Method for separating RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) from human serum/blood plasma sample and PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) verification method thereof
A human serum and sample technology, applied in the fields of biotechnology and medicine, can solve the problems of low content, low quality, difficulty in obtaining RNA, etc., and achieve the effects of accurate quantification, simple and fast operation, and improved extraction efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Embodiment 1, a kind of method for isolating RNA from human serum, carries out following steps successively:
[0052] 1) Acquisition of serum samples:
[0053] ①. Pour 3 mL of peripheral blood (taken on an empty stomach in the morning) into a clean and dry centrifuge tube, immediately place it in a 37°C constant temperature incubator for 2 hours, and then place it in a 4°C refrigerator for 4 hours;
[0054] ②. Centrifuge the clot at 4°C, 4000rpm for 10min, and carefully pipette the supernatant into a 1.5mL centrifuge tube;
[0055] ③. The clinical serum samples separated in step 1) ② were mixed and stored in a -80°C refrigerator until use.
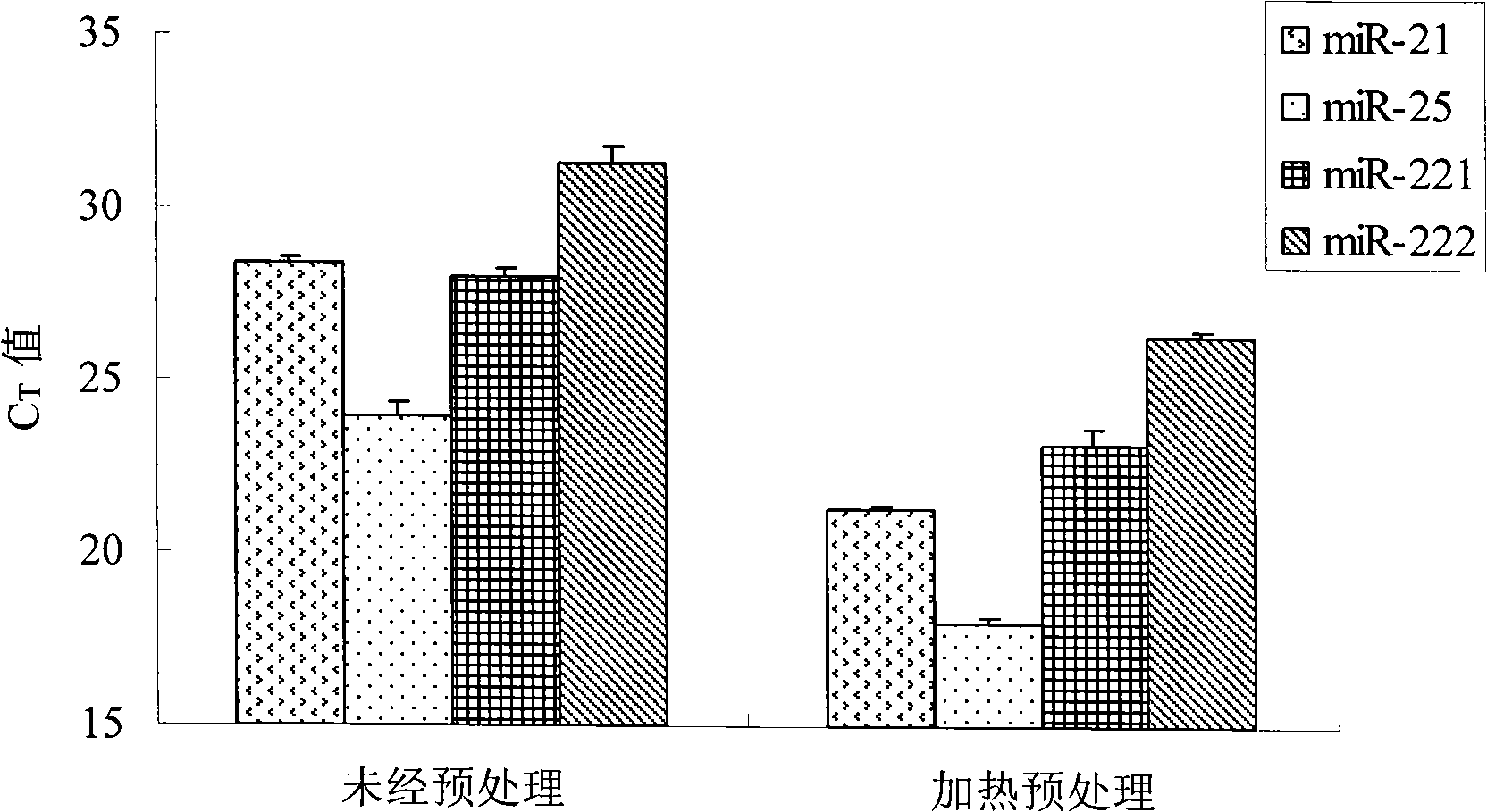
[0056] 2), heating pretreatment:
[0057] Select 250 μL of serum obtained in step 1) as a sample, heat at 75°C for 5 minutes, and then incubate at 42°C for 1 hour to obtain a pretreated serum sample;
[0058] 3) Add an equal volume of Trizol reagent to an RNase-free 1.5mL centrifuge tube to the above-mentioned pretreated serum sa...
