Method for removing pigment of molasses alcohol wastewater by using biotechnology
A technology of molasses alcohol waste liquid and biotechnology, which is applied in the field of removing pigment from molasses alcohol waste liquid by using biotechnology, can solve the problems of heavy burden on enterprises, secondary pollution, high aerobic load, etc., and achieve good economic and social benefits, equipment Small footprint and short processing time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
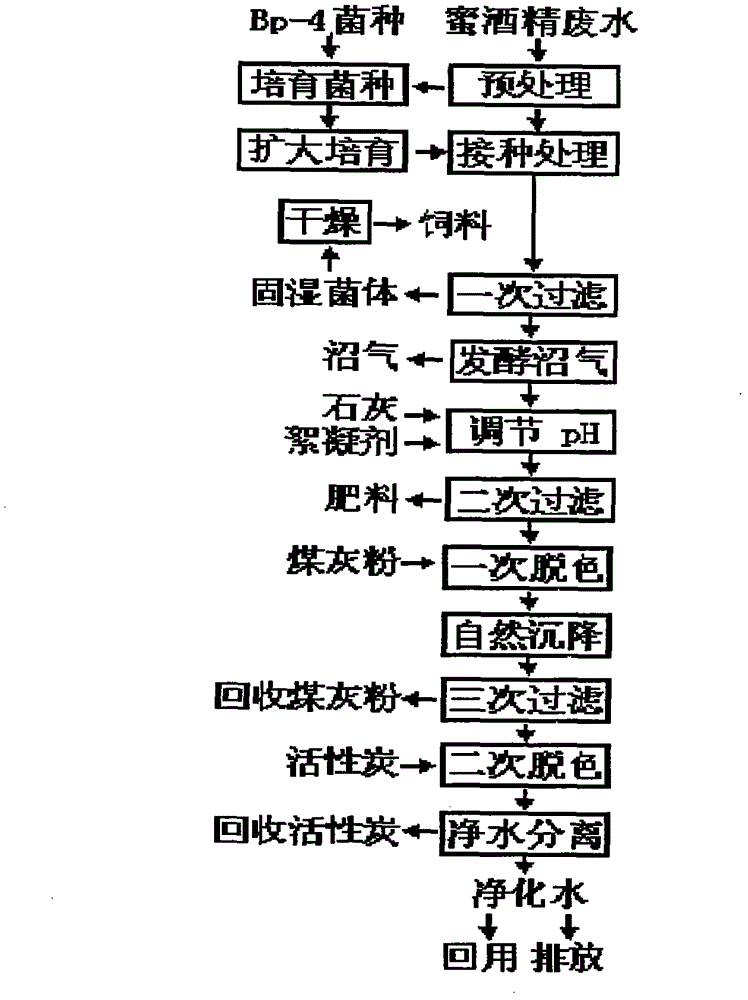
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] The molasses alcohol waste liquid and cellulose were used as raw materials and cultivated at a temperature of 30° C. to obtain the molasses alcohol waste liquid bacterial strain Bp-4. The molasses alcohol waste liquid is adjusted and treated so that the concentration reaches 3BX and the pH is 6. The molasses alcohol waste liquid strain Bp-4 is used, and the pretreated molasses alcohol waste liquid is used as a culture medium. After cultivating at a temperature of 30°C for 22 hours, Then take the pretreated molasses alcohol waste liquid as the culture base to expand and cultivate the molasses alcohol waste liquid bacterial classification Bp-4, and the cultivation conditions are cultivated for 24 hours at a temperature of 30° C. to be used for processing the molasses alcohol waste liquid; 10% molasses alcohol waste strain Bp-4 of molasses alcohol waste liquid, control the treatment temperature at 30°C, and treat for 8 hours; the molasses alcohol waste liquid treated with m...
Embodiment 2
[0035] The molasses alcohol waste liquid and cellulose were used as raw materials and cultivated at a temperature of 31° C. to obtain the molasses alcohol waste liquid bacterial strain Bp-4. Adjust the molasses alcohol waste liquid to make the concentration reach 3.2BX, and the pH is 6.2. Use the molasses alcohol waste liquid strain Bp-4, use the pretreated molasses alcohol waste liquid as the culture medium, and cultivate it at a temperature of 31°C for 23 hours. , then use the pretreated molasses alcohol waste liquid as the culture medium to expand the cultivation of the molasses alcohol waste liquid bacterial classification Bp-4, and the cultivation conditions are cultivated at a temperature of 31° C. for 23 hours for the use of the molasses alcohol waste liquid; the added weight is adjusted to handle molasses alcohol waste liquid 10% molasses alcohol waste liquid bacterial classification Bp-4, control treatment temperature 31 ℃, treatment time 7 hours; With the molasses alc...
Embodiment 3
[0039] The molasses alcohol waste liquid and cellulose were used as raw materials and cultivated at a temperature of 32° C. to obtain the molasses alcohol waste liquid bacterial strain Bp-4. Adjust the molasses alcohol waste liquid to make the concentration reach 3.5BX, and the pH is 6.3. Use the molasses alcohol waste liquid strain Bp-4, use the pretreated molasses alcohol waste liquid as the culture medium, and cultivate it at a temperature of 32°C for 24 hours. , and then use the pretreated molasses alcohol waste liquid as the culture medium to expand the cultivation of the molasses alcohol waste liquid bacterial classification Bp-4, and the cultivation conditions are cultivated at a temperature of 32° C. for 22 hours for the treatment of the molasses alcohol waste liquid; molasses alcohol waste liquid 10% molasses alcohol waste liquid bacterial classification Bp-4, control treatment temperature 32 ℃, treatment time 7.5 hours; With the molasses alcohol waste liquid that the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com