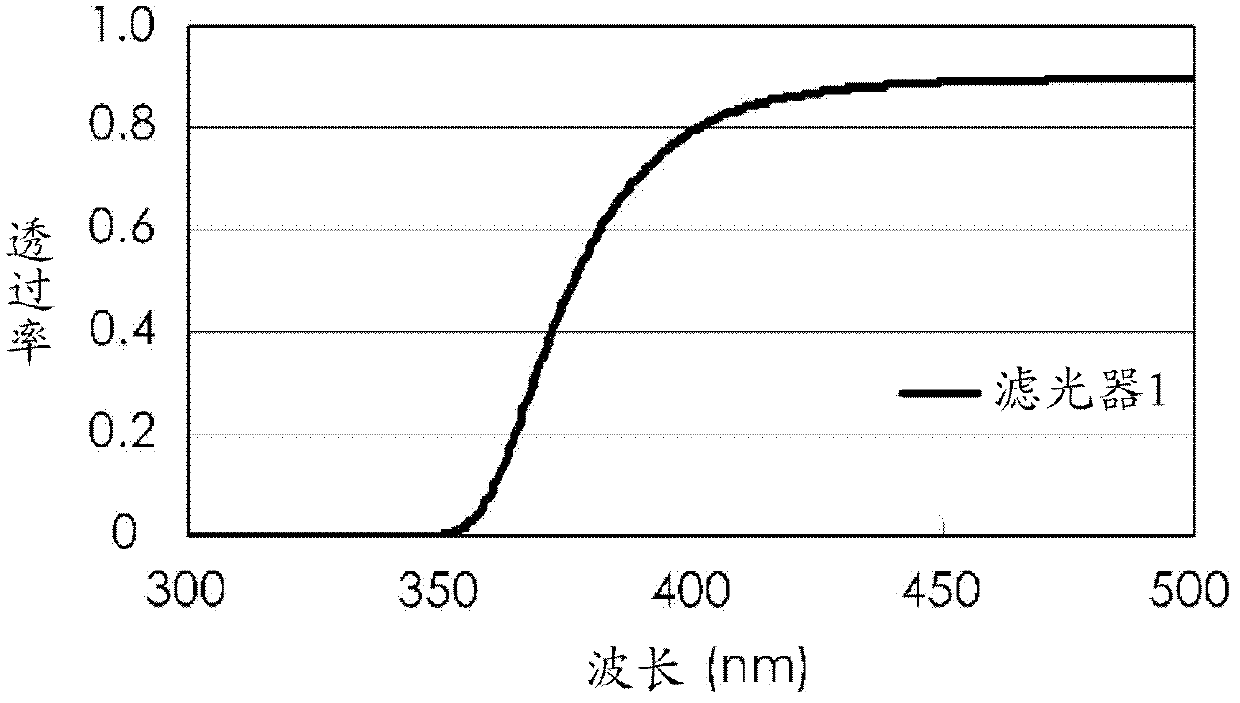
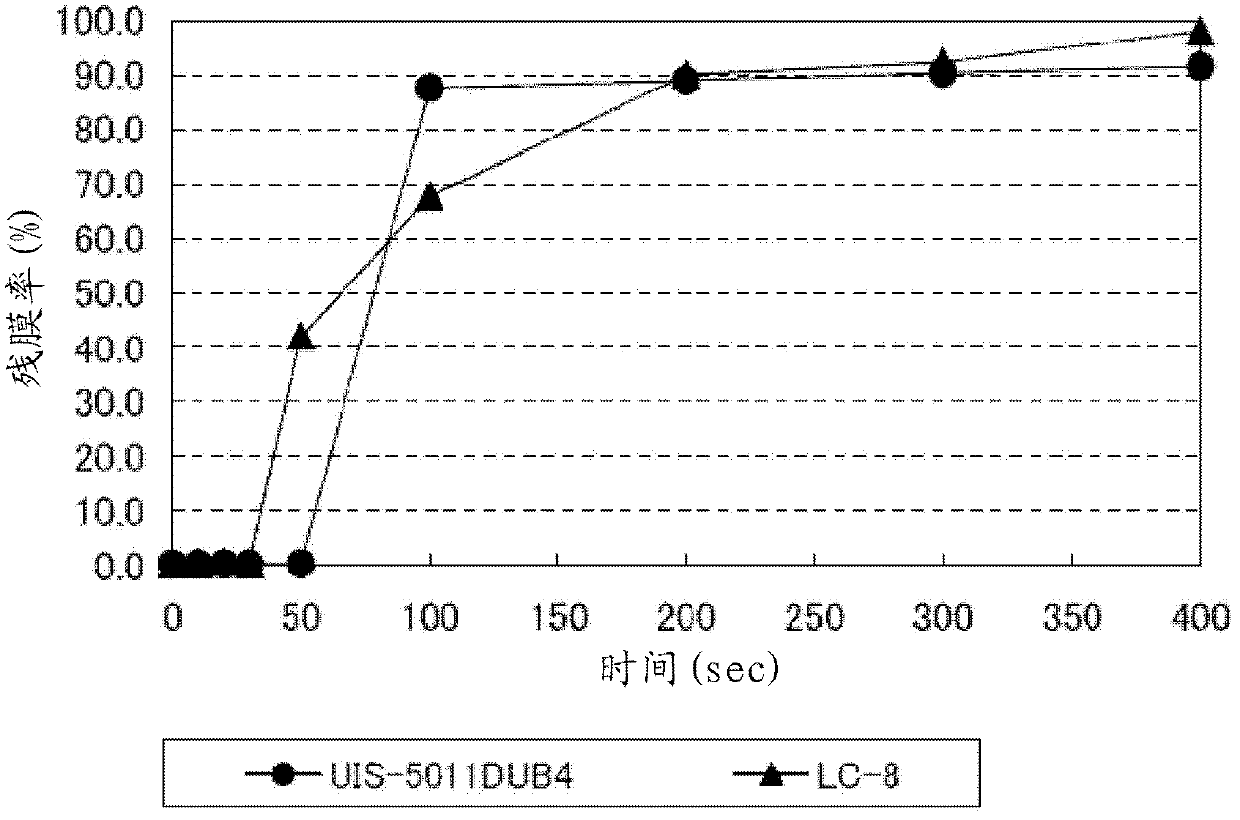
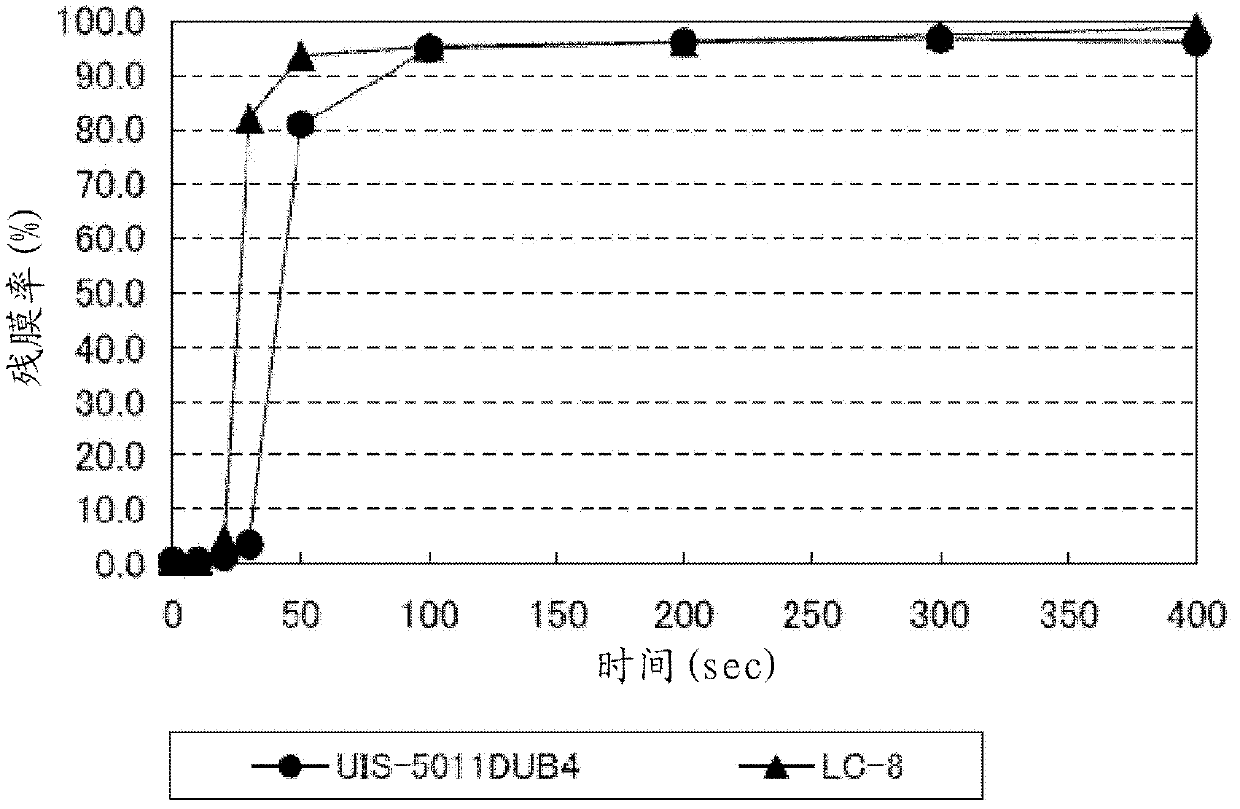
Photobase generator
A compound and general formula technology, applied in the field of photobase generators, can solve the problems such as the reduction of the base generation efficiency of the photobase generators
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0173] The present invention will be specifically described below based on examples, but the present invention is not limited to these examples.
Synthetic example 1
[0174] Synthesis Example 1: Synthesis of 9-Anthracenylmethyl 4'-Nitrophenyl Carbonate (First Step)
[0175] To a solution obtained by dissolving 5.0 g (24 mmol; manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.) of 9-anthracenemethanol in 250 mL of dehydrated dimethylacetamide (dehydrated DMAc), 7.3 g (72 mmol) of