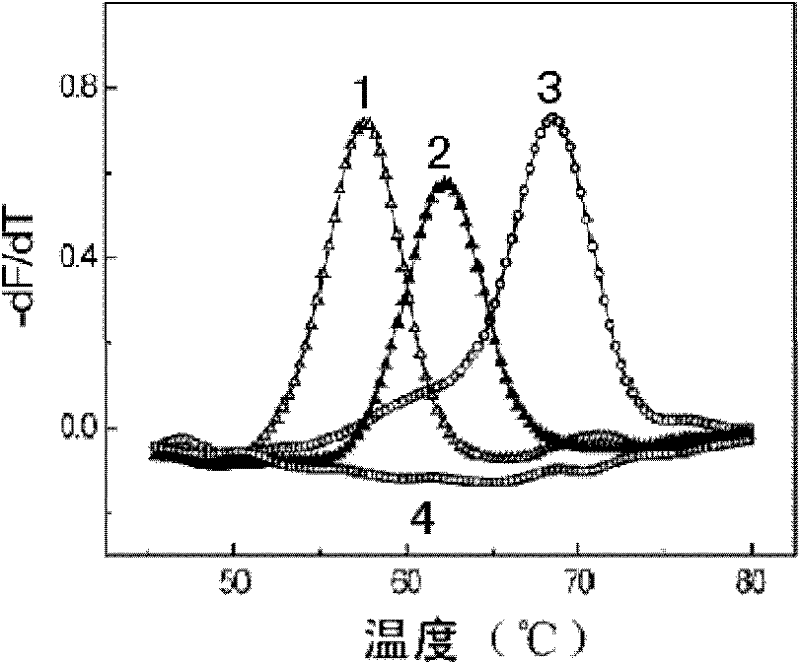
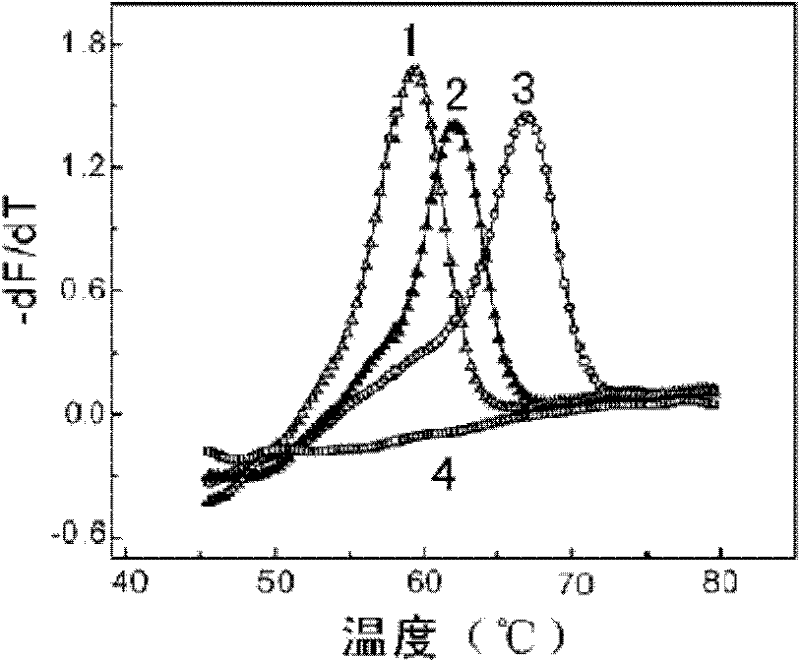
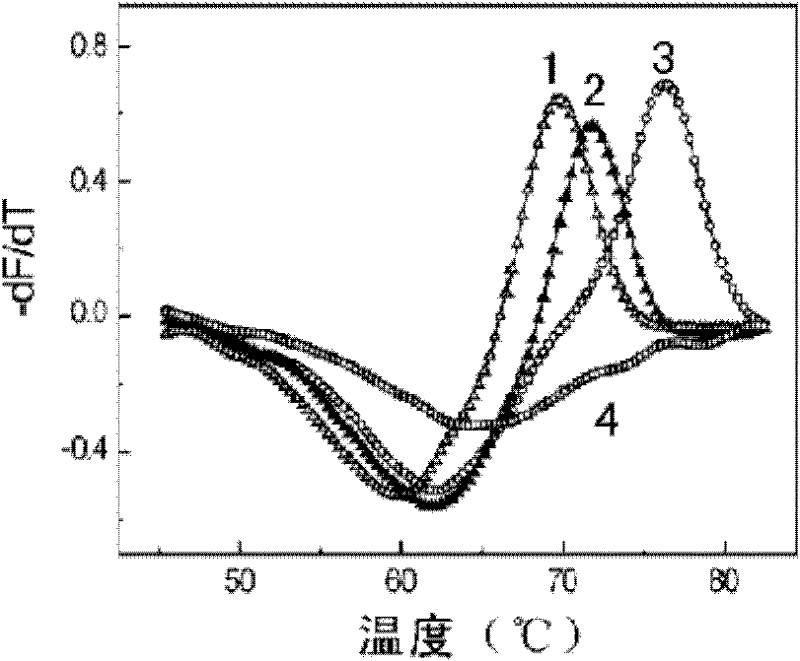
Method for detecting resistant mutation of mycobacterium tuberculosis to rifampin and kit thereof
A technology for Mycobacterium tuberculosis and drug-resistant mutations, which is applied to the determination/testing of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, and material stimulation analysis, etc. It can solve the problems of increased PCR product contamination and cumbersome detection steps.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] Example 1 Extraction of Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA
[0084] 1) Culture of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain
[0085] Mycobacterium tuberculosis was cultured in acidic Roche medium.
