Method for producing biological organic acid by using dynamic expanding adsorption reactor system
An organic acid and reactor technology, which is applied in the field of bio-organic acid production in a dynamic expansion adsorption reactor system, can solve the problems of low raw material utilization rate, low product yield, production efficiency decline, etc., and achieve increased product output, high biomass The effect of improving and restoring growth vitality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
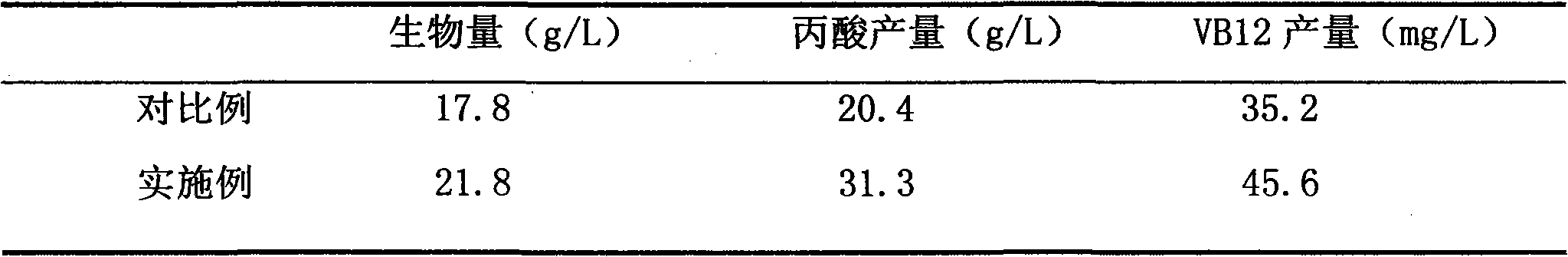
[0052] Embodiment 1. Application of dynamic expansion type adsorption reactor system to produce propionic acid / VB12
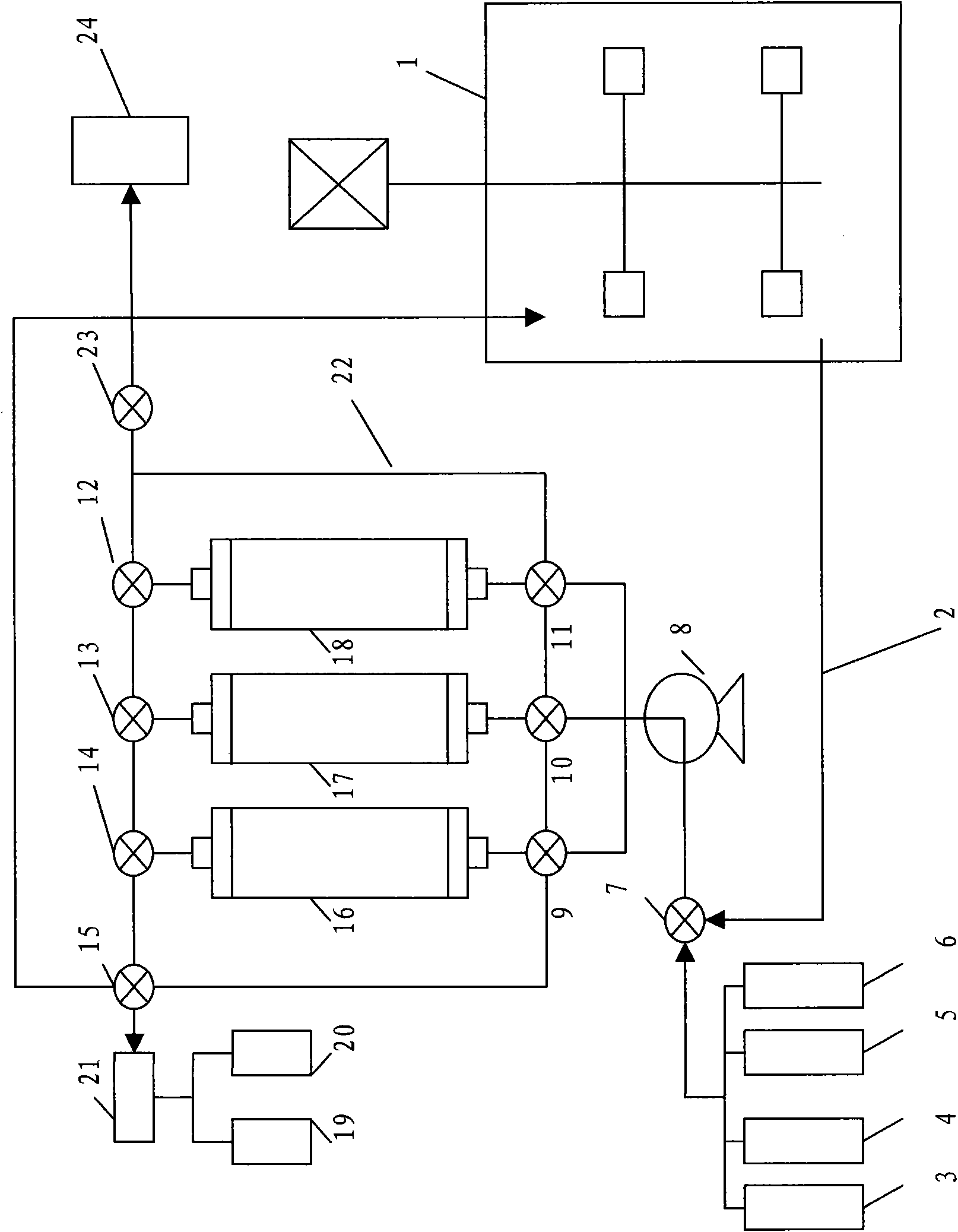
[0053] See figure 1 . The dynamic expansion adsorption reactor system used includes a fermenter 1 with a stirring device, a pipeline 2, an eluent storage tank 3, an eluent storage tank 4, a regeneration liquid storage tank 5, an equilibrium liquid storage tank 6, and a solenoid valve 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 and 23, liquid pump 8, chromatography column 16, 17 and 18, product storage tank 19, waste liquid storage tank 20, detector 21, pipeline 22, Conversion tank 24 and so on.
[0054] The bottoms of the three parallel expanded bed chromatography columns 16, 17, 18 are all provided with circulating fluid inlets, and the tops of the expanded bed chromatography columns are all opened with circulating fluid outlets.
[0055] A circulating fluid main pipeline 22 forming a circulating fluid circuit has three three-way solenoid valves 12, 13 and 14 and four fou...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Example 2. Production of lactic acid using a dynamic expansion adsorption reactor system.
