Bioremediation method for petroleum contamination and its special strains
A technology for petroleum hydrocarbons and bacterial agents, applied in the field of bioremediation of oil pollution, can solve the problems of harmful chemical extractants, expensive equipment costs, and restrictions on widespread use, and achieve the effects of high activity, accelerated progress, reduced complexity and safety.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
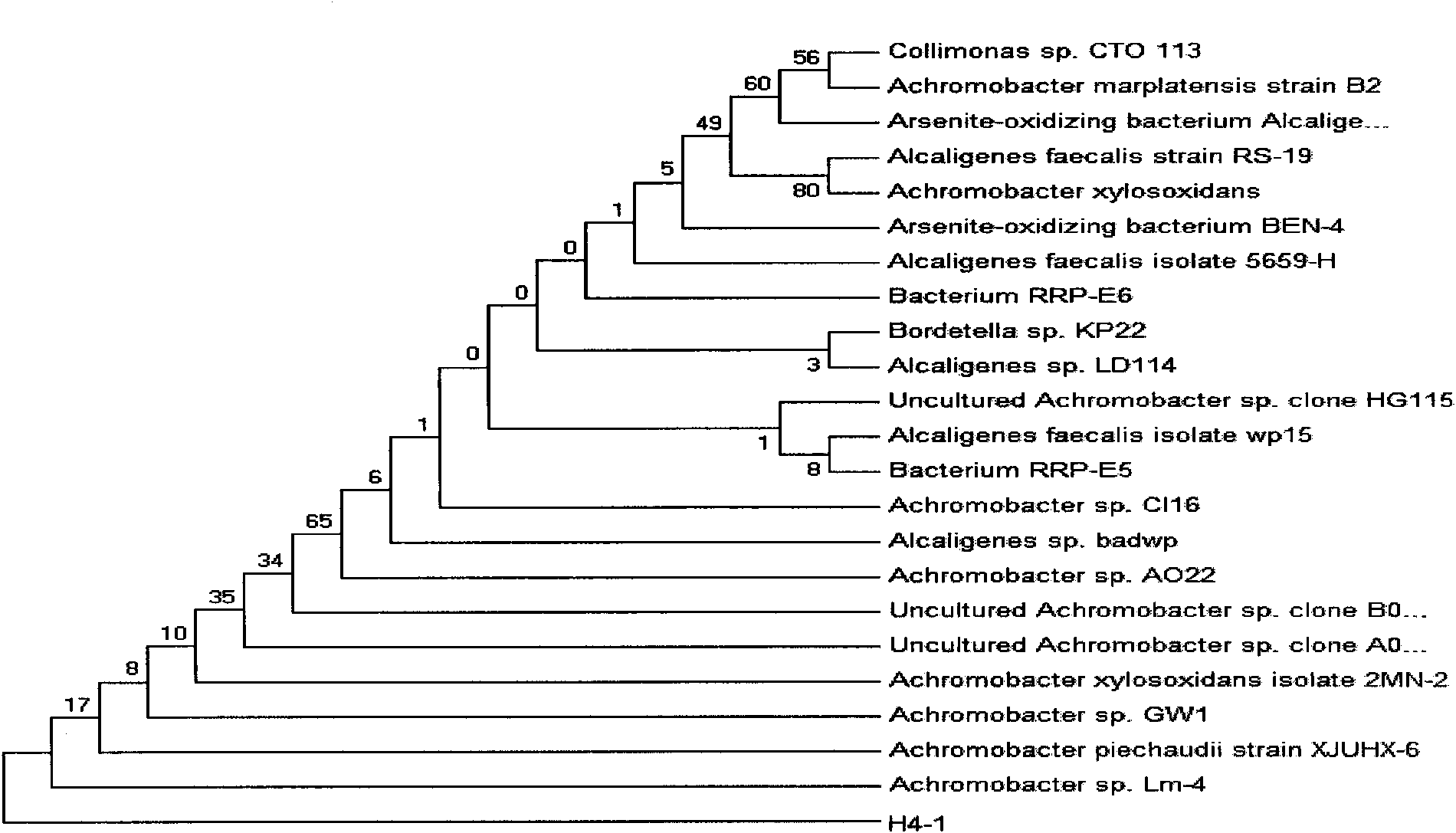
[0044] Embodiment 1, isolation and identification of bacterial strain
[0045] 1. Separation
[0046] Soil source: Select contaminated soil samples from Xinjiang Oilfield. The oilfield here is currently the main oil production area in my country, and its oil pollution is also the most serious. Therefore, the content and degradation ability of oilophilic bacteria in the soil should also be very strong.
[0047] Enrichment and screening of oleophilic bacteria by plate culture: Take 5.0g of oil-contaminated soil sample and put it into a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask containing 100ml of MSM medium, and place it at 30℃, 150r min -1 Cultivate in a shaker under certain conditions for 4 days; then take a certain amount of supernatant liquid into a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask containing 100ml of fresh medium, 30°C, 160r min -1 Cultivate in shaker under the condition for 7d; so repeat 3 times. Dip the enriched culture solution with an inoculating loop and streak on the plate; after multiple strea...
Embodiment 2
[0106] Embodiment 2, the cultivation of bacterial strain and the preparation of solid microbial agent
[0107] In many oil sludge bioremediation, the addition of bacteria is a very troublesome step, because the bacteria liquid is added to the oil sludge, but the biggest defect of the bacteria liquid is that it is not conducive to transfer, that is, it is not easy to safely and quickly remove the bacteria from the experiment The room is transferred to the actual site.
