Wire-cutting wire of structural electrodeposited abrasive material
A kind of wire cutting wire and structural technology, applied in the field of hard and brittle material cutting and processing consumables, can solve the problems of poor cooling effect, large cutting force, time-consuming, etc., achieve sufficient lubrication and cooling, enhance chip removal ability, and overcome aging failure Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
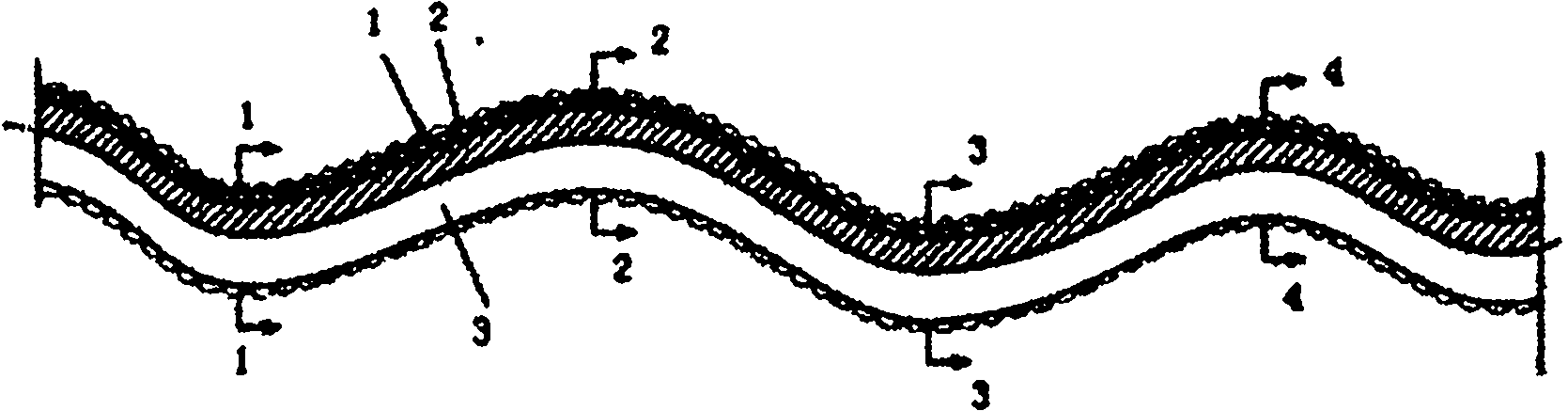
[0026] See attached figure 1 , the present invention chooses that the curved surface shape is an S-shaped structural metal wire, the wire diameter is 0.10 mm, and the projected wire diameter is a metal embryo wire of 0.13 mm. The diamond particle size is 5 to 20 μm, and the average particle size is 13 μm. The structure Degreasing and derusting metal embryo wires, composite electrodeposited diamond and metal nickel, cleaning and drying to obtain structural electroplated diamond wires, and using the same wire diameter, same diamond particle size, and linear diamond wire prepared by the same process. Cut comparison. On the same cutting machine, slice two polysilicon ingots of the same size, and when the linear electroplated diamond wire basically has no cutting ability, measure the slice area and other parameters, as shown in Table 1:
[0027] Table 1
[0028]
[0029] The structural electrodeposited diamond wire basically has no broken wires, and the cutting efficiency and ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] See attached figure 1 , the present invention chooses that the curved surface shape is an S-shaped structural metal wire, the wire diameter is 0.20 mm, and the projected wire diameter is a metal embryo wire of 0.27 mm. The diamond particle size is 30-45 μm, and the average particle size is 36 μm. The structure Degreasing and derusting metal embryo wires, compounding electrodeposited diamond and metal nickel, cleaning and drying to obtain structural electrodeposited diamond wires, and linear diamond wires prepared with the same wire diameter, the same diamond particle size, and the same process Compare cuts. On the same cutting machine, slice two polysilicon ingots of the same size, and measure parameters such as the slice area when the linear diamond wire has no cutting ability, as shown in Table 1:
[0032] Table 1
[0033]
[0034] The structural electrodeposited diamond wire basically has no broken wires, and the cutting efficiency and slice quality are signific...
Embodiment 3
[0036] See attached figure 1 , the choice of the present invention is a Z-shaped structural metal wire with a curved surface, a wire diameter of 0.50 mm, and a metal embryo wire with a projected wire diameter of 0.6 mm. The particle size of cubic boron nitride particles is 50-70 μm, and the average particle size is 58 μm. , remove oil and rust from the structural metal embryo wire, composite electrodeposited cubic boron nitride and metal nickel, wash and dry to obtain a structured electrodeposited cubic boron nitride wire, and use the same wire diameter and the same cubic boron nitride The particle size and the linear cubic boron nitride wire prepared by the same process were cut and compared. On the same cutting machine, slice two polysilicon ingots of the same size, and measure parameters such as the slice area when the linear cubic boron nitride wire basically has no cutting ability, as shown in Table 1:
[0037] Table 1
[0038]
[0039] The structural electrodeposited ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com