[0082] Utilize the production process adopted in the production of lactic acid by dynamic expansion type adsorption reactor, and the applied dynamic expansion type adsorption reactor system used is basically the same as embodiment 1, the difference is:
[0083] (1) The microbial cell seed is: Lactobacillus plantarum.
[0084] (2) The N source in the seeds and fermentation medium was changed from corn steep liquor to peptone, the mass concentration of peptone in the seed medium was changed to 2%, and the mass concentration of peptone in the fermentation medium was changed to 2%.
[0085] (3) The fermentation process is changed to an aerobic mode.
[0086] (4) Since there is only one target product of lactic acid in this embodiment, it enters the fermentation process, and the link of adding inducers during the growth of microbial cells to the late logarithmic period is omitted dur...
Embodiment 3
[0090] Example 3. Production of succinic acid using a dynamic expansion adsorption reactor system.
[0091] Utilize the production technique adopted in the production of succinic acid by dynamic expansion type adsorption reactor, and the applied dynamic expansion type adsorption reactor system used is basically the same as embodiment 1, difference is:
[0092] (1) The microbial cell seed is: Actinobacillus succinate.
[0093] (2) The N source in the seeds and fermentation medium was changed from corn steep liquor to yeast powder, the mass concentration of yeast powder in the seed medium was changed to 2%, and the mass concentration of yeast powder in the fermentation medium was changed to 2%.
[0094] (3) Since there is only one target product, succinic acid, in this embodiment, it enters the fermentation process, and the link of adding inducers during the growth of microbial cells to the late logarithmic period during the fermentation process is omitted.
[0095] Experimenta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com