Embodiment 2
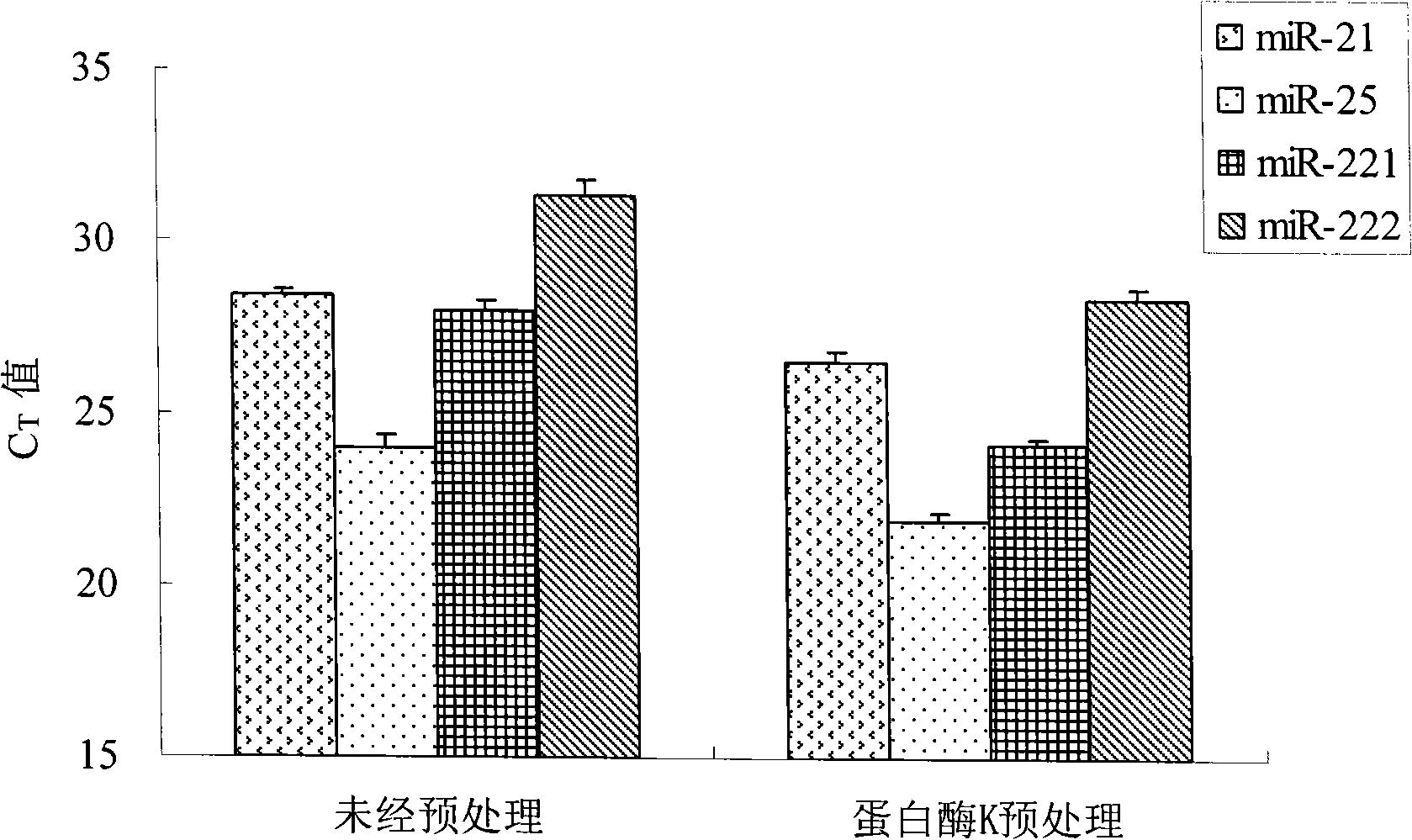
[0062] Example 2, a method for isolating RNA from human serum, changing the pretreatment in step 2) to the following: protease pretreatment: 250 μL serum sample and 10 μg proteinase K were digested at 42° C. for 1 hour to obtain pretreated serum Sample; All the other are with embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
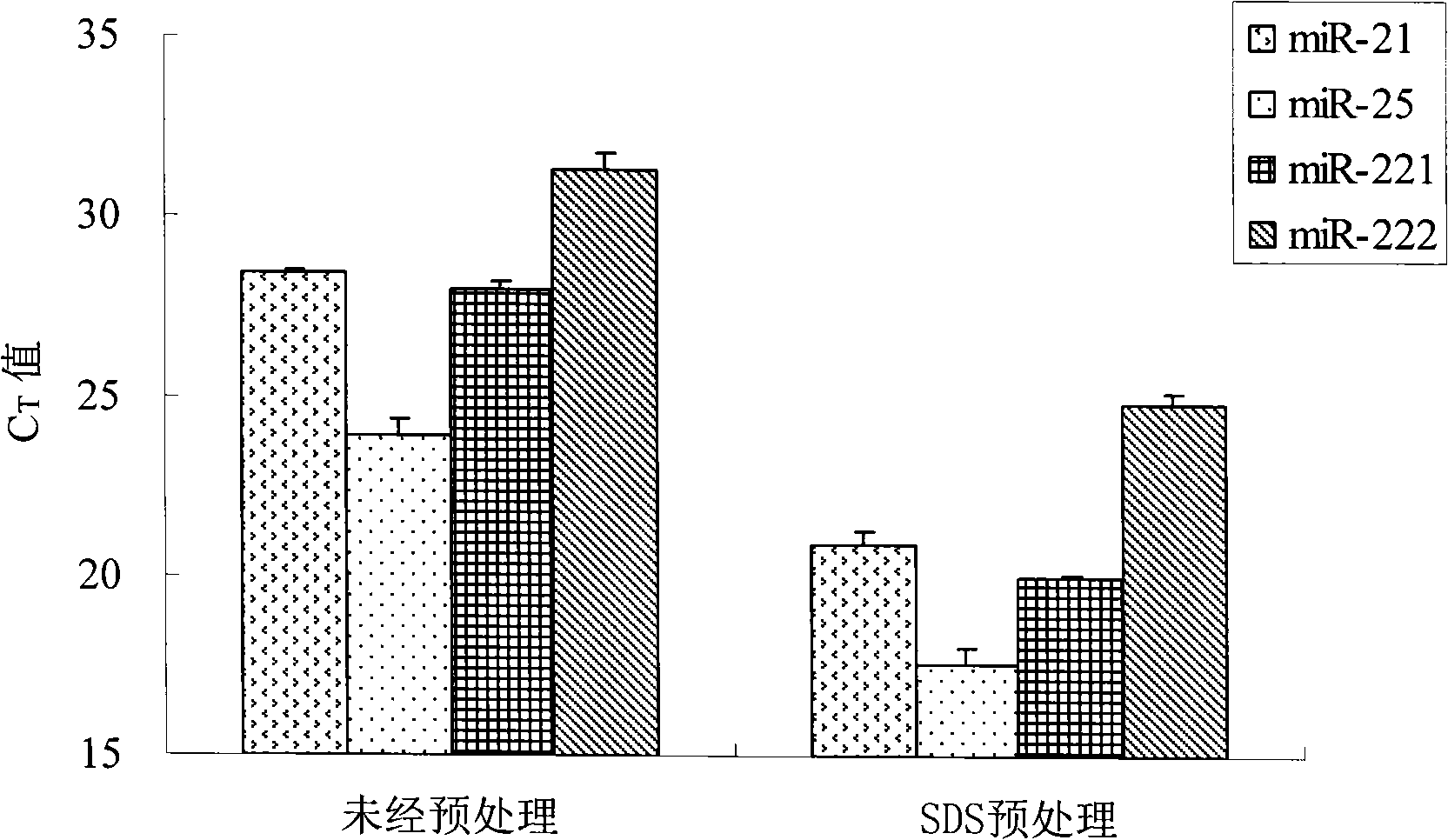
[0063] Embodiment 3, a method for isolating RNA from human serum, change the pretreatment of step 2) to the following content: SDS pretreatment: 250 μ L serum sample is mixed with an equal volume of 10% SDS (mass concentration) solution, 4 ° C conditions Incubate for 1 h to obtain a pretreated serum sample; the rest are the same as in Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com