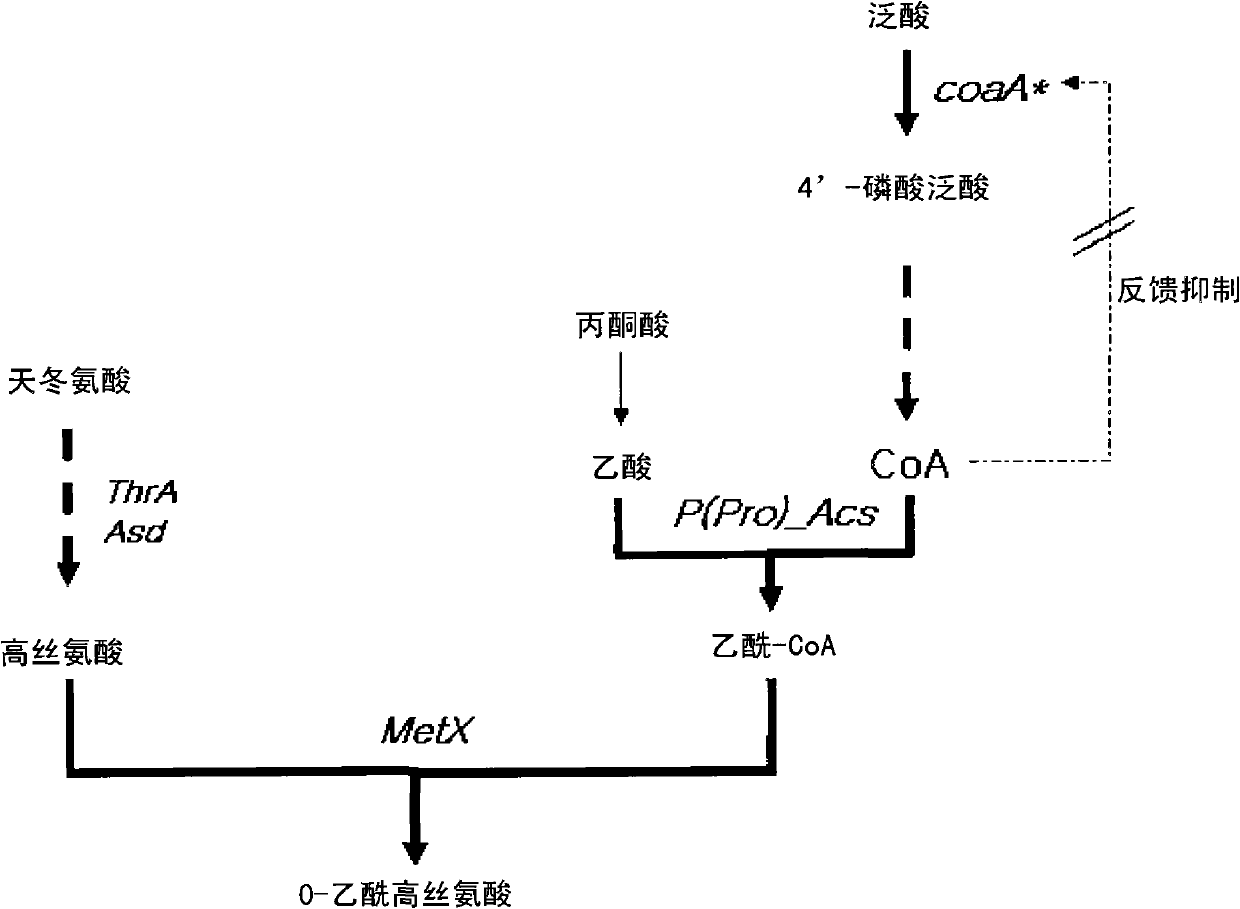
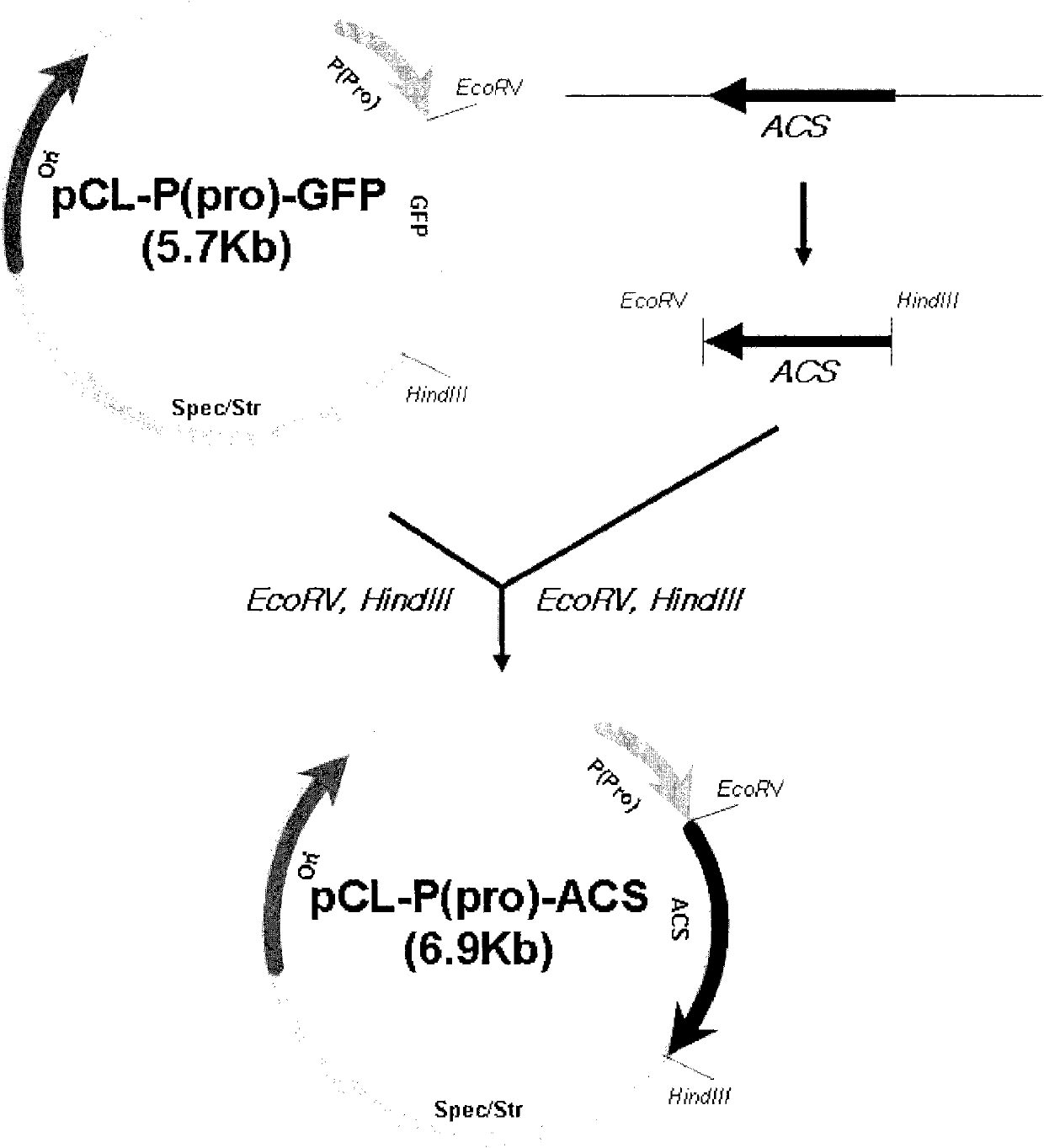
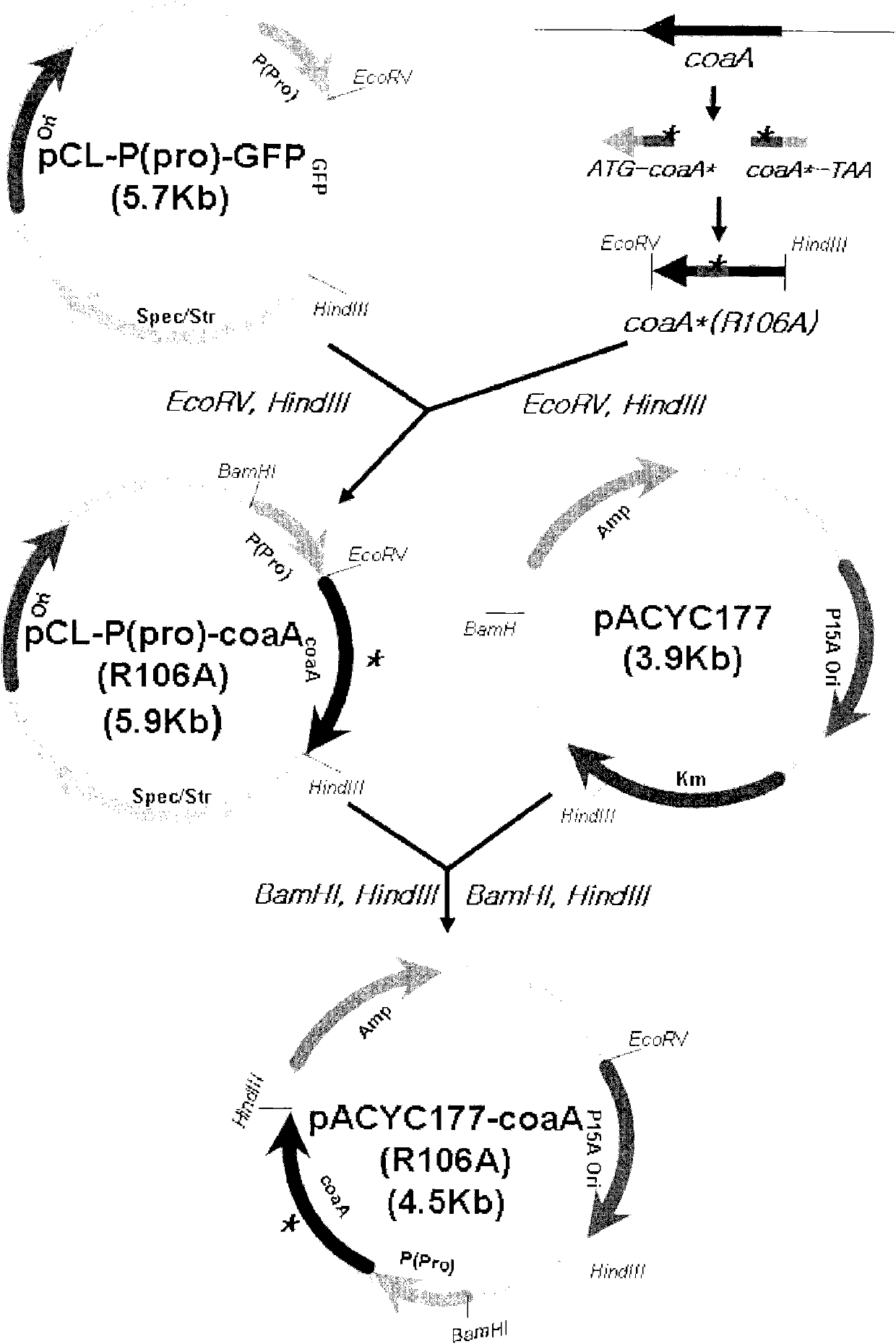
Microorganism producing O-acetyl-homoserine and the method of producing O-acetyl-homoserine using the microorganism
An acetyl and amino acid technology, applied in the field of microbial strains, can solve the problems of reduced catalytic activity and achieve high environmental friendliness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Example 1: Preparation of O-acetylhomoserine-producing strain
[0058] Cloning of acs gene
[0059] For the cloning of the acs gene, the acs gene encoding acetyl-CoA synthase was amplified by PCR using the genomic DNA of E. coli W3110 (ATCC 27325) as a template. The base sequence of the acs gene was obtained from the GenBank