triethylamine was added. To this solution, 4.9 g (24 mmol; manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.) of chloroformic acid-4-nitrophenyl was added, followed by stirring at room temperature for 24 hours to perform a reaction. After the reaction was terminated, ice water was poured into the reaction liquid, the mixed liquid was extracted with dichloromethane, and the extracted organic layer was further washed with water, and then the organic layer was concentrated. Next, water was poured into the concentrated residue, and the crystals generated therein were collected by filtration, and the obtained crystals were dried to obtain 4.8 g of 9-anthracenylmethyl ...
Embodiment 1
[0177] Embodiment 1: Synthesis of 9-anthracenylmethyl 1-piperidine carboxylate (second process)
[0178] After adding 1.4 g (16 mmol) of piperidine to a solution obtained by dissolving 4.8 g (13 mmol) of 9-anthracenylmethyl 4′-nitrophenyl carbonate obtained in Synthesis Example 1 in 100 mL of dichloromethane, the The reaction was carried out by stirring at room temperature for 1 hour. After the reaction was terminated, the reaction solution was washed with water, and the washed organic layer was concentrated. The obtained concentrated residue was purified by column chromatography (filler: silica gel (Wakogel C-200; manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.), developing solvent: dichloromethane) to obtain the above formula [10] in light yellow crystals. 1.3 g of the indicated 9-anthrylmethyl 1-piperidine carboxylate (yield: 32%). Shown below 1 Measurement results of H-NMR and melting point.
[0179] 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ (ppm): 1.39 (2H, br, CH 2 ), 1.53 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com