[0086] 2) DNA extraction
[0087] DNA was extracted from samples of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains by boiling and lysis. Specific steps are as follows:
[0088] A. For Mycobacterium tuberculosis growing on solid medium, use 22SWG standard inoculation loop to collect 1 loop of bacteria, and suspend in 250 μL TB DNA extraction solution. Take 1 mL of Mycobacterium tuberculosis grown in liquid medium, centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 15 min, discard the supernatant and resuspend the bacteria in 250 μL of TB DNA extract.
[0089] B. Seal with parafilm and heat at 99°C for 20 minutes. Centrifuge at 14000rpm for 10min, transfer the supernatant to a new 1.5mL centrifuge tube. The supernatant is the template for PCR amplification.
[0090] C. Samples should be stored at -20°C and the test...
Embodiment 2
[0091] The design of embodiment 2 Mycobacterium tuberculosis detection primers and probes
[0092] According to the rpoB (GenBank: L27989) sequence of the rifampicin resistance-related gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, it was completed with software such as Primer 5, TmUtility v1.3 and mfold. The primer and probe sequences are as follows:
[0093] Primer-F: 5′-GGAGGCGATCACACCGCAGACGTT-3′
[0094] Primer-R: 5′-TGACAGACCGCCGGGCC-3′
[0095] Probe A: 5'-FAM-CGAGCTCAGCTGGCTGGTGCGCTCG-BHQ1-3'
[0096] Probe B: 5'-FAM-GCTACGGAGCCAATTCATGGACCAGACGTAGC-BHQ1-3'
[0097] Probe C: 5'-TET-CCGACGCCGACAGCGGGTTGTTCGTCGG-BHQ1-3'
[0098] Probe D: 5'-TET-CCTGCCGCCGACTGTCGGCGCTGGCAGG-BHQ1-3'.
[0099] Primers and probes were synthesized by Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Technology Service Co., Ltd. Store the probes in the dark after quantification.
Embodiment 3
[0100] Example 3 Mycobacterium tuberculosis rifampicin-resistant mutation detection kit detects rifampicin-resistant mutation
[0101] Two reaction systems are used for double-color detection:
[0102] Each part of RIF PCR MIX A is 19.6μl, each reaction solution contains 1×PCR buffer (10mM Tris-HCl, pH8.6, 50mM KCl, 50% glycerol), 3.0mM MgCl 2 , dATP, dCTP, dGTP each 0.2mM, dUTP 0.4mM, 0.1μM Primer-F, 2μM Primer-R, 0.1μM Probe-A, 0.1μM Probe-C. 2U of enzyme mixture (0.4 μl) was added before detection, and the amount of template to be tested was 5 μl.
[0103] Each part of RIF PCR MIX B is 19.6μl, and each reaction solution contains 1×PCR buffer (10mM Tris-HCl, pH8.6, 50mM KCl, 50% glycerol), 3.0mM MgCl 2 , dATP, dCTP, dGTP each 0.2mM, dUTP 0.4mM, 0.1μM Primer-F, 2μM Primer-R, 0.1μM Probe-B, 0.1μM Probe-D. 2U of enzyme mixture (0.4 μl) was added before detection, and the amount of template to be tested was 5 μl.
[0104] Take the concentration as 10 4 Copies / μl RIF wild-ty...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com