Method for simply and rapidly identifying transgenic seeds and estimating copy numbers
A technology for transgenic and screening marker genes, applied in the field of plant breeding and biology, it can solve the problems of mixing non-transgenic seedlings, killing of transgenic seedlings, and difficulty in screening transgenic plants, and achieves the effect of high accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Example 1: Construction of expression vectors
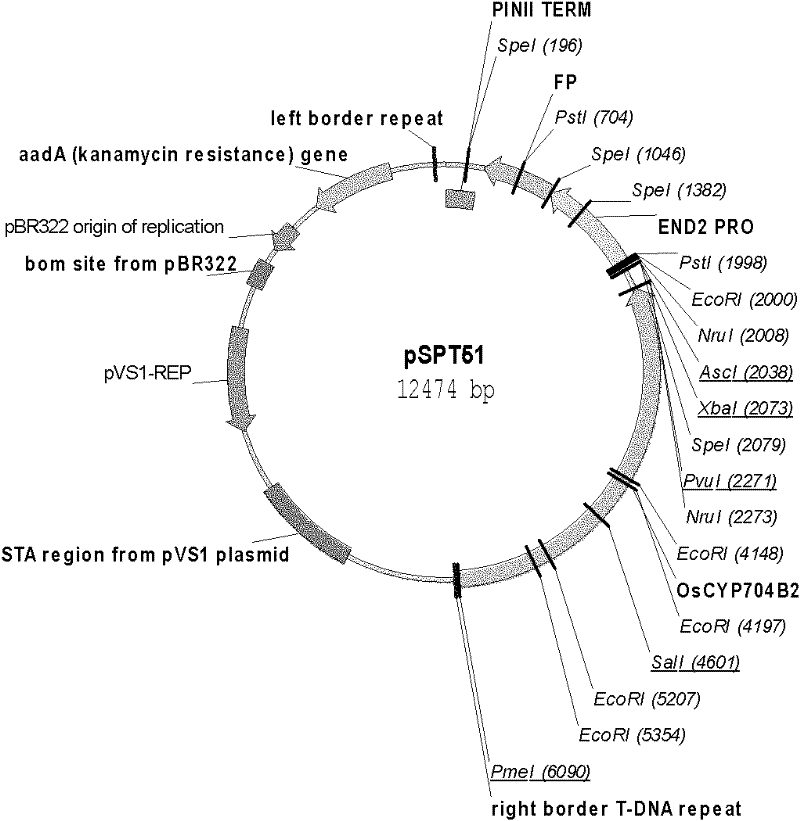
[0025] The name of the expression vector used for transformation in the present invention is pSPT51 ( figure 1 ). The vector is artificially constructed on the basis of pPZP. There are 2 gene expression cassettes on the expression vector: one is OsCYP704B2 gene expression cassette, the expression cassette consists of OsCYP704B2 Genes and their own endogenous promoters and terminators. In order to distinguish the endogenous OsCYP704B2 Genes and expression vectors transformed into rice OsCYP704B2 gene, in the wild-type allele OsCYP704B2 The three SNPs were mutated from G to C at bases 1468, 1470 and 1473, respectively. None of these changes affected the encoded amino acid sequence. Modified OsCYP704B2 The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.3, wherein the SNP is marked by a box; the second is the reporter / screening marker gene FP Gene (SEQ ID NO.1) expression cassette, the gene is driven ...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Example 2: Transformation of rice ms26 male sterile mutant material to obtain transgenic rice plants
[0028] The expression vector in Example 1 was introduced into the Agrobacterium strain AGLO by electric shock method, and used to transform the callus of rice ms26 male sterile material. Transformed callus was screened by red fluorescent protein, attached figure 2 In order to express the callus of exogenous gene, it was further differentiated to regenerate transformed plants expressing exogenous gene (attached image 3 ).
[0029]
Embodiment 3
[0030] Embodiment 3: PCR detection of transgenic plants
[0031] The leaves of the transgenic rice plants in Example 2 were taken, and the total DNA was extracted. by FP The gene sequence is used as a template to design primers, for T 0 Genomic DNA of transgenic rice was amplified by PCR. The fragment of the amplified product is 789bp. The amplification program was: 94°C 10min; 94°C 1min, 60°C 1min, 72°C 1min; 37 cycles; 72°C 10min. The forward primer sequence is 5'-GGACTTGAACTCCACCAGG-3'; the reverse primer sequence is: 5'-ATAATGCCAATACGACACC-3'. attached Figure 4 It is the PCR amplification result of some transgenic plants, indicating that the exogenous gene has been integrated into the rice recipient genome.
[0032]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com