[0108] 1. Composition and preparation of bacterial agent I
[0109] 1. Composition:
[0110] Bacteria agent I is made of soybean flour, H4-1 bacteria, (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 and MgSO 4 Mixed composition, wherein, soybean flour, (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 , MgSO 4 The ratio of bacteria and bacteria is 15g soybean flour: 0.9g (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 : 0.02g MgSO 4 : 15×10 9 CFU bacteria.
[0111] 2. Preparation steps of bacterial agent
[0112] (1) Culture of bacteria
[0113] Cultivate H4-1 bacteria with LB medium at 30°C...
Embodiment 3
[0134] Embodiment 3, the application of bacterial strain
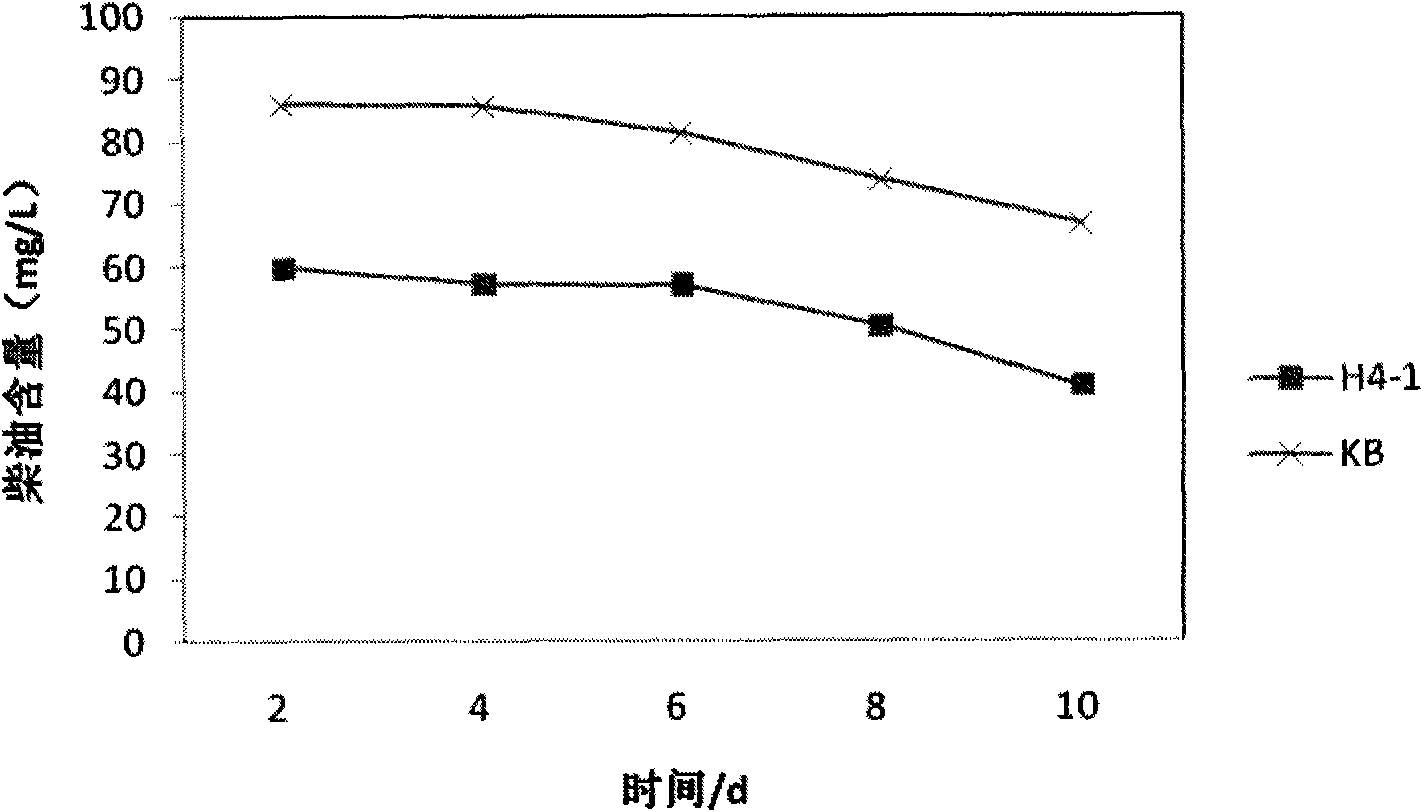
[0135] 1. Degradation of diesel by strain H4-1
[0136] Infrared spectrophotometry (GB / T16488-1996) was used to measure the degradation rate of the strain.
[0137] The specific steps are as follows: take a 50ml triangular flask, add 20ml MSM culture solution, 0.2ml sterilized diesel oil, and 1ml concentration of about 10 9 CFU / ml fresh bacterial solution, 30°C, 150r min -1 Cultivate under conditions for 10 days, and measure the diesel content in the Erlenmeyer flask (ie in the reaction system) every two days. During the measurement, the liquid in the Erlenmeyer flask was put into a centrifuge, and centrifuged at a speed of 10000r / min for 10min. Pour all the supernatant into a 125ml separatory funnel. Add 3 drops of 1:1 sulfuric acid for acidification, a small amount of NaCl as a demulsifier, and 5ml of refined CCl 4 Clean the original triangular flask with the solution, pour it into a separatory funnel, and add a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com