Confocal optical scanner
A scanner and confocal technology, which is applied in the field of biomedical microscopy imaging, can solve the problems of uneven illumination intensity, high stray light background noise, and slow scanning speed of the turntable confocal scanner, and achieve high-sensitivity confocal optical imaging , avoid stray light background noise, avoid the effect of scanning fringe interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
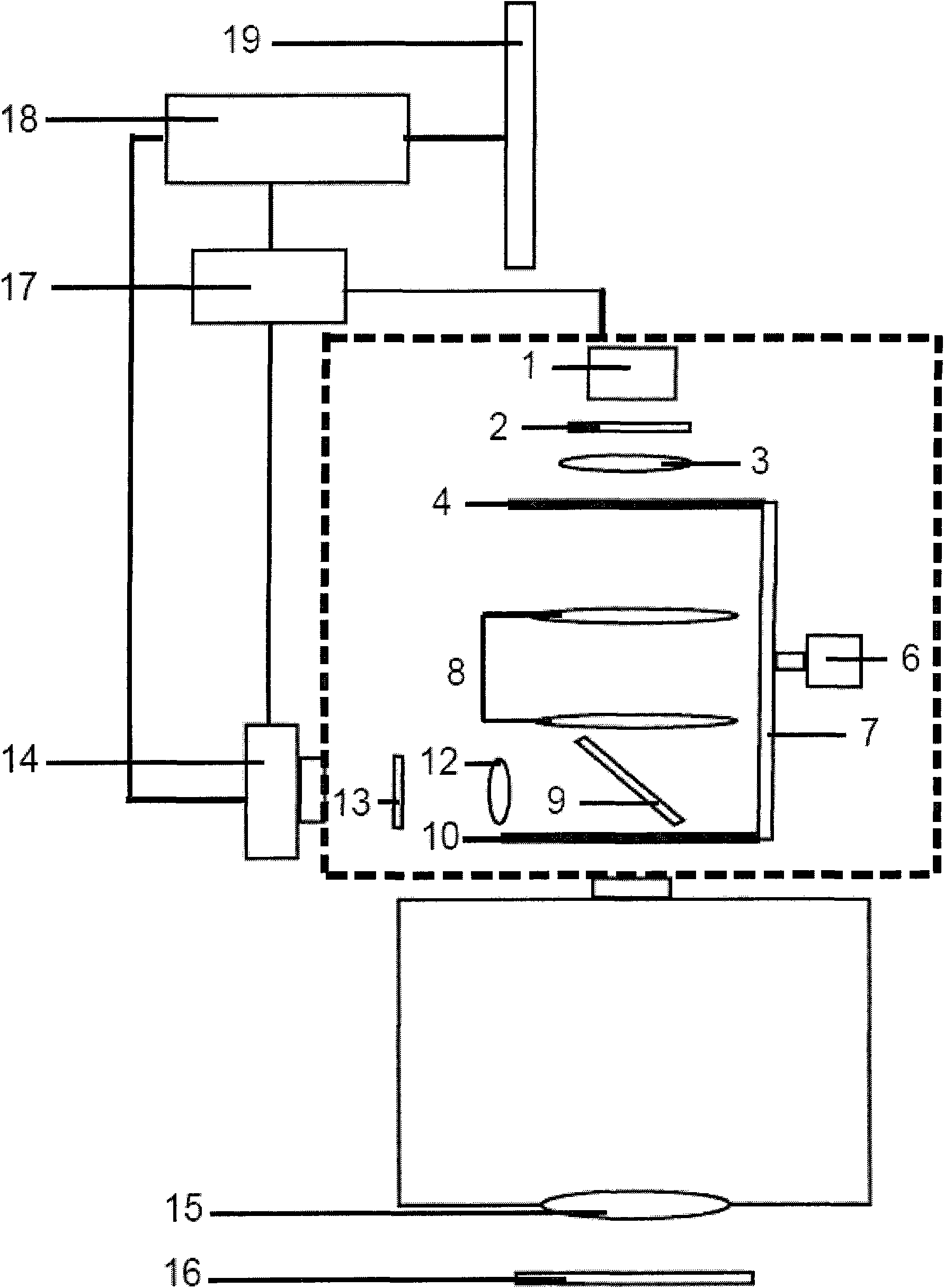
[0044] figure 2 It is a structural schematic diagram of the first confocal optical scanner related to the present invention, Figure 6 It is a structural schematic diagram of the illumination slider 4 and the imaging slider 10 used in this embodiment.
