Voltage zero-crossing detecting circuit and DC-DC converter with same
A detection circuit and voltage zero-crossing technology, applied in the direction of output power conversion devices, measuring current/voltage, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of difficult integration, large volume, expensive, etc., and achieve improved conversion efficiency, simple circuit structure, and energy saving area effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
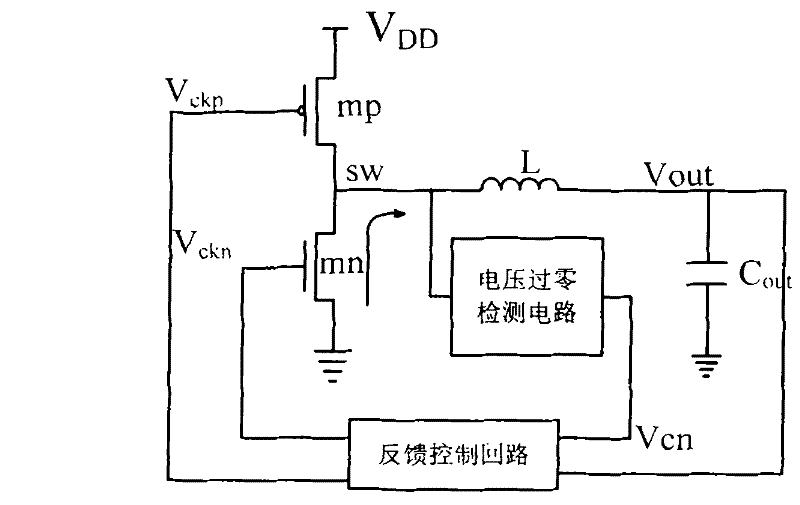
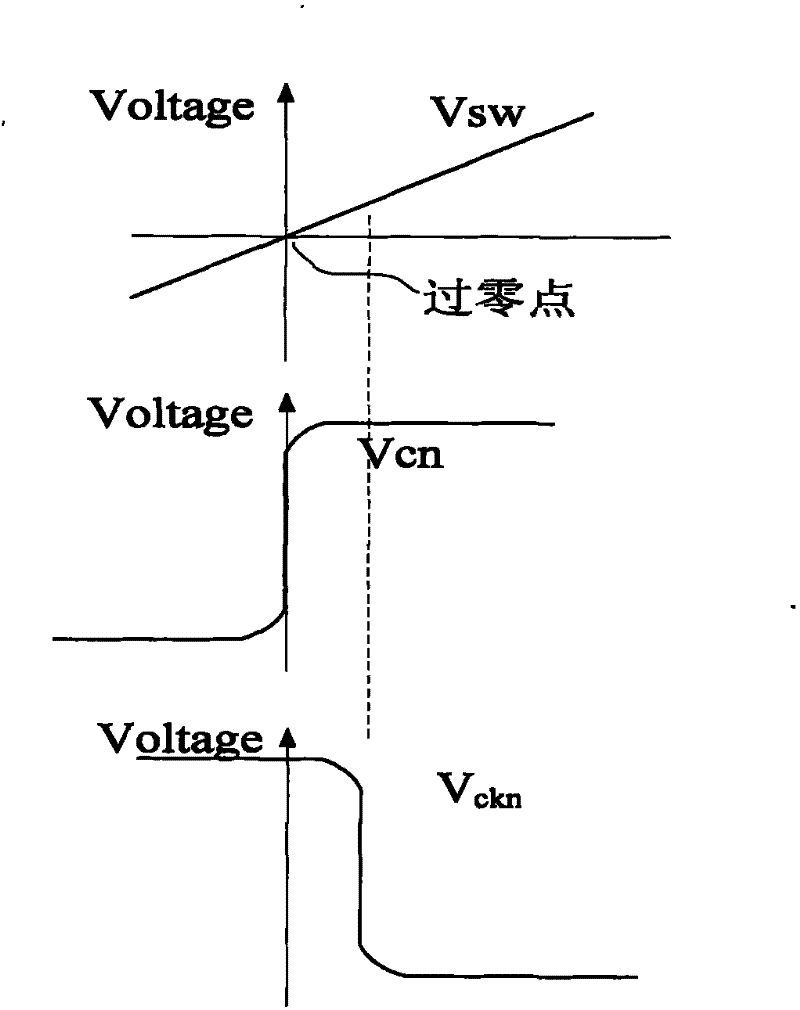
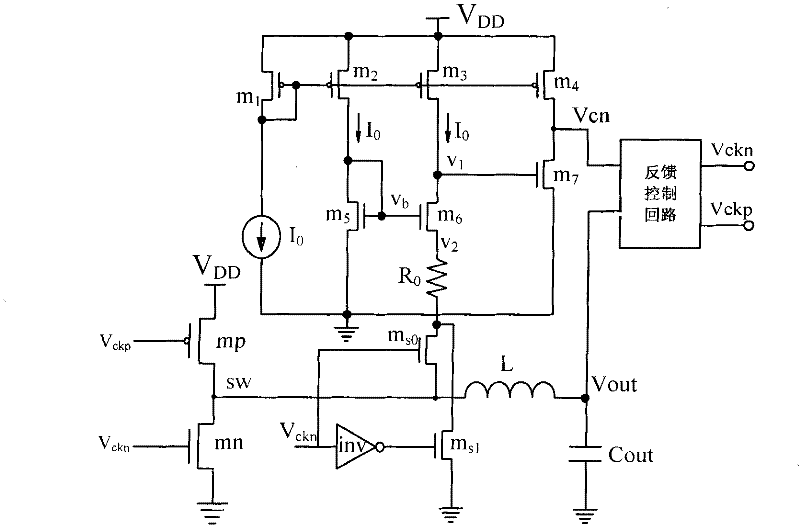
[0028] In the first embodiment, the voltage zero-crossing detection circuit adopts such as image 3 Described circuit structure, this structure comprises PMOS tube m 1 、m 2 、m 3 、m 4 , NMOS tube m 5 、m 6 、m 7 , switch tube m s0 、m s1 , inverter inv, current source I 0 and resistance R 0 , supply voltage V DD , the following combination as figure 1 The shown DC-DC converter illustrates the connection relationship of the voltage zero-crossing detection circuit described in this embodiment and the working principle applied to the DC-DC converter: wherein, the current source I 0 As a reference current source, it provides bias current to the amplifier, when V ckn When it is at a high level, the synchronous rectifier mn is turned on, and the inductance L is freewheeling, and the freewheeling direction is from the ground to the drain SW of the rectifier mn, and the voltage at the drain SW is input to the PMOS transistor m 3 、m 4 and NMOS tube m 6 、m 7 Composed of ampl...