Method for producing carotinoid through cordyceps solid culture
A technology of carotene and solid culture, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problem of low extraction rate of mycelium carotenoids, achieve low price, high yield, Source Rich Effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
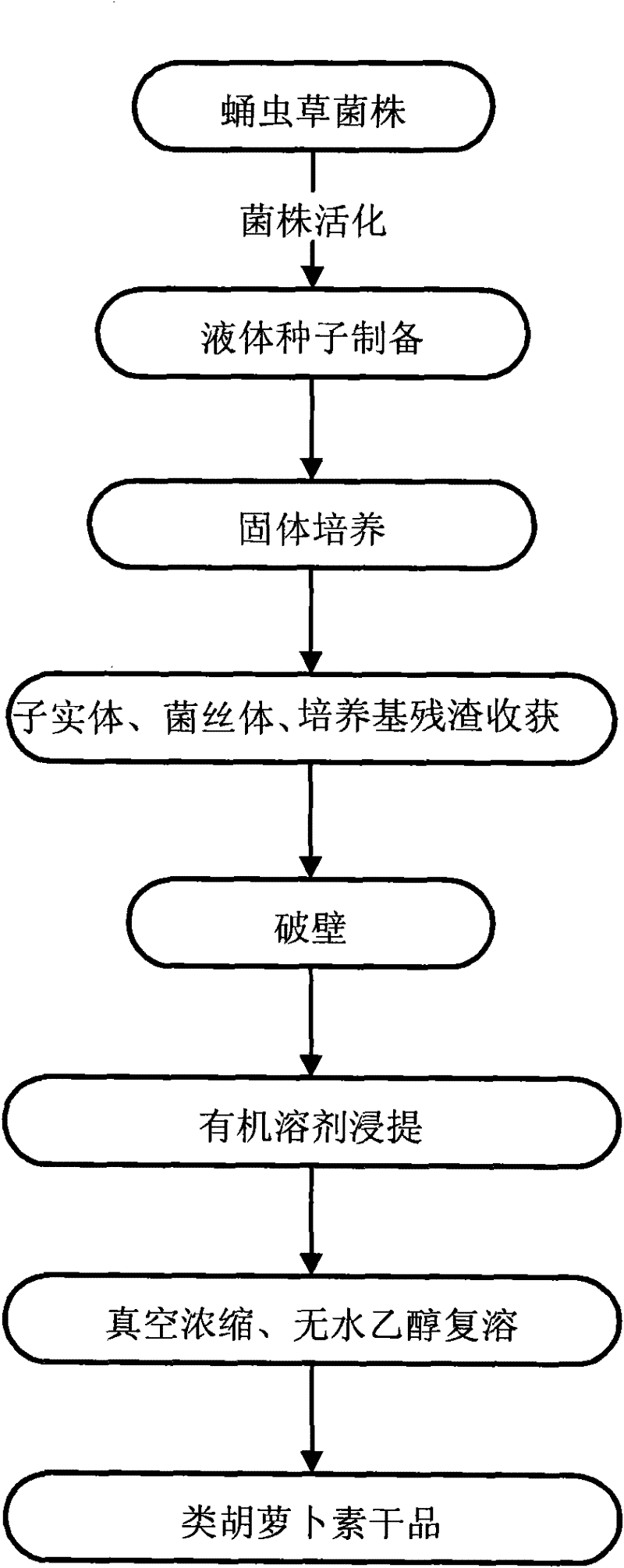
[0023] Embodiment 1, the method for extracting carotenoids from the fruiting bodies of Cordyceps militaris solid culture
[0024] (1) Strain activation
[0025] Cordyceps militaris 1065 (preservation number: CGMCC 5.1973) was inoculated on potato solid medium (PDA) for activation, the culture temperature was 20° C., and the culture time was 10 days.
[0026] (2) Strain cultivation: with the mycelia of step (1), inoculate under aseptic conditions into PDA liquid culture medium (medium consists of: potato 200g boiled juice, glucose 20g, constant volume to 1000ml), culture temperature At 20°C, the culture method is to use a vortex shaker to cultivate at a rotation speed of 150 rpm, and cultivate to the logarithmic growth phase.
[0027] (3) Solid culture: insert the liquid strain activated in step (2) into the rice culture medium, and place it in an incubator for cultivation. First, under the condition of a temperature of 20° C., cultured in the dark for 10 days; then irradiate...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Embodiment 2, the method for extracting carotenoids from Cordyceps militaris solid medium residue
[0030] (1) