Application of dihydroquercetin and glucoside compounds to preparing drug-resistance bacteria medicine
A technology of dihydroquercetin and compounds, applied in the field of dihydroflavonol compounds
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
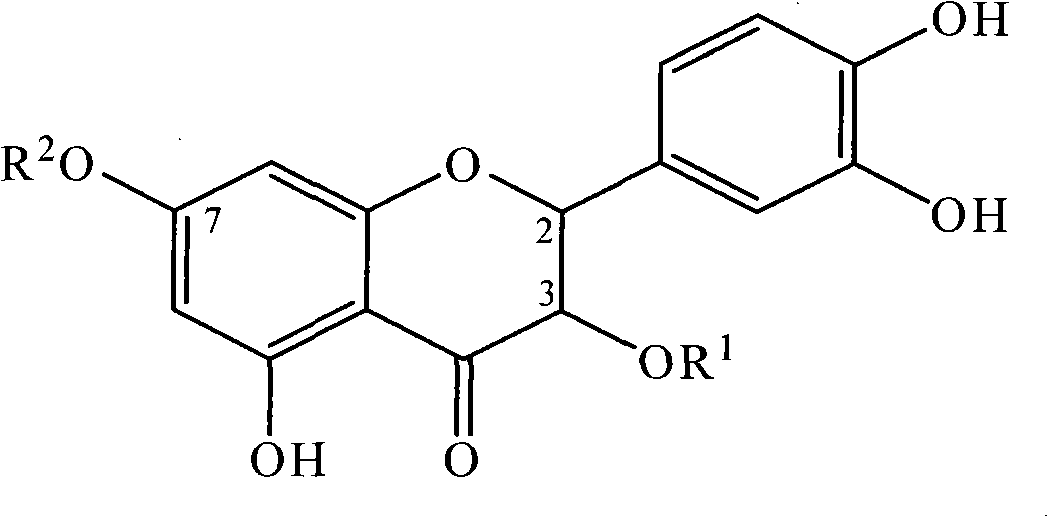
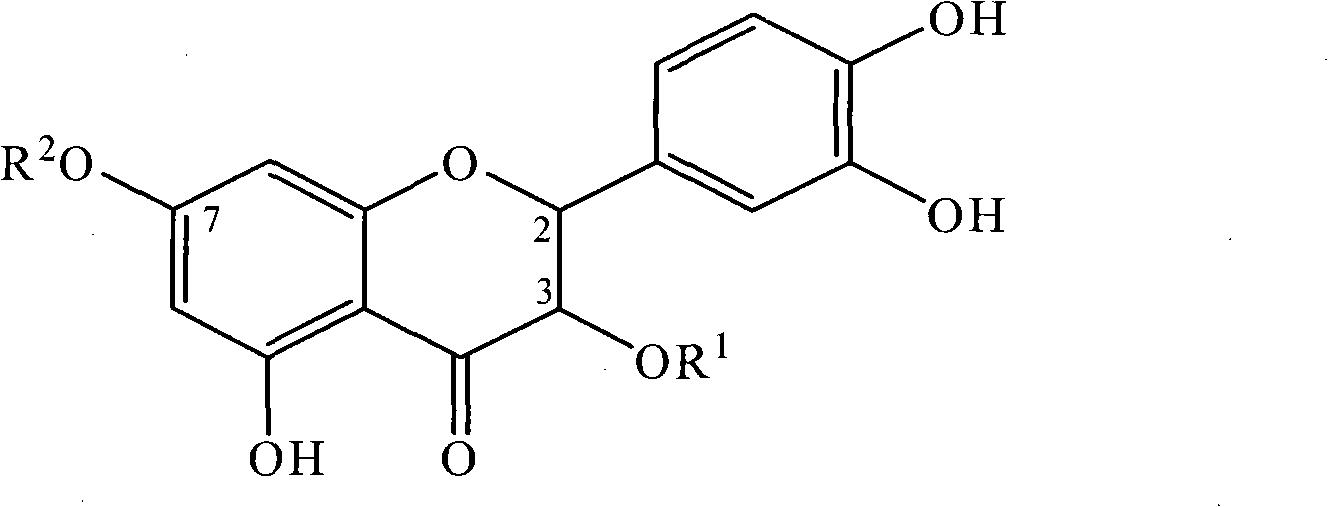
[0031]Example 1: Extraction and separation of monomer Taxifolin-7-rhamnoside (III) from the whole grass of Dirnaceae
[0032] Take Hypericum japonicum Thunb Murray dried whole herb powder 4.76kg, soak it in 23L of 80% ethanol at room temperature for 7 days, filter, repeat 3 times. The extracts were combined and concentrated under reduced pressure to obtain 505 g of extract. The extract was made into a suspension with distilled water, and then distributed and extracted with petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, and n-butanol in sequence. After each organic layer was evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure, 90g, 160g, and 105g of extract were obtained respectively, and the remainder was water. Take 90 g of the extract from the ethyl acetate layer and use a silica gel column (200-300 mesh, 2 kg) to elute with a gradient of ethyl acetate-methanol (1:0-0:1) as the eluent, in which 5% methanol elutes (8g) and then use a silica gel column (300-400 mesh, 300g) to elute with petroleum...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2: Physicochemical and spectral data of taxifolin-7-rhamnoside (III)
[0034] Yellow powder (methanol), C 21 h 23 o 11 + , mp 150-153°C. ESI MS (positive ion mode) m / z: 451. 1 HNMR (CD 3 OD, 400MHz): δ H 6.97 (1H, s, J=11.6Hz, H-2′), 6.83 (1H, dd, J=1.0, 8.0Hz, H-6′), 6.79 (1H, d, J=8.1Hz, H-5 '), 6.26 (1H, d, J = 1.9Hz, H-8), 6.17 (1H, d, J = 1.8Hz H-6), 5.47 (1H, d, J = 5.4Hz, H-1), 4.95(1H, d, J=11.6Hz, H-2), 4.56(H, d, J=11.6Hz, H-3), 3.96(1H, s, Rha-H-2), 3.76(H,dd , J=3.1, 9.4Hz, Rha-H-3), 3.53(1H, m, Rha-H-5), 3.43(1H, t, Rha-H-4), 1.22(3H, d, J=6.0 Hz Rha-Me); 13 C NMR (CD 3 OD, 100MHz): δ C 115.9 (d, C-2), 73.8 (s, C-3), 199.3 (s, C-4), 164.9 (s, C-5), 98.0 (d, C-6), 166.2 (s, C -7), 96.9 (d, C-8), 164.2 (s, C-9), 103.4 (s, C-10), 129.6 (s, C-1′), 115.9 (d, C-2′) , 146.3 (s, C-3″), 147.2 (s, C-4′), 116.1 (d, C-5′), 120.9 (d, C-6′), 99.6 (d, C-1″) , 71.6 (d, C-2″), 72.0 (d, C-3″), 73.6 (d, C-4″), 71.2 (d, C-5″), 18.0 (d, C-6″) .
Embodiment 3
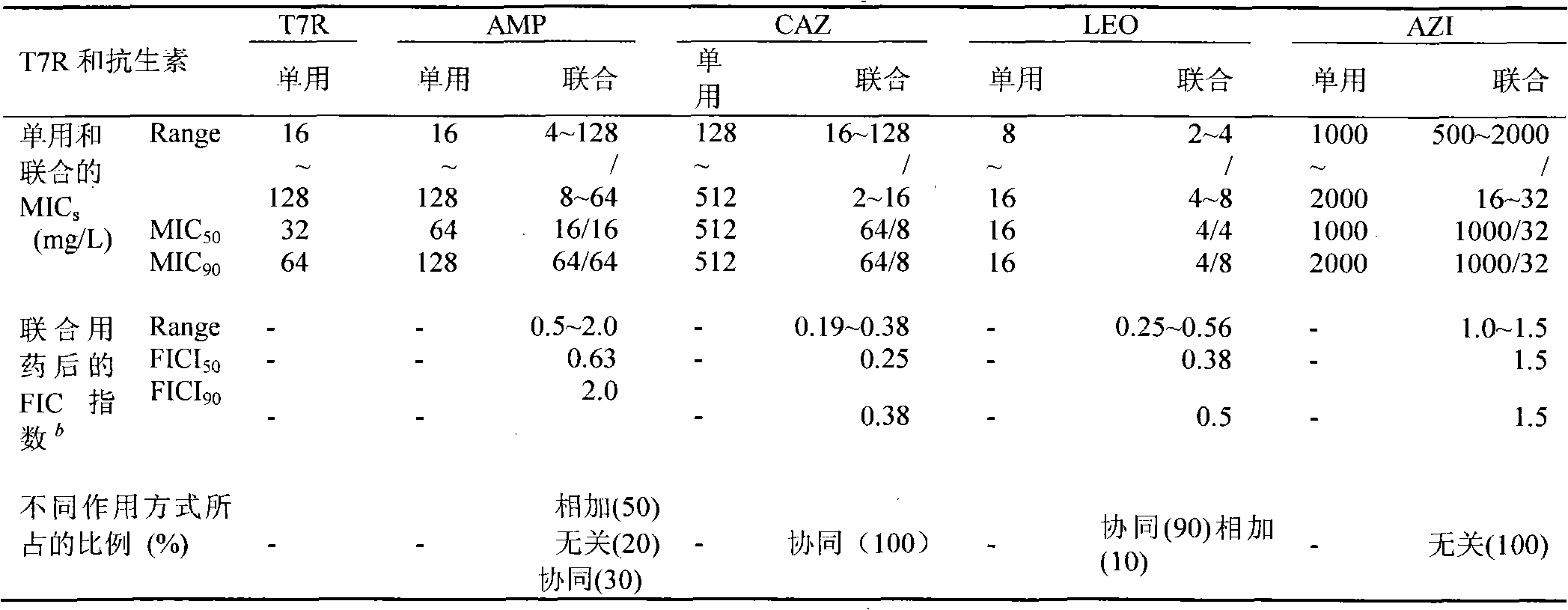
[0035] Embodiment 3: as the screening of the clinical drug-resistant strain MRSA of drug susceptibility test
[0036] 1. Test material
[0037] Antibiotic-sensitive paper sheets (China Institute for the Control of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products), MH agar (Hangzhou Tianhe Microbiological Reagent Co., Ltd.).
[0038] 2. Specimen source
[0039] Isolate and screen 10 strains of bacteria from the applicant's clinical specimens, numbered MRSA189, MRSA155, MRSA328, MRSA144, MRSA247, MRSA4, MRSA92, MRSA55, MRSA330, MRSA123, and store them in the refrigerator at -20°C for later use.
[0040] 3. Bacteria identification
[0041] According to the "National Clinical Inspection Operation Regulations" and the bacterial identification method known to those skilled in the art, the above-mentioned sample bacteria are isolated and cultivated, and it is identified as Staphylococcus aureus (SA), and according to the known routine test method for antibiotic susceptibility (K-B Disc meth...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com