm. According to this calculation, the mud layer gradually moves down to the bottom of the water for about 20m. It takes 4 minutes, that is, the contact time of the soil with the water body during the sinking process is about 4 minutes. Carry out laboratory test according to this condition, the result is as follows:
[0028] Example 1: Add 1.0% (g / mL) φ0.045mm (300 mesh) Yunnan red soil 1 (9.2% iron content, pH 5.4, clay content 42%) to 1000mL surface water containing arsenic 3.47mg / L, After shaking for 5 minutes and filtering, the arsenic content in the clear liquid was 0.0614mg / L, and the adsorption rate reached 82.3%.
[0029] Example 2: Add 0.03% (w / v) φ0.076mm (200 mesh) Yunnan red soil 2 (iron content 10.8%, pH 5.3, clay content 45% to 10...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2: Adsorption Capacity (Adsorption Thermodynamics)
[0032] In polluted water bodies, arsenic is evenly distributed in the water body. In the process of purifying water bodies with soil, not only the soil particles are required to have a faster adsorption rate, but also the soil is required to have sufficient adsorption capacity to improve the arsenic fixation capacity as much as possible. . To this end, the following two sets of adsorption capacity tests were designed.
[0033] Example 1: 100mL 2.0mg / L arsenic-containing aqueous solution, add 0.03% (g / mL) φ0.076mm (200 mesh) red soil 2 (10.8% iron content, pH 5.3, clay content 45%), shake After 2 hours of filtration, the amount of arsenic in the clear liquid was 1.59 mg / L, the adsorption rate was 20.8%, and the adsorption capacity of the soil was 1386 mg / kg, that is, 1386 mg of arsenic could be adsorbed per kilogram of soil.
[0034] Example 2: Add 2.0% (w / v) φ0.1mm (150 mesh) red soil 1 (9.2% iron content, p...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment 3: Security Analysis
[0037] (1) Re-release of arsenic-fixed soil
[0038] Arsenic is a poisonous inorganic element. After settling into the bottom mud, whether it will be released again and cause secondary pollution is an important issue that needs attention. Tests have shown that after nearly two months of treating polluted water with soil, the arsenic content in the treated water has not risen any more, and has a tendency to gradually decrease. This shows that the arsenic deposited in the sediment did not re-release, which is consistent with the low solubility of iron arsenate mentioned above.
[0039] Generally, the forms of arsenic in polluted water are mainly pentavalent arsenic and trivalent arsenic, of which pentavalent arsenic accounts for about 70-80% and trivalent arsenic accounts for 20-30%. Tests have shown that both forms of arsenic have strong adsorption capacity for iron; iron in nature has two forms of trivalent and divalent, and iron in r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com