[0045] In this embodiment, the illuminating light emitted by the light source 1 composed of mercury lamp, xenon lamp, light emitting diode or laser passes through the pinhole 5 on the illuminating color filter 2, illuminating lens 3, and illuminating slider 4 which are sequentially placed in the optical path. , the pinhole lens group 8, the dichroic beam splitter 9, the pinhole 11 and the microscope objective lens 15 on the imaging slider 10, shine on the sample 16 of the imaging focal plane of the microscope objective lens 15, wherein only the illumination light of a specific wavelength can pass through Lighting filter 2. Fluorescence emitted by the illuminated sample 16 returns through the microscope objective lens 15 and ...
Embodiment 2
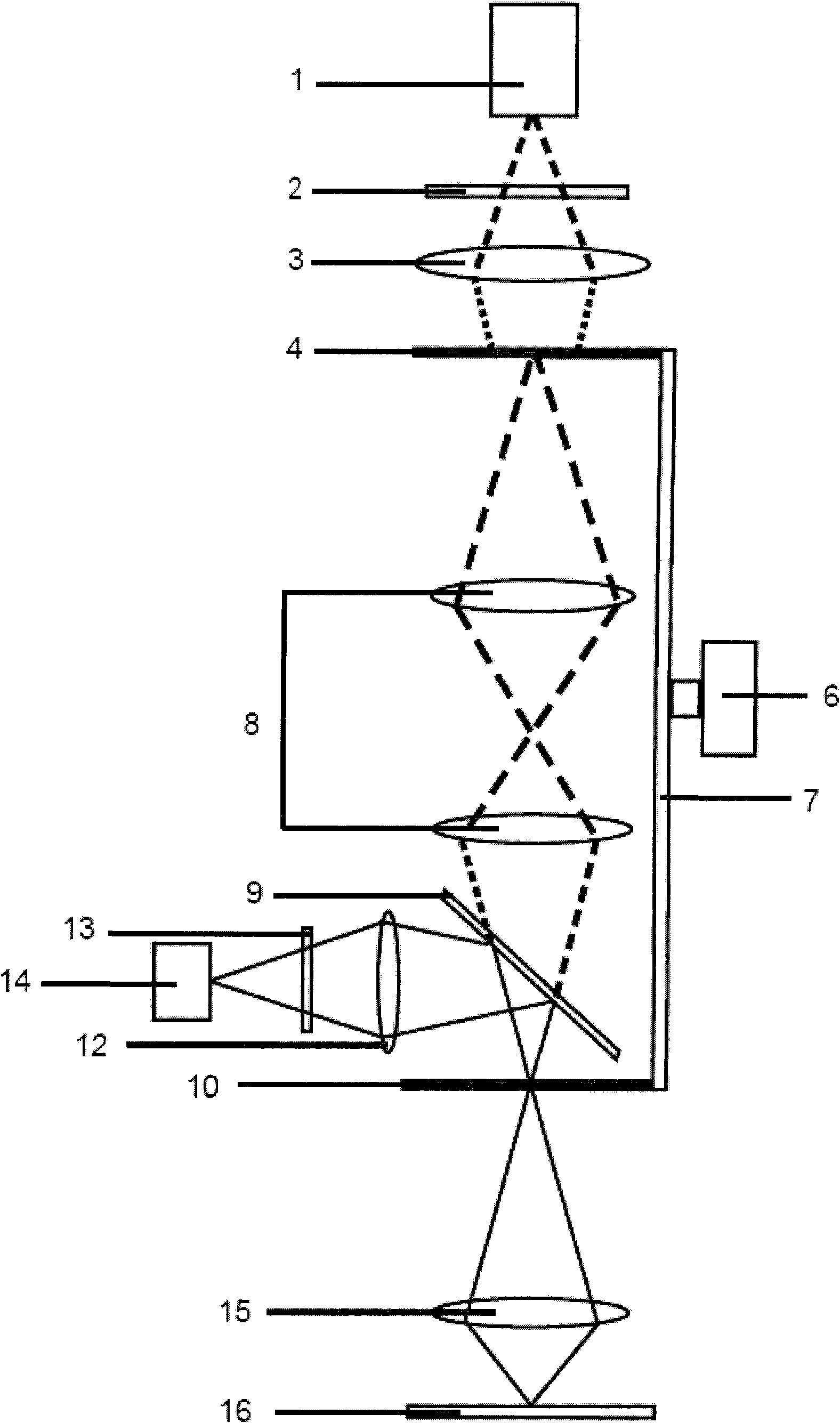
[0050] image 3 It is a schematic diagram of the structure of the second confocal optical scanner related to the present invention. The structure and scanning mode of the illumination slider 4 and the imaging slider 10 are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and the specific differences are as follows:
[0051] The dichroic beam splitter 9 is moved from the middle of the pinhole lens group 8 and the imaging slider 10 to the middle of the pinhole lens group 8, and the distance between the pinhole lens group 8 and the imaging slider 10 is shortened. Therefore, the pinhole lens group 8 can use a lens with a short focal length and a large numerical aperture.
