Method for removing impurity MgCl2 from lithium electrolyte KCl-LiCl
An electrolyte and impurity technology, applied in the field of alkali metal Li purification process, can solve the problems of low distillation efficiency, liquid lithium corrosion, large power consumption, etc., and achieves the effects of convenient and simple operation, eliminating process flow and reducing cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
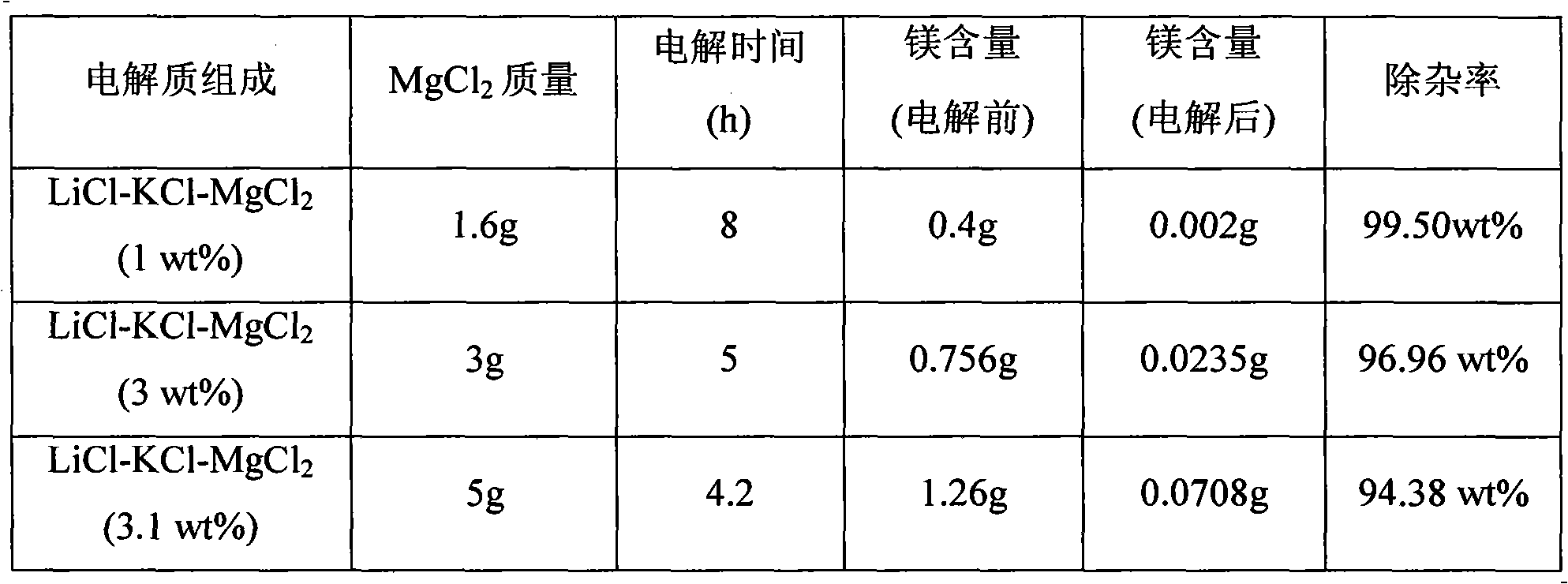
