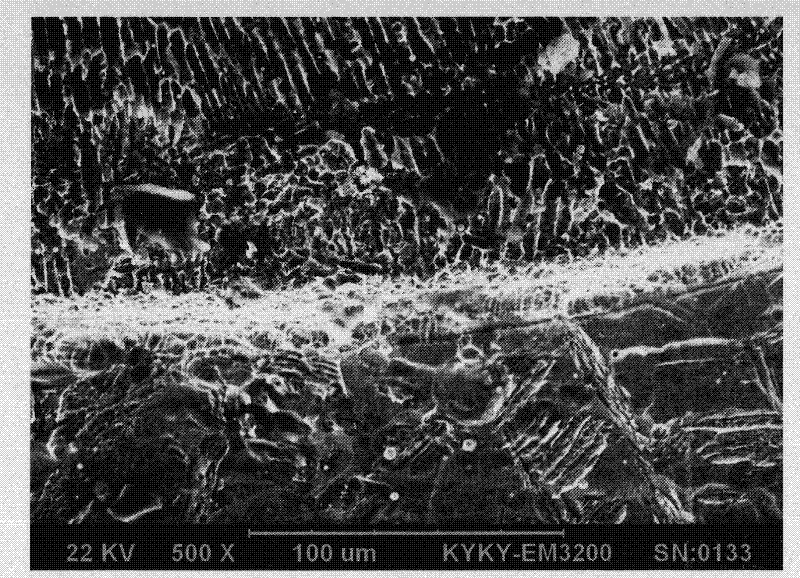
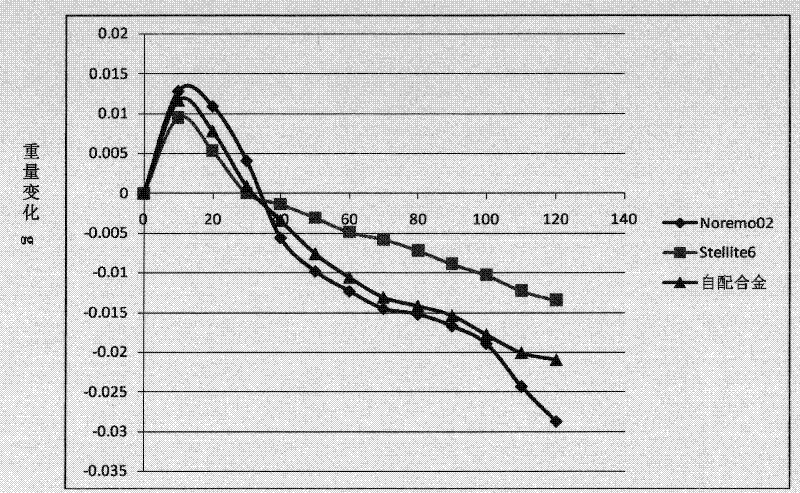
No-co ferrous alloy powder composition and its uses
An alloy powder, cobalt-iron-based technology, applied in the field of cobalt-free iron-based alloys for strengthening materials, to achieve good high-temperature wear resistance and prolong service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Use GS-TFL-10KW type high power cross-flow CO 2 For a 10,000-watt-class laser, a 1Cr18Ni9Ti stainless steel substrate with a size of 50mm×40mm×10mm is selected, and the substrate sample is installed on the workbench of a 6-axis 5-linkage CNC processing machine for cladding processing. The mode is selected as multi-mode, and the iron-based alloy is used The powder feeding method adopts the annular hollow light vertical powder feeding method, and uses the coaxial nozzle for powder feeding inside the light to feed the powder, and simultaneously blows inert gas protection to the molten pool.
[0055] According to the following steps, a laser cladding process is used to prepare a nuclear power valve sealing surface coating using a cobalt-free iron-based alloy powder composition:
[0056] (1) Mix powder according to the following mass percentage: chromium (Cr) 21%; nickel (Ni) 3.5%; manganese (Mn) 3.0%; silicon (Si) 2.5%; carbon (C) 1.0%; molybdenum (Mo) 1.5%; Tungsten (W) 1...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Use GS-TFL-10KW type high power cross-flow CO 2 For a 10,000-watt laser, a 1Cr18Ni9Ti stainless steel substrate with a size of 60mm×50mm×10mm is selected, and the substrate sample is installed on the workbench of a 6-axis and 5-linkage CNC processing machine for cladding processing. The mode is selected as multi-mode, and the iron substrate is used Alloy powder, inert gas protection is blown to the molten pool.
[0070] According to the following steps, a laser cladding process is used to prepare a nuclear power valve sealing surface coating using a cobalt-free iron-based alloy powder composition:
[0071] (1) Mix powder according to the following mass percentage: chromium (Cr) 21.5%; nickel (Ni) 3.0%; manganese (Mn) 3.5%; silicon (Si) 2.0%; carbon (C) 0.9%; molybdenum (Mo) 2.0%; Tungsten (W) 0.7%; Vanadium (V) 0.3%; Phosphorus (P) 0.02%; Sulfur (S) 0.02%; Yttrium (Y) 0.5%; Base alloy powder composition, the powder particle size reaches 300 mesh, and the powder densit...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com