Organic solar cell adopting weak epitaxial growth film as donor
A weak epitaxial growth and solar cell technology, applied in the field of organic solar cells, can solve the problems of increasing the complexity and cost of device preparation, limiting device performance, short-circuiting of thin-film devices, etc., to achieve effective transmission, overcome roughness increase, and device The effect of performance improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] A kind of donor that the present invention adopts the preparation method of the organic solar cell of weak epitaxial growth thin film, its steps and conditions are as follows:
[0037] Spin-coat PEDOT / PSS conductive coating 2 on the surface of ITO glass 1, vacuum-deposit 10 nanometers of induction layer 3, 50 nanometers of donor material 4, 60 nanometers of acceptor material layer 6, and 5 nanometers on the PEDOT / PSS surface The metal electrode buffer layer 7 is finally deposited with a stencil with an area of 0.0314cm 2 , Ag with a thickness of 100 nm as the cathode 8 is formed as Image 6 Device configuration shown. The background vacuum is 8×10 -4 Pa, substrate temperature 155°C, deposition rate 1 nm / min, induction layer material is BP2T, donor material is ZnPc, acceptor material is C60, metal electrode buffer layer is Alq3.
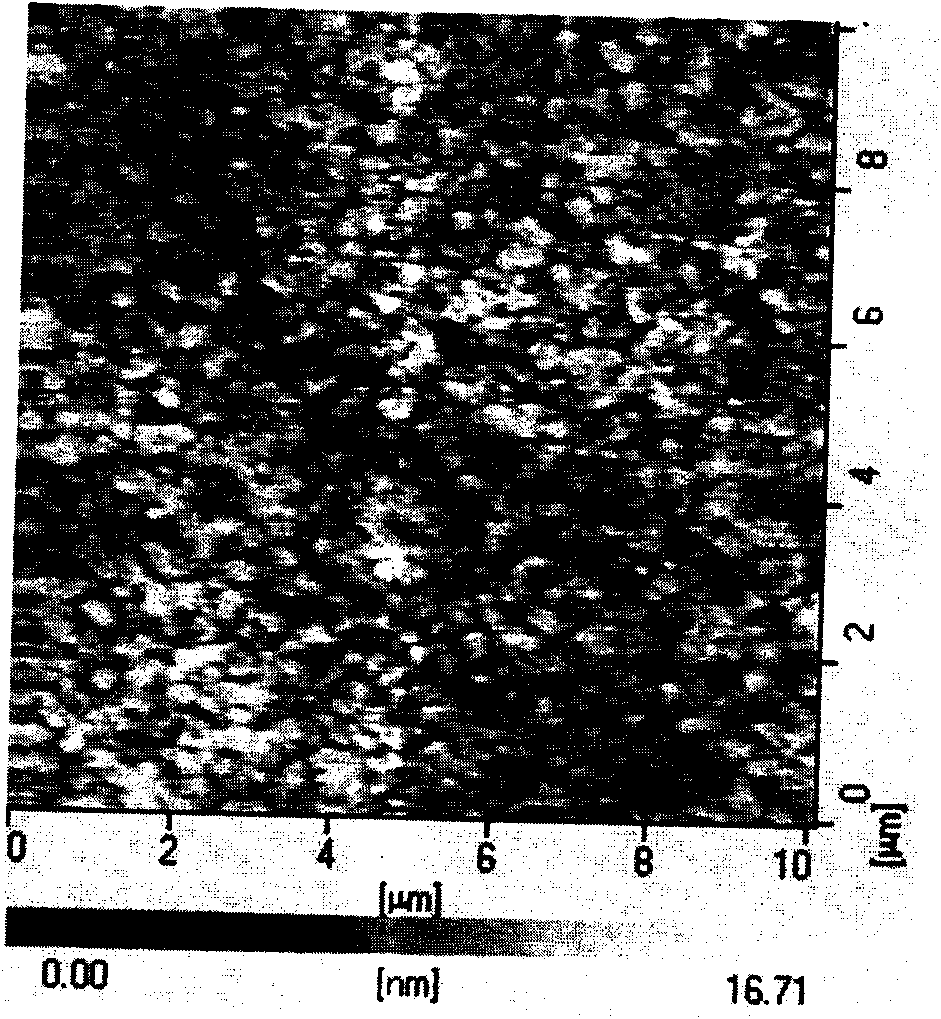
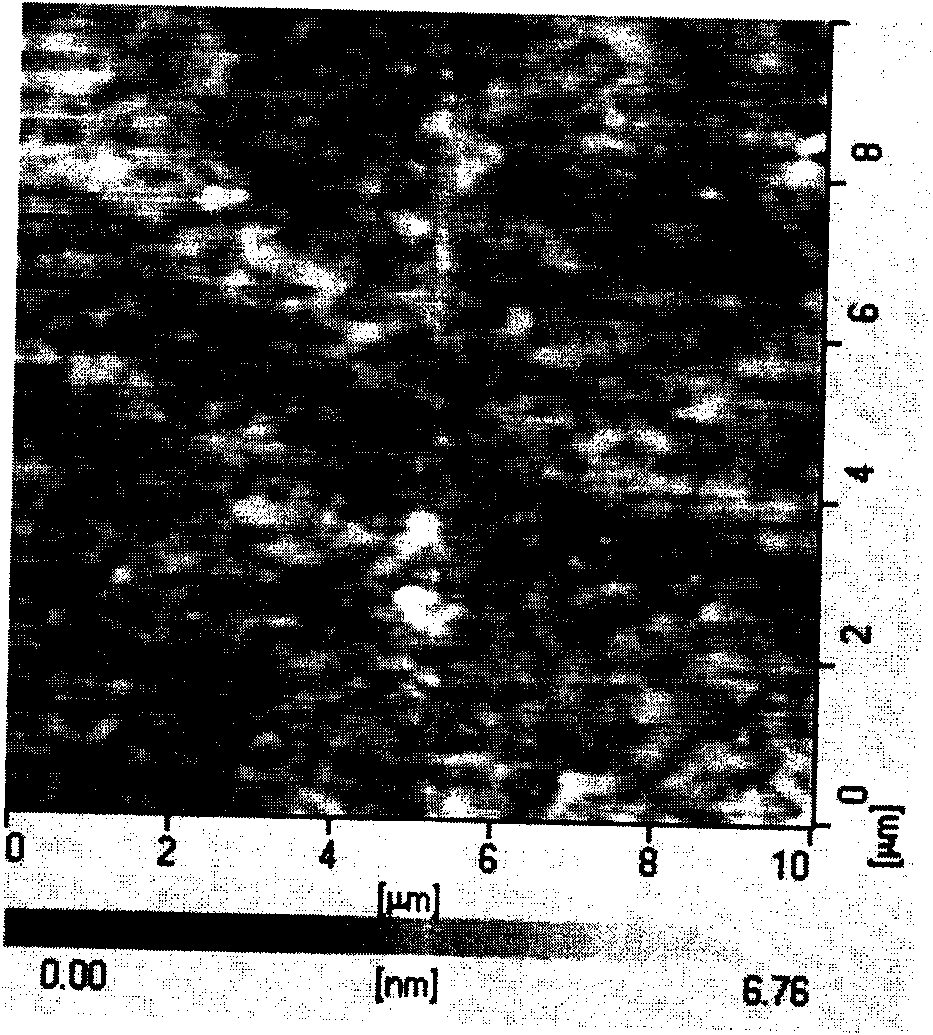
[0038] figure 1 It is the atomic force topography diagram of the surface of ITO conductive glass, and the surface roughness is 2.64nm. ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] A layer of PEDOT / PSS 2 was spin-coated on the surface of ITO glass 1, and a 12-nanometer induction layer 3, a 10-nanometer donor material 4, and a blend layer of 15-nanometer donor material and acceptor material were