Process for producing molten hot molten iron
A molten iron and process technology, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of complex gas treatment process and high cost, and achieve the effect of reducing the amount of coke used and the cost of molten iron
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
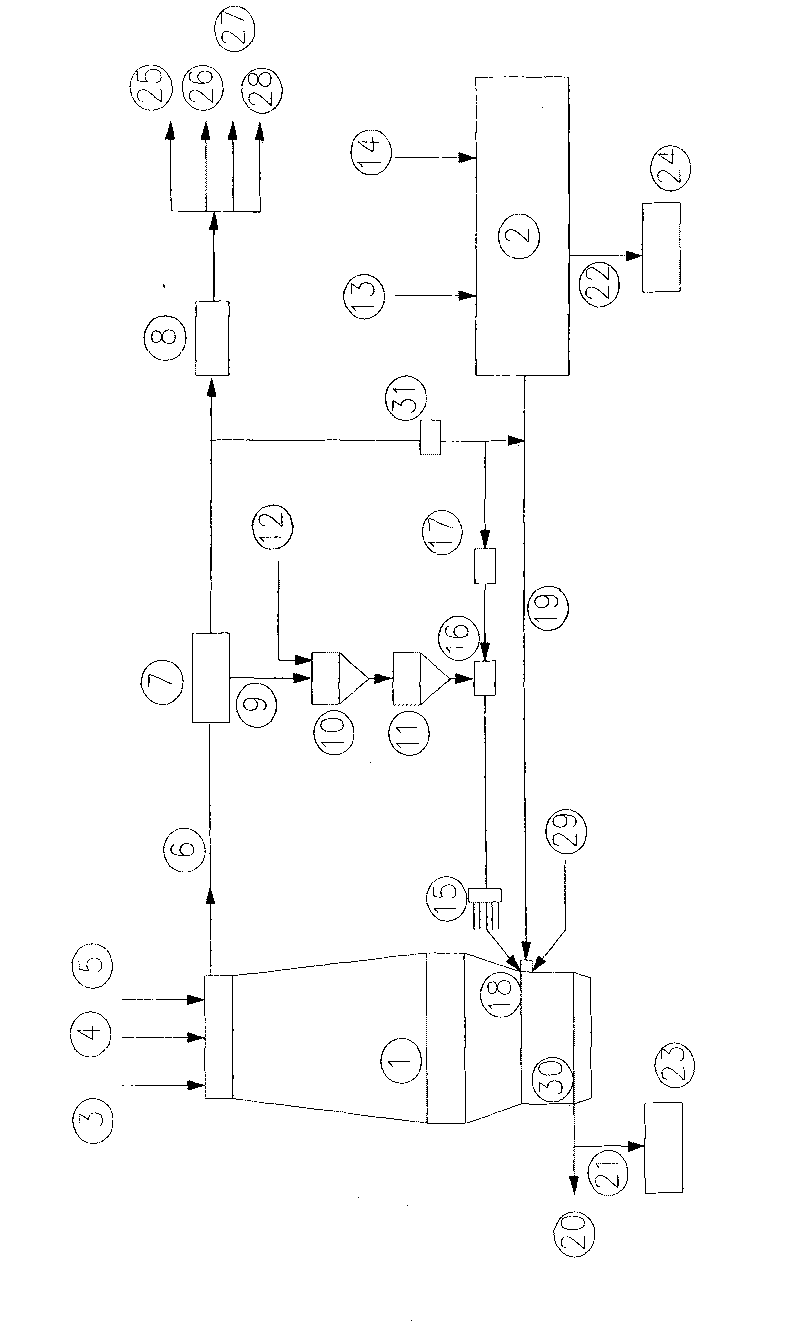
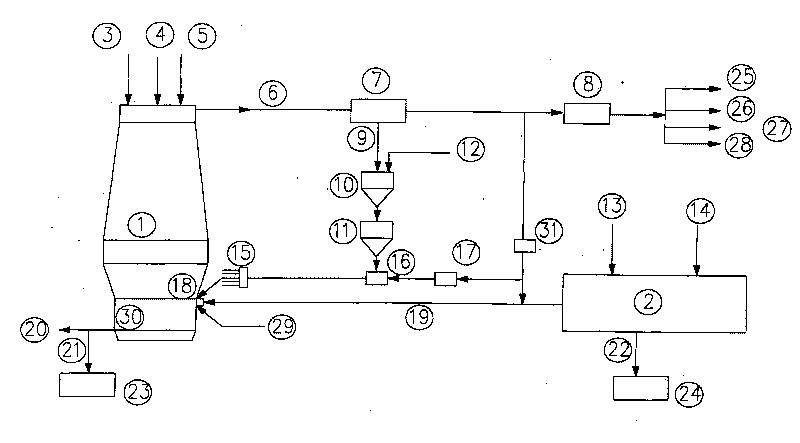
[0016] Embodiment is further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing:
[0017] Lump ore / pellet 3, limestone / dolomite 4 and coke 5 from the raw material yard are added from the top of blast furnace 1. A blast furnace 1 is connected to a coal gasifier 2 . Coal gasifier 2 uses non-coking pulverized coal (~800kg / t iron) 13 and oxygen (~450m 3 / t iron) 14 to produce high-temperature reducing gas (1200-1700°C, containing dust, containing H 2 S) The reducing gas pipeline is directly blown into the blast furnace 1 through the blast furnace tuyere 18, and the amount of high-temperature reducing gas is about 1600m 3 / t Iron.
[0018] Blow a small amount of oxygen into the tuyere (~100m 3 / t iron) 29, the temperature of the high-temperature reducing gas is raised to (~2100°C). The high-temperature reducing gas moves upwards in the furnace to heat the falling charge added to the top of blast furnace 1 and reduce iron oxides. Only a small amount of coke or non-coking...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com