Process for preparing composite sulfonated membranes with IPN structures
A technology of sulfonated polymers and non-sulfonated dihalides, applied in chemical instruments and methods, structural parts, organic diaphragms, etc., can solve the problems of narrow application range and high raw material cost, and achieve good water stability, high conductivity, The effect of simple synthesis process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
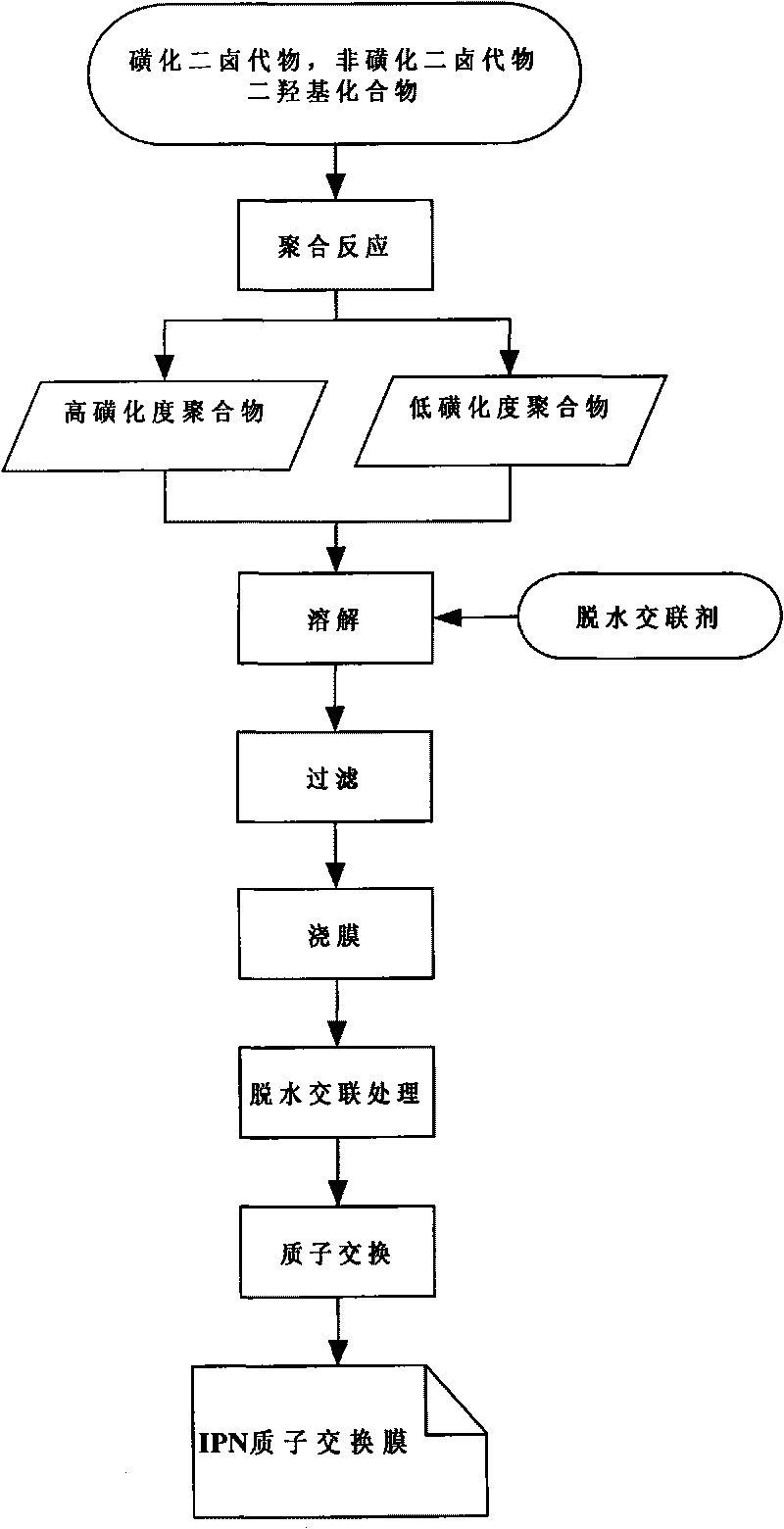
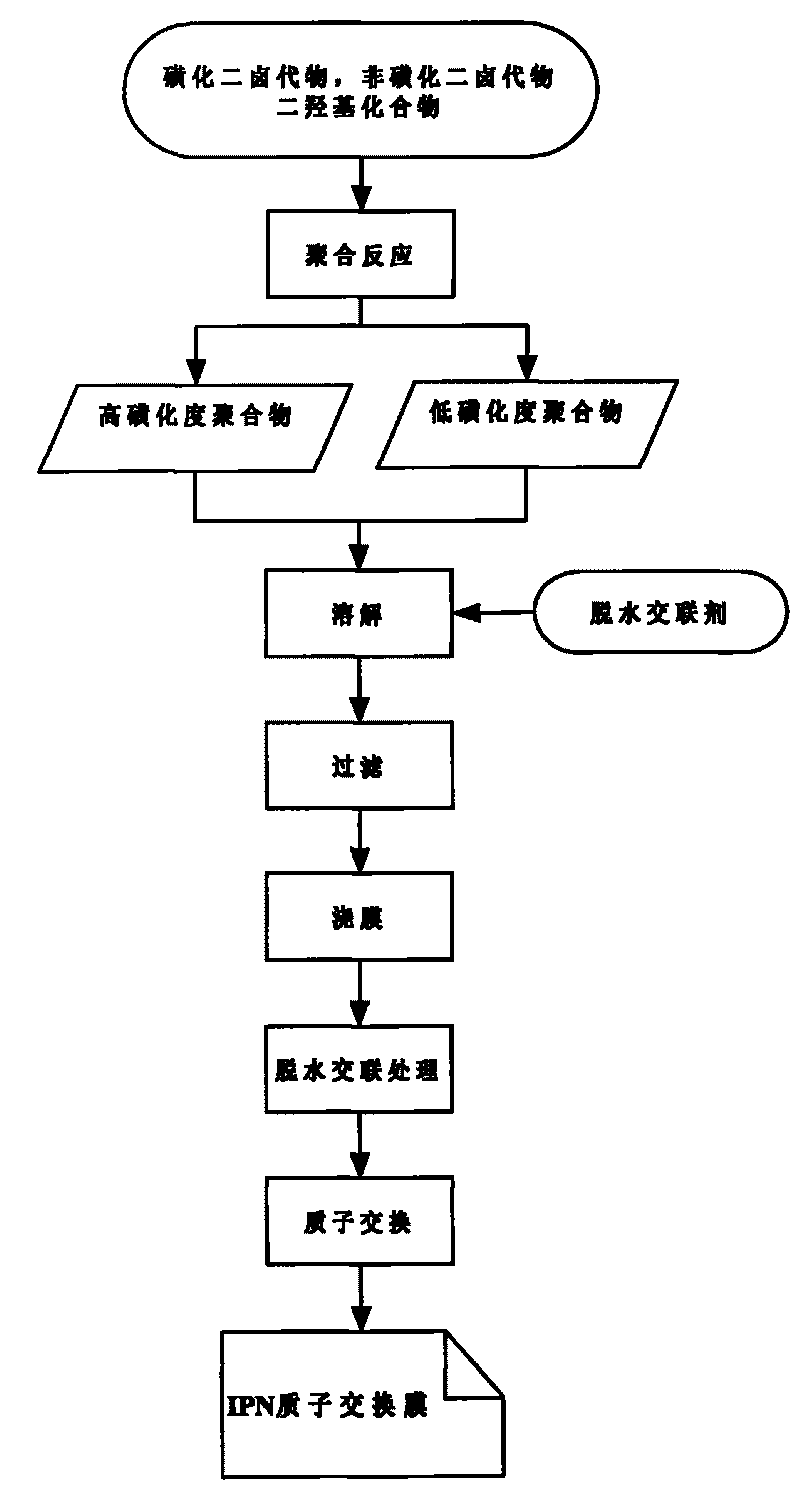
[0014] The preparation method of the composite sulfonated membrane with IPN structure of the present invention uses a dehydration cross-linking agent to introduce an IPN structure between two polymers to prepare a polymer with an IPN structure, and obtains an IPN composite sulfonated proton exchange membrane through a solution casting method, that is, by Sulfonated dihalides, non-sulfonated dihalides, and dihydroxy compounds, adjusting the molar ratio of sulfonated and non-sulfonated compounds, or changing the structure of sulfonated dihalides, non-sulfonated dihalides, and dihydroxy compounds, Different types of linear sulfonated polymers are obtained through polymerization. The different types of linear sulfonated polymers undergo proton exchange to form proton-type polymers. The proton-type polymers are cast at high temperature in the presence of dehydrating cross-linking agents. An IPN composite sulfonated polymer membrane was obtained. For the preparation process, see fi...