[0016] This impurity removal process uses LiCl-KCl as the basic electrolyte, adding different contents of MgCl 2 Preparation of different LiCl-KCl-MgCl 2 Electrolyte system, MgCl 2 Accounting for LiCl-KCl-MgCl 2 3.0wt% of the total mass; in LiCl-KCl-MgCl 2 (3.0wt%) system, adopt constant potential electrolysis method to remove Mg, concrete operation is as follows:
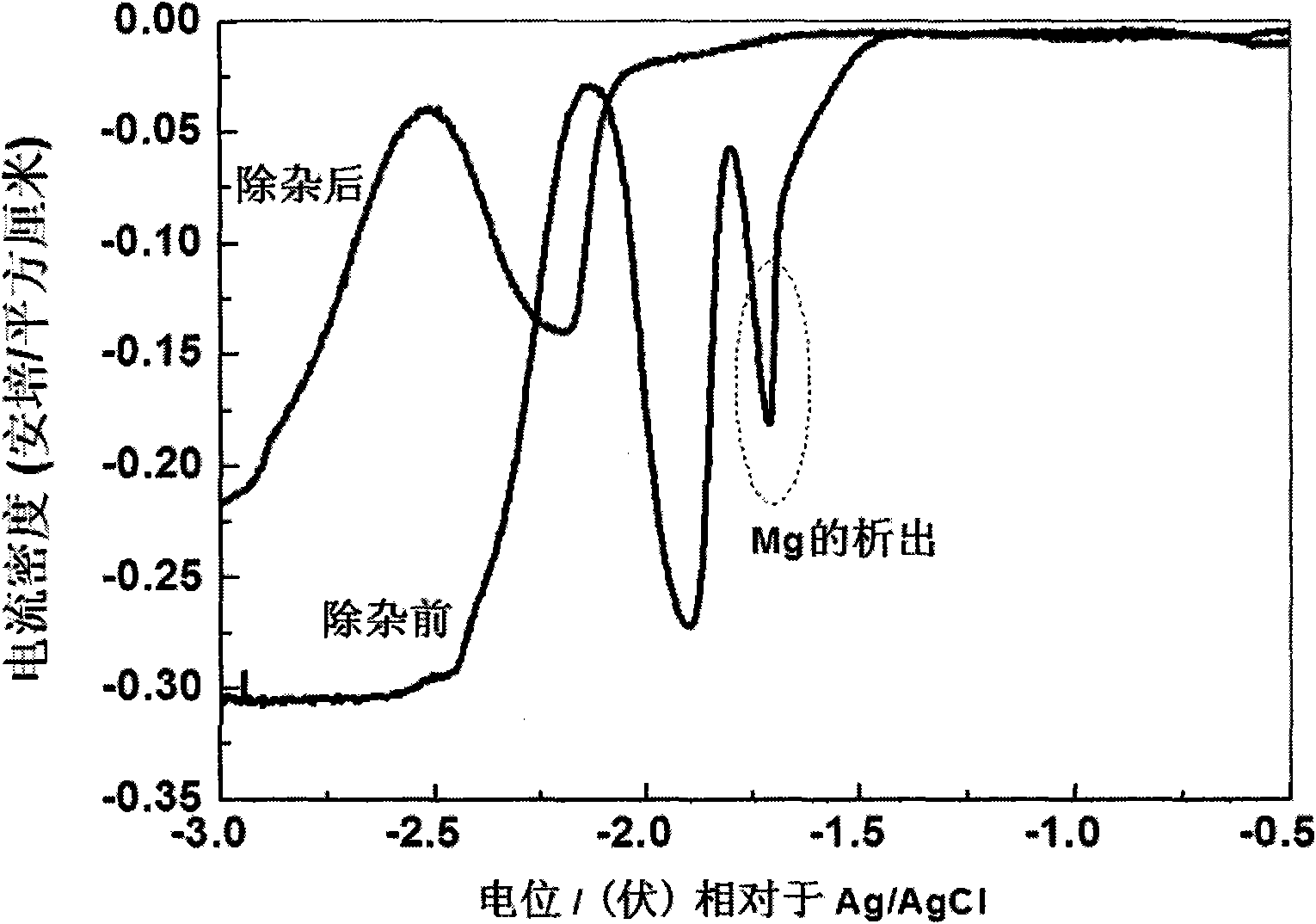
[0017] Determine the precipitation potential of Mg by square wave voltammetry: take W (0.1649cm 2 ) as the working electrode; Ag / AgCl (same as above) as the reference