Embodiment 3
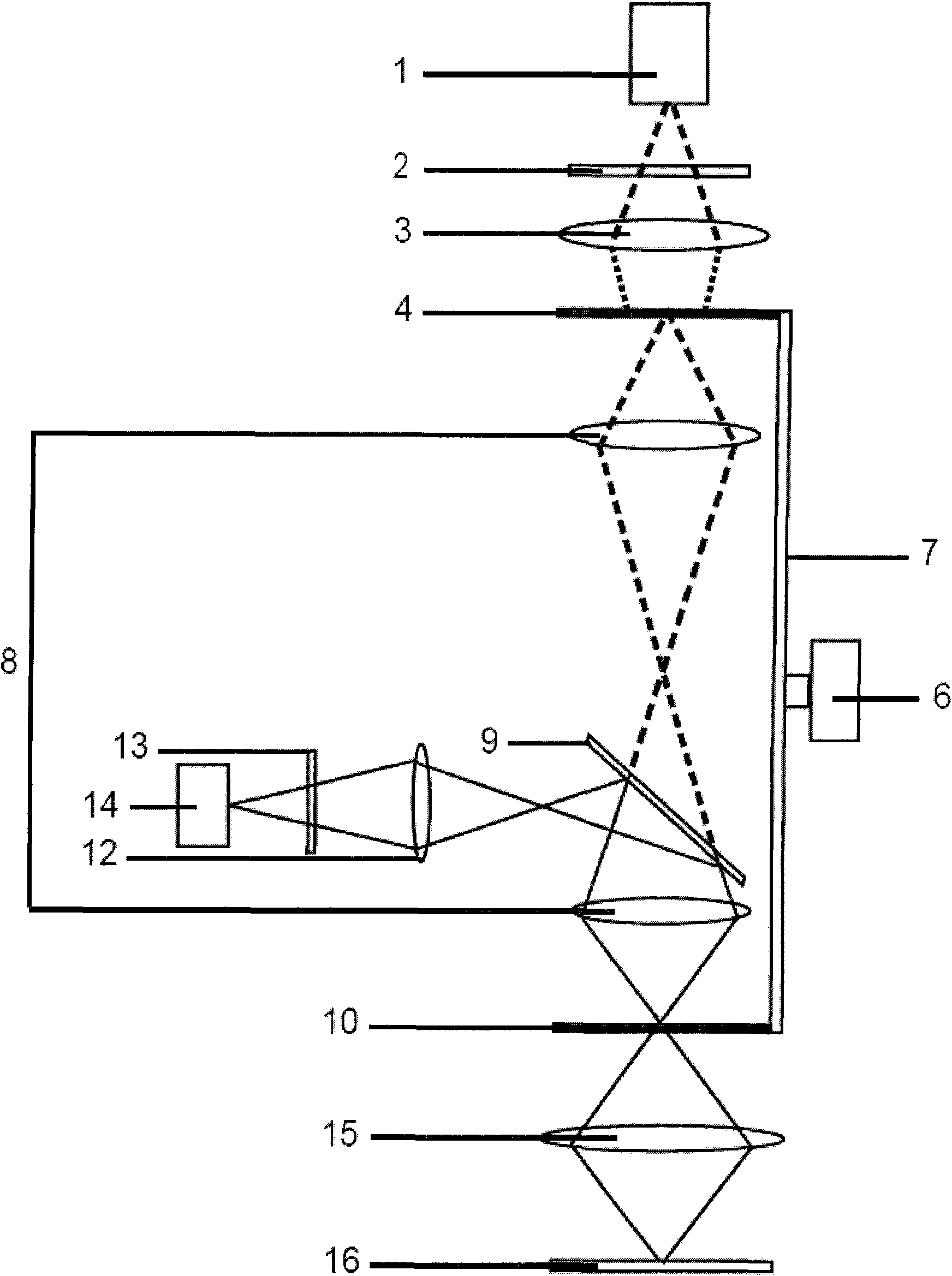
[0053] Figure 4 It is a schematic diagram of the structure of the third confocal optical scanner related to the present invention. The structures and scanning methods of the illumination slider 4 and the imaging slider 10 are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and the specific differences are as follows:
[0054] The illumination slider 4 and the imaging slider 10 are not on the same straight line, but are respectively located on two straight lines perpendicular to each other; the dichroic beam splitter 9 is the most commonly used common dichroic beam splitter, which can pass through the illumination filter The illumination light of 2 reflects the fluorescent light emitted by the sample 16 . After the illumination emitted by the light source 1 sequentially illuminates the color filter 2, the illumination lens 3, the pinhole 5 on the illumination slider 4, and the pinhole lens group 8, it is reflected by the dichroic beam splitter 9 and passes through the holes on the imaging ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com