Embodiment 1
[0044] Embodiment 1: the preparation of linear polymer
[0045] Preparation of SPAES70 polymer: add fully dried 1.925g (4.20mmol) SDFDPS, 0.458g (1.80mmol) DFDPS, 1.117g (6.00mmol) BP into a four-necked flask, add 17mL DMSO, after completely dissolving, add 0.953 g (6.90mmol) of potassium carbonate and 8.5mL of anhydrous toluene as an entrainer for water. The temperature was raised to 140°C for 4 hours, and the water produced in the reaction was removed by azeotroping with toluene, then the temperature was raised to 165°C, and 8.5 mL of anhydrous toluene was added dropwise through a constant pressure dropping funnel. React for 30 hours. After the reaction, add about 17mL DMSO to dilute, lower the temperature, pour it into about 200mL ethanol, and precipitate a fibrous product. After fully washing with water, vacuum dry at 100°C for 24 hours to obtain a linear sulfonated polymer product. The sulfonated polymer was exchanged with hydrochloric acid to obtain the protic sulfonat...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2: Preparation of SPAES70 / SPAES30 (5 / 5-1) (M(1)). Theoretical IEC=2.08meq / g before treatment, measured IEC=1.90meq / g after treatment
[0050] Take dry proton type linear sulfonated polymer SPAES701.0g and SPAES301.0g respectively, join in DMSO and form a 5% (w / v) solution, add 0.02g P 2 o 5 , stirred, dissolved and filtered, cast on a glass plate, dried in a constant temperature oven at 60°C for 10 hours, and then heated to 120°C for 10 hours. Then move the glass plate to a vacuum oven for drying at 60°C for 5 hours, at 120°C for 5 hours, and at 180°C for 10 hours. After the temperature drops to room temperature, soak in water to peel off, soak in water for 48 hours, then exchange with hydrochloric acid for 72 hours, and wash with water for 48 hours. It was taken out and dried at 150° C. for 2 hours to obtain a proton type sulfonated polymer membrane M (1).
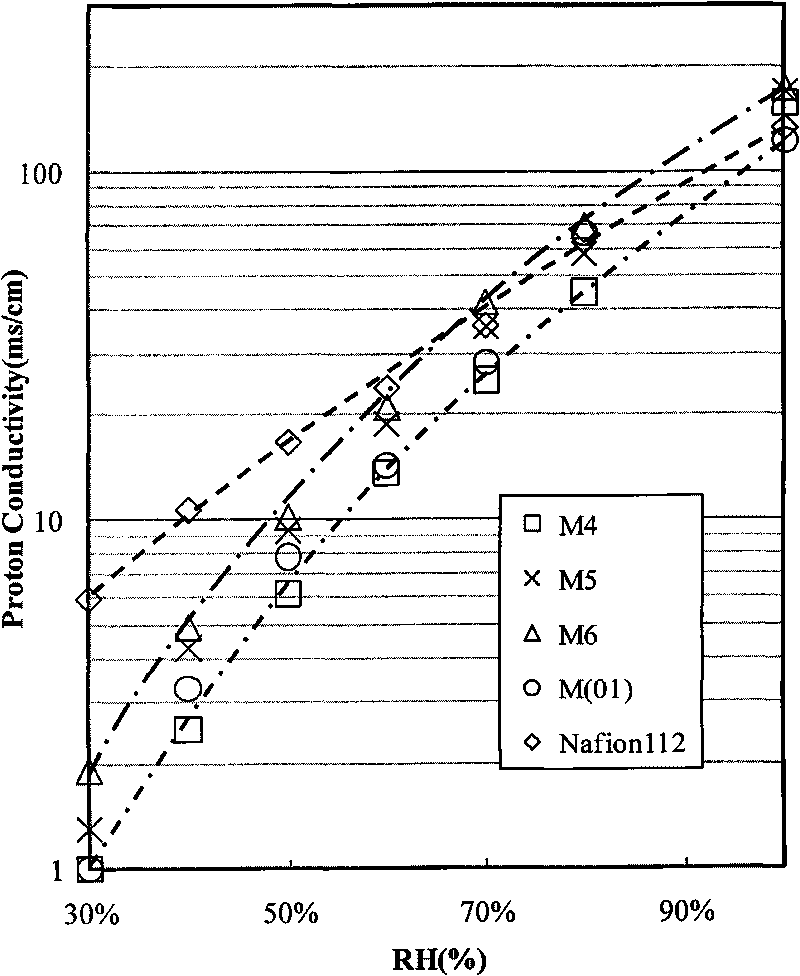
[0051] Its performance data are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com