vacuum-deposited sequentially on the surface of PEDOT:PSS 5. A receptor material layer 6 of 40 nanometers, a metal electrode buffer layer 7 of 0.5 nanometers, and finally deposit a layer with an area of 0.0314 cm by using a stencil 2 , Al with a thickness of 100 nm as the cathode 8 is formed as Figure 8 Device configuration shown. The background vacuum is 8×10 -4 Pa, the substrate temperature is 155°C, the deposition rate is 1 nm / min, the material of the induction layer is BP2T, the material of the donor is ZnPc, the material of the acceptor is C60, and the buffer layer of the metal electrode is LiF.
[0051] Figure 9 is adopted Figure 8 The second device configuration shown, the current-voltage curve of the solar cell with weak epitaxial growth fi...
Embodiment 3
[0057] On the surface of ITO glass 1, a 2-nanometer induction layer 3, a 60-nanometer blend layer 5 of a donor material and an acceptor material, and a 10-nanometer metal electrode buffer layer 7 are vacuum-deposited in sequence, and finally a layer with an area of 0.0314 cm is deposited using a stencil. 2 , Al with a thickness of 100 nm as the cathode 8 is formed as Figure 10 Device configuration shown. The background vacuum is 8×10 -4 Pa, substrate temperature 155°C, deposition rate 1 nm / min, induction layer material is BP2T, donor material is ZnPc, acceptor material is C60, metal electrode buffer layer is Alq3.
[0058] Figure 11 is adopted Figure 10 The third device configuration shown, the current-voltage curves of the solar cell with weak epitaxial growth film as the donor under the dark state and under the irradiation of simulated solar light source, where the substrate temperature is 155°C, the donor material is ZnPc, and the acceptor The material is C60. At ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com