Magnesium alloy surface zinc-calcium series phosphating solution and conversion treatment process thereof
A magnesium alloy and solution technology, which is applied in the field of zinc-calcium phosphating solution and its conversion treatment process on the surface of magnesium alloy, can solve the problems of high cost, weak adhesion of protective film, and difficult operation, and achieve low cost and protection Good performance, simple operation and easy control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1: Each liter of aqueous solution contains 15 grams of disodium hydrogen phosphate, 4 grams of zinc nitrate, 2 grams of sodium nitrite, 0.5 grams of sodium fluoride, and 0.5 grams of calcium nitrate; the pH of the phosphating solution is 2, using phosphoric acid And / or sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH.
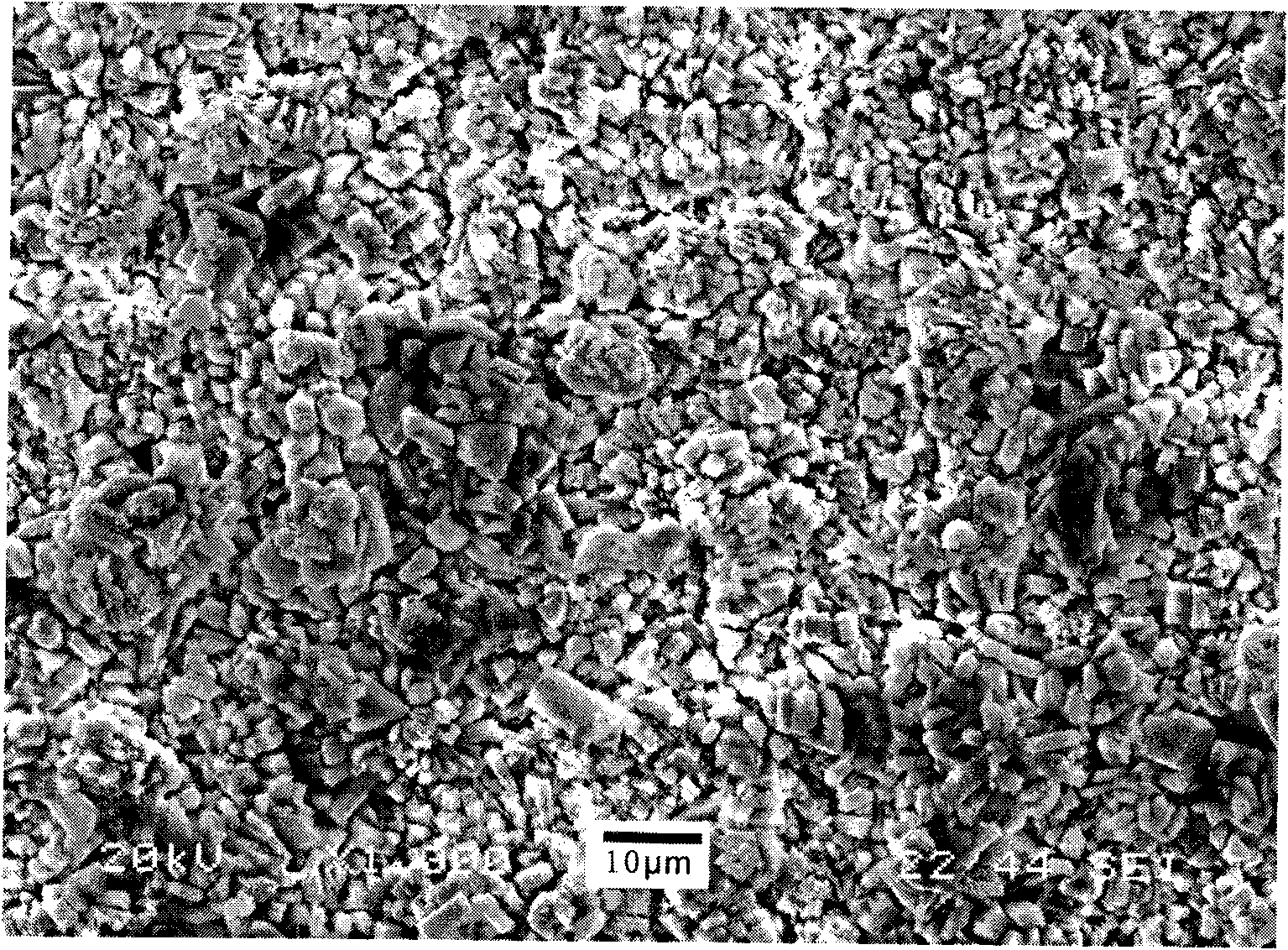
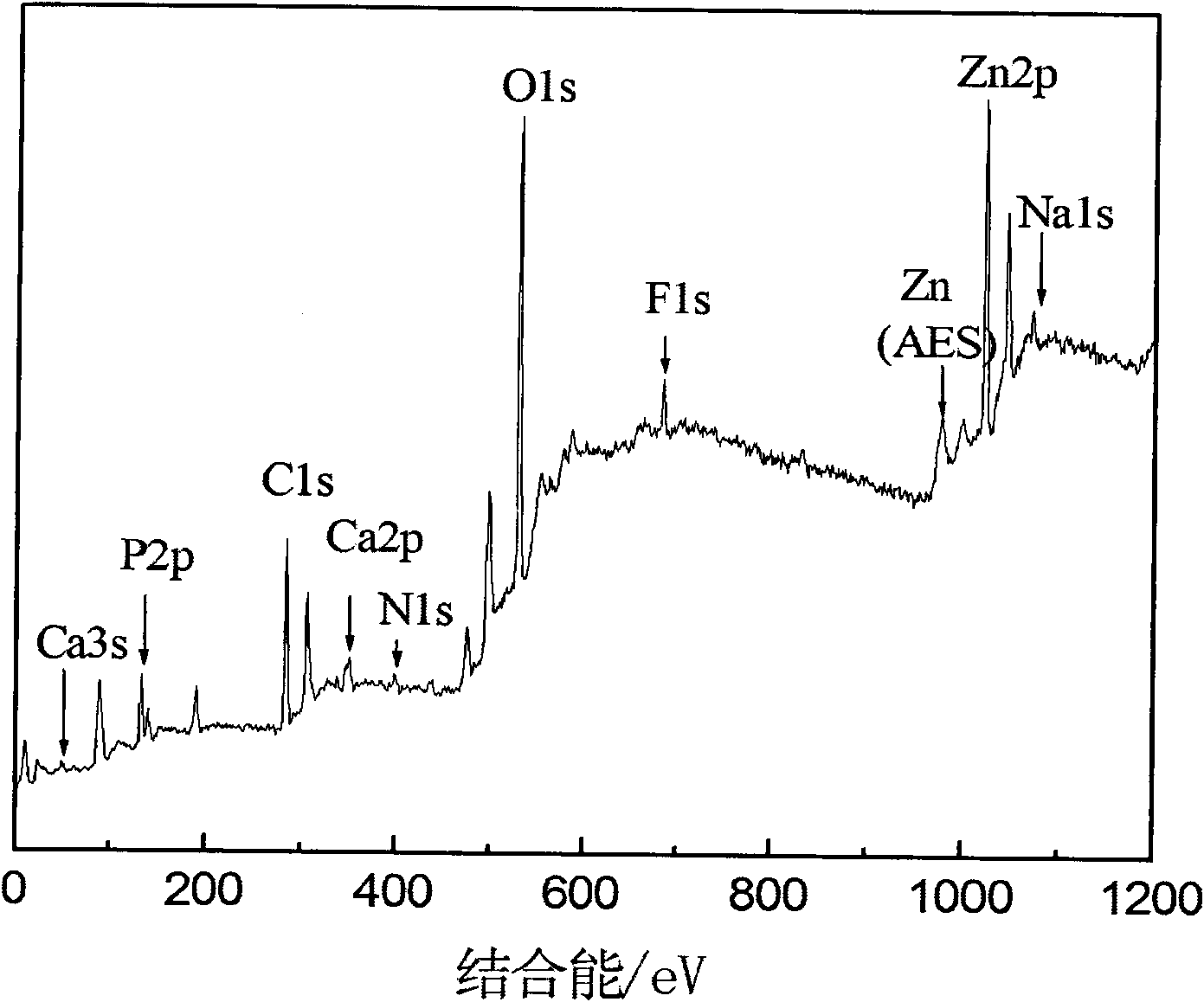
[0028] The surface of the magnesium alloy sample is degreased and the oxide scale is removed (surface activation treatment), then washed with water, and then immersed in the above-prepared phosphating solution adjusted to pH 2.5 with phosphoric acid and / or sodium hydroxide at 50°C Let stand for 20 minutes, then wash and dry. The film layer obtained by the present invention is black, and the corrosion current density of the conversion film layer obtained on the surface of the extruded AZ31 in 3.5% NaCl solution is 23 μA / cm 2 about. The SEM photo of the phosphating film obtained in this example is attached figure 1 And the composition analysis of the film is attach...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example 2: Each liter of aqueous solution contains 20 grams of disodium hydrogen phosphate, 5 grams of zinc nitrate, 3 grams of sodium nitrite, 1 gram of sodium fluoride, and 1 gram of calcium nitrate; the pH value of the phosphating solution is 2.5.
Embodiment 3
[0031] Example 3: Each liter of aqueous solution contains 30 grams of disodium hydrogen phosphate, 6 grams of zinc nitrate, 4 grams of sodium nitrite, 2 grams of sodium fluoride, and 2 grams of calcium nitrate; the pH of the phosphating solution is 3.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion current density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com