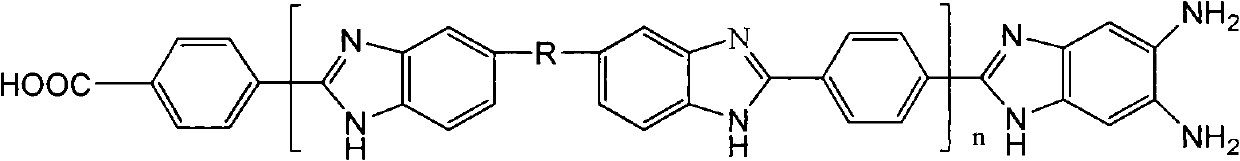
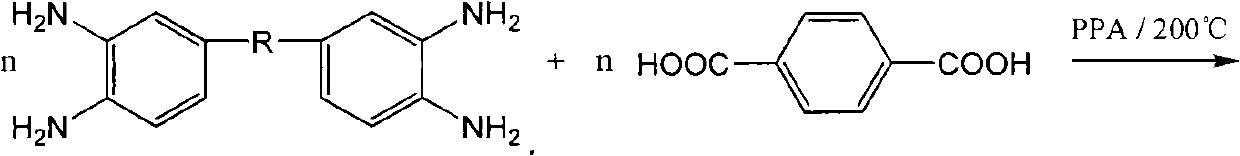Method for protecting amino end groups in polybenzimidazole high-molecular material
A technology of polybenzimidazole and polymer materials, which is applied in the field of protection of terminal amino groups, can solve the problems affecting the stability and service life of materials, and achieve the effect of high yield and easy reaction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] The reaction equation is as follows:
[0054]
[0055] In the formula: (1) is polybenzimidazole; (2) is urea; (3) is PBI with protected amino groups (that is, polymers that generate terminal benzimidazolones)
[0056] In a 250mL four-neck flask equipped with a stirrer, a reflux condenser, a thermometer, and a dropping funnel, add polybenzimidazole (15g), urea (18-28g), and 70mL of dimethylacetamide to be protected successively, and stir heating. Stir under the protection of nitrogen, heat the oil bath to 100°C~108°C, add 95% sulfuric acid dropwise, keep the pH value of the reaction solution between 5~6, and react at 100°C~180°C. And add 4.5g urea every 1h, continue to react for 6h, slowly pour the reaction mixture into water to spin, and wash with deionized water for 3~5 times. The solid polymer was pulverized and washed three times with deionized water, and filtered to obtain PBI (light yellow or brown powder) with protected amino groups.
Embodiment 2
[0057] [Example 2] Microwave-assisted solid-phase synthesis
[0058] Microwave-assisted solid-phase synthesis was used. In a three-necked flask equipped with a condenser tube and inert gas protection, add the polybenzimidazole to be protected, urea, water and concentrated sulfuric acid (the amount added is the same as in Example 1), first feed the protective gas nitrogen for 10min, and then Microwave intermittent heating reaction, every heating 3mim, intermittent 10min, after the temperature drops, add 5g of urea. Respond intermittently for 6 to 8 times. The reaction solution was slowly poured into water for spinning. Other processing methods are with embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0060] With the method of embodiment 1, just change urea into equimolar substituted urea, thiourea, substituted thiourea and can obtain other protected situations in the general formula.
[0061] Polybenzimidazole can be of any structure, but the amount of urea added in the reaction process of PBI with different structures is different. For example, the amount of urea required for general long-chain PBI is 2 to 4 times that of its terminal amino group. And hyperbranched PBI has a large amount of terminal amino groups, so the amount of urea should be more. The amount of urea is 2 to 5 times that of its terminal amino group. If the quality of PBI is used as a benchmark, the amount of urea used in hyperbranched PBI is 5 to 10 times that of chained PBI.
[0062] The solvent can be selected from dimethylacetamide, dimethylsulfoxide, N-methylpyrrolidone and the like.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com