Nucleic acid vaccine adjuvant designed based on MCP-1 and construction method thereof
A MCP-1, nucleic acid vaccine technology, applied in the fields of botany equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, genetic engineering, etc., can solve the problem of no nucleic acid vaccine adjuvant research reports and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1: Construction of pcDNA.3.1-MCP-1 plasmid
[0030]First, according to the Internet database information (http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / gene / 20296), the mouse MCP-1 molecular sequence (Gene ID: 20296) was searched, and PCR primers were designed for its flanking genome coding sequence (Xbal I and EcoR I restriction sites were added upstream and downstream, respectively), using genomic DNA extracted from mouse peripheral blood mononuclear cells for PCR, the MCP-1 molecular sequence and PCR primers for cloning are shown in the table below. Thus, a DNA fragment containing the coding sequence of MCP-1 molecule was obtained.
[0031]
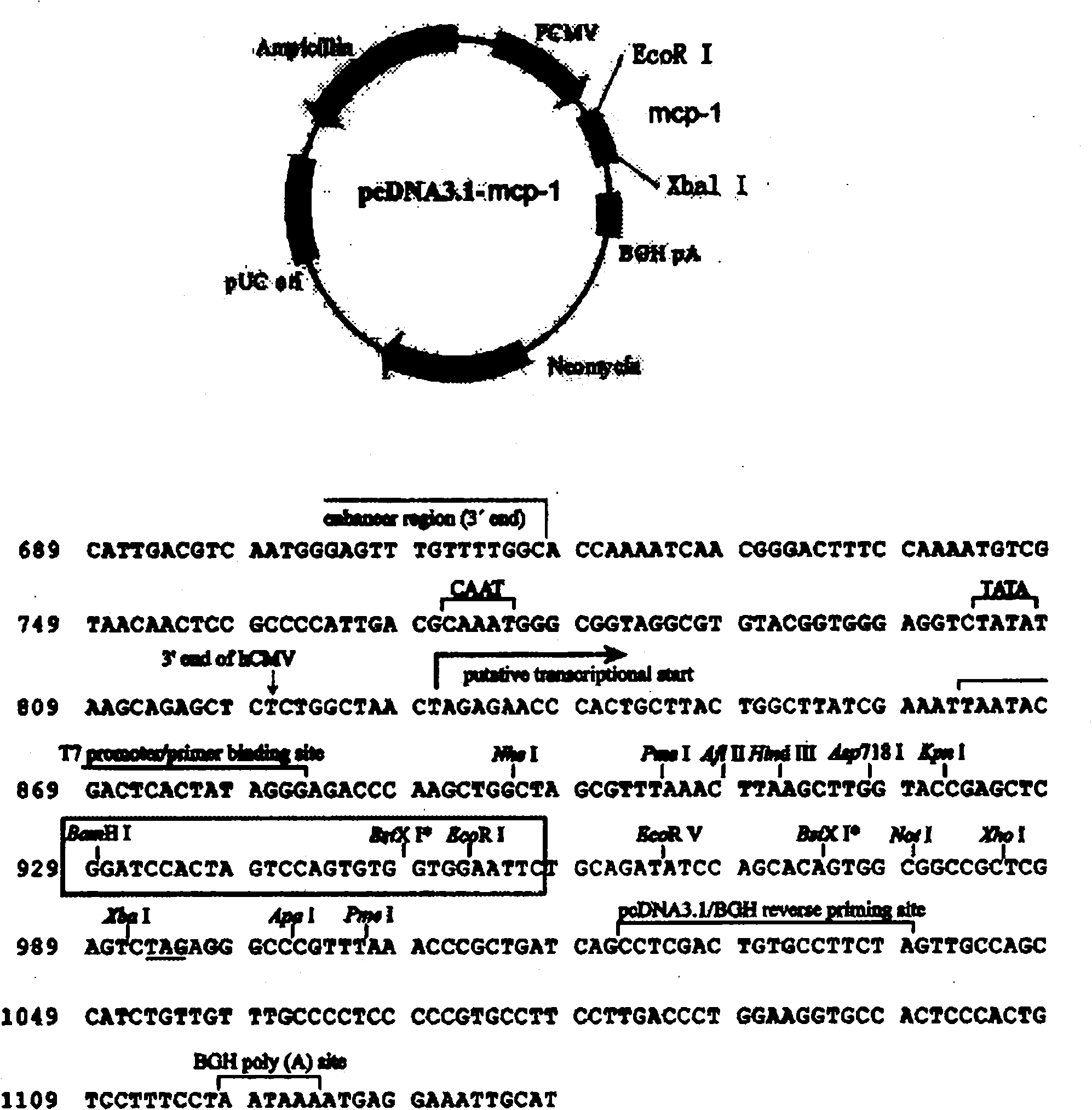
[0032] The DNA fragment comprising the pcDNA.3.1-MCP-1 coding sequence ( figure 1 ), using Xbal I and EcoR I restriction sites. The polyclonal restriction sites flanking the insertion sequence are still retained and can be used to insert the antigen sequence without affecting its effective expression. The above is the MCP-1 expre...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2: In vitro expression ability detection experiment under the condition of co-transfection of pcDNA3.1-MCP-1 plasmid and pVAX1-HBsAg nucleic acid vaccine
[0034] Using mice as an experimental animal model, inject pcDNA3.1-MCP-1 plasmid into the legs of mice, and use immunohistochemistry to analyze the recruitment of DC in the injection site 24 hours later, and found that pcDNA3.1-MCP-1 plasmid Compared with the control group after immunization, the immunization group had significant DC recruitment and activation.