database of NIH (NCBI-gi: 89110790), and represented as SEQ ID NO.7. On the basis of the base sequence, primer pairs (SEQ ID NOS. 1 and 2) containing selective restriction sites EcoRV and HindIII were used, and the genomic DNA of E. PfuUltra TM The ORF from ATG to TAA was amplified by PCR in the presence of (Stratagene). The PCR included 30 cycles of denaturation at 96°C for 30 seconds, annealing at 50°C for 30 seconds and extension at 72°C for 2 minutes to synthesize an approximately 2.0 kb acs gene containing EcoRV and HindIII sites.
[0060] After digestion with restriction enzymes EcoRV and HindIII, the amplified acs gene was ligated into...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Example 2: Fermentation to produce O-acetylhomoserine
[0070] In order to examine the ability of the strains prepared in Example 1 to produce the methionine precursor O-acetylhomoserine, these strains were grown in Erlenmeyer flasks.
[0071] For this cultivation, the O-acetylhomoserine titer medium shown in Table 1 was used.
[0072] Table 1
[0073] Composition of the medium for the production of O-acetylhomoserine
[0074] composition
Concentration ( / L)
glucose
60g
17g
KH 2 PO 4
1.0g
MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O
0.5g
FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O
5mg
[0075] MnSO 4 ·8H 2 O
5mg
ZnSO 4
5mg
CaCO 3
30g
Yeast extract
2g
0.15g
0.15g
[0076] Single colonies produced on LB plates cultured overnight at 32°C were taken out using platinum rings, inoculated into 25 mL of O-acetylhomoseri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com