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Such as Figure 5 Shown is another voltage zero-crossing detection circuit of the present invention, the circuit structure is as follows image 3 On the basis of the voltage zero-crossing detection circuit shown, 5 PMOS transistors are added 8 、m 9 、m 10 、m 11 、m 12 and a reference current source I 0 , where the PMOS tube m 8 , PMOS tube m 9 , PMOS tube m 10 , PMOS tube m 11 Mirror connection, and in series with the PMOS transistor m 1 , PMOS tube m 2 , PMOS tube m 3 , PMOS tube m 4 source and supply V DD between, forming a folded current source structure; PMOS tube m 12 and reference current source I 0 in series with the power supply V DD and ground, and the PMOS tube m 12 The gate drain is connected to the PMOS tube m 1 、m 2 、m 3 、m 4 Provide bias voltage to ensure that the four PMOS tubes are in a deep saturation state; PMOS tube m 8 The gate and PMOS tube m 1 The drain is connected to the mirrored PMOS transistor m 8 、m 9 、m 10 、m 11 Provi...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Such as Image 6 Shown is another voltage zero-crossing detection circuit of the present invention, which removes the second-stage amplifier on the basis of the voltage zero-crossing detection circuit described in Embodiment 1, that is, removes the PMOS tube m 4 and NMOS tube m 7 , directly from the output terminal V of the first-stage amplifier 1 As V in Example 1 cn Output to the feedback control loop. The working principle of this circuit for detecting zero-crossing voltage is the same as that of the circuit shown in Embodiment 1. The gain of the one-stage amplifier is smaller than that of the two-stage amplifier, but the circuit structure is simple and the chip area is saved.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com