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3: In vivo immune efficacy detection experiment after co-immunization of pcDNA3.1-MCP-1 plasmid and pVAX1-HBsAg nucleic acid vaccine
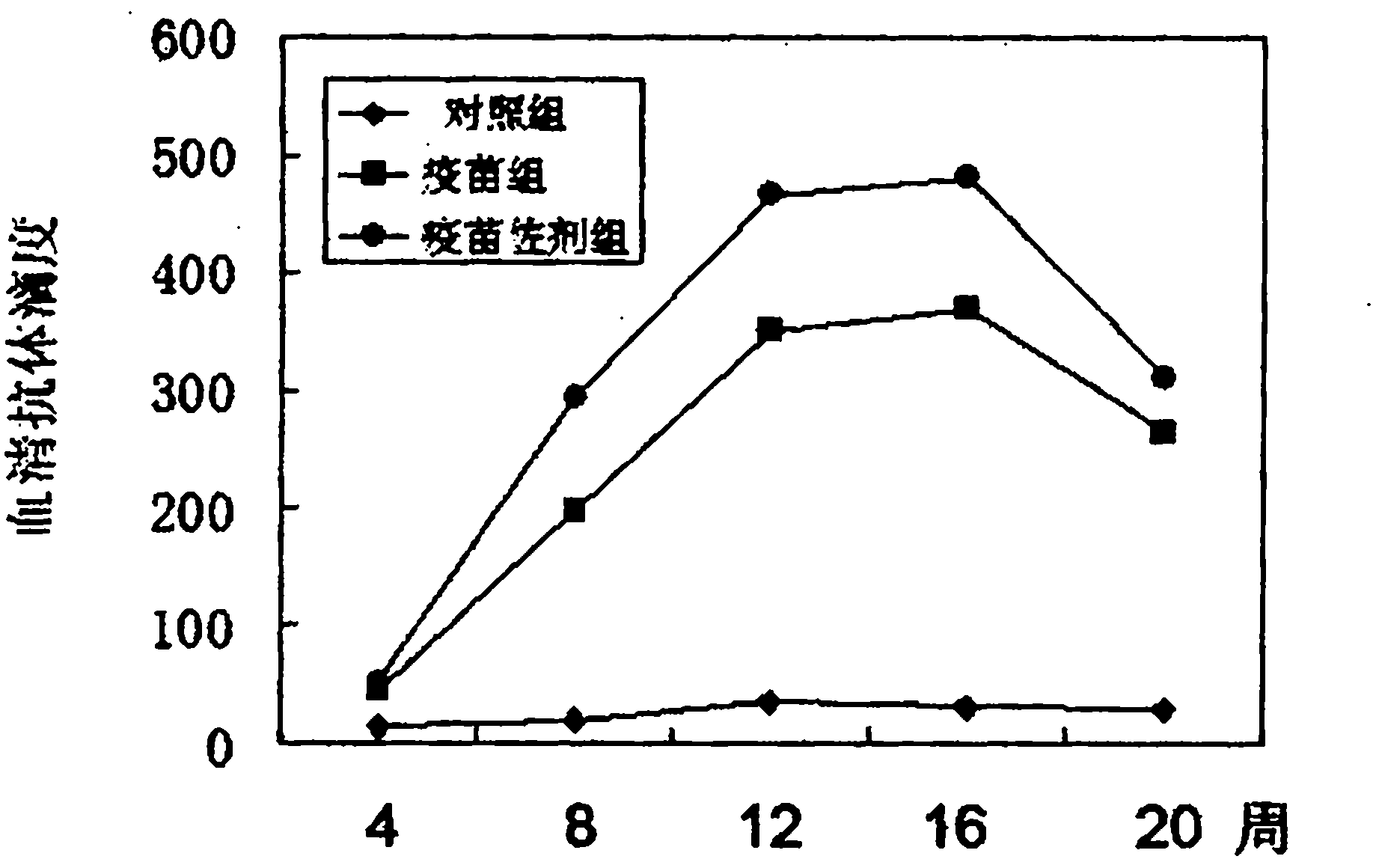
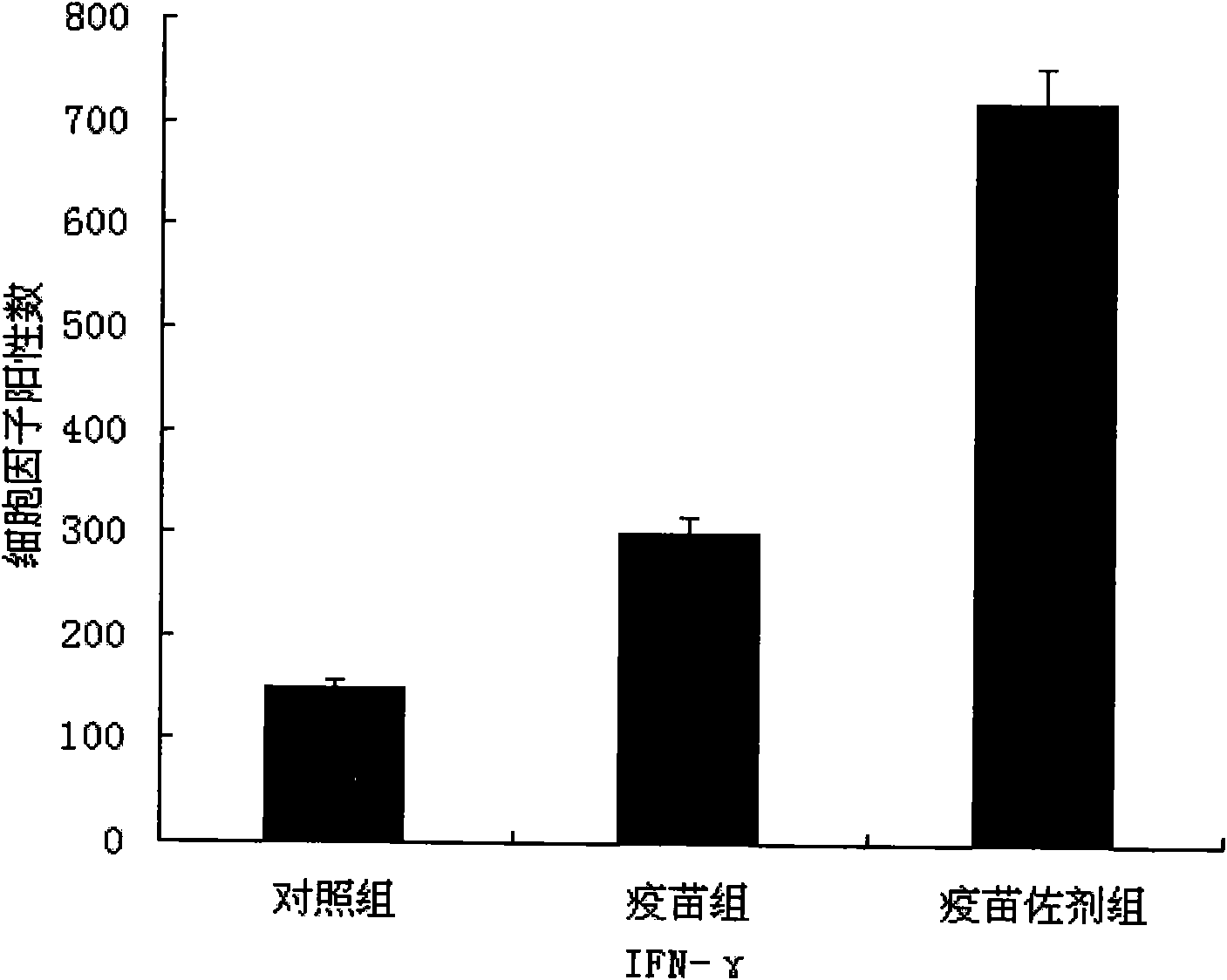
[0036] Immunize 6-8 week-old C57BL / 6J mice with 0.1mg / mouse of pcDNA3.1-MCP-1 and 0.1mg / mouse of pVAX1-HBsAg, immunize 3 times in total with 2-week intervals, and recombine with HBsAg at the end of the 6th week Protein (10 μg / cause) was mixed with incomplete Freund's adjuvant to boost immunization once. In terms of humoral immunity, ELISA was used to detect the antibody titer and IgG subtype (see figure 2 ); In terms of cellular immunity, the ELISPOT method was used to detect the secretion of IFN-γ in spleen T cells, and the in vitro induced spleen CTL target killing assay was used to detect antigen-specific CD8 + number of T cells. The HBsAg nucleic acid vaccine pVAX1-HBsAg was used as a parallel control, normal saline was used as a blank control, and the HBsAg subunit protein vaccine was used as a positive control. The resul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com