electrode; spectroscopically pure graphite as the counter electrode, using an electrochemical workstation to scan Mg at 450 ° C 2+ The cyclic square wave spectrum (such as figure 2 shown), so as to establish the precipitation potential of Mg as -1.5Vvs.Ag / AgCl;
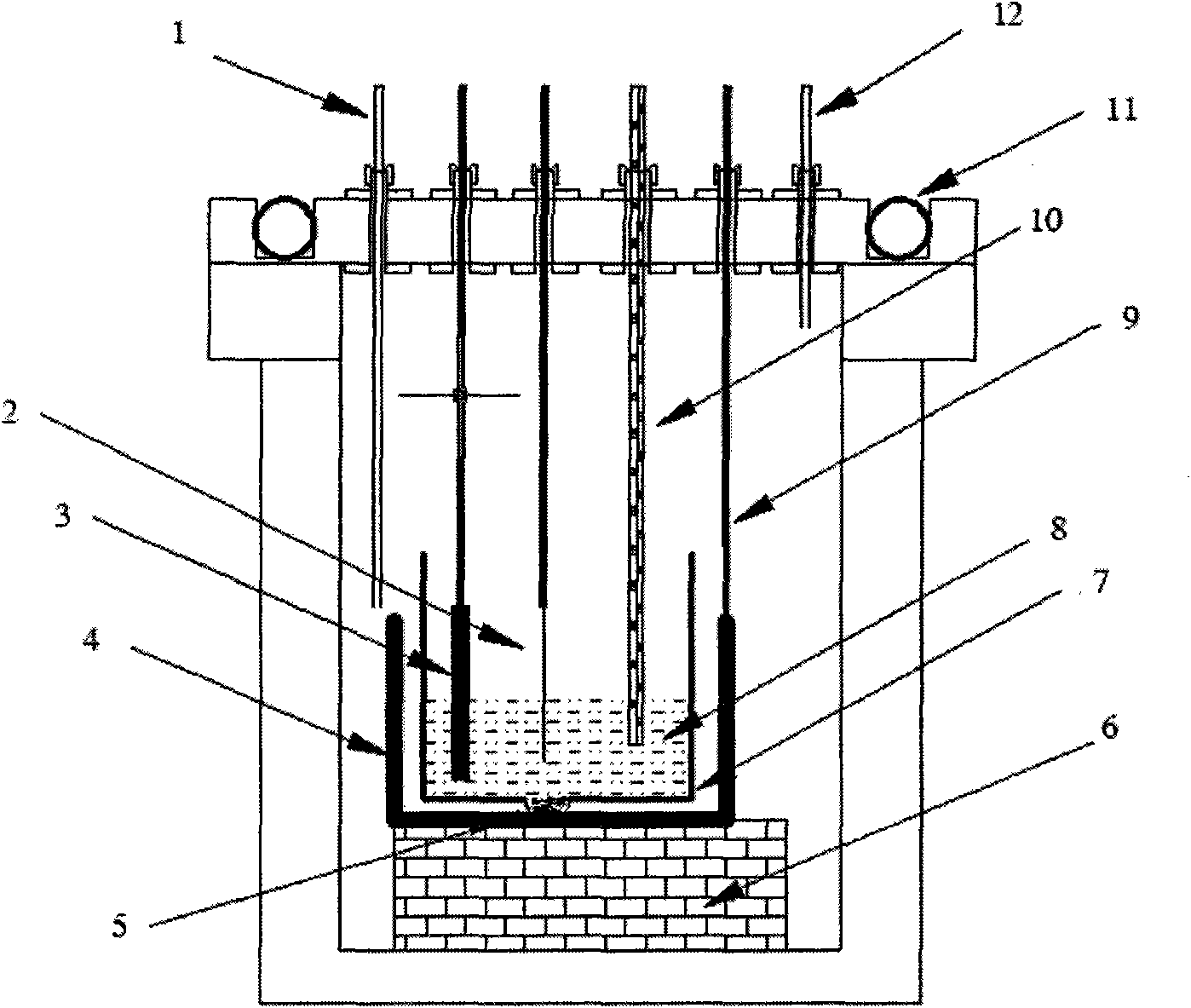
[0018] Constant potential electrolytic removal of impurity Mg: as attached figure 1 As shown, in the electrolysis device, a double-layered crucible structure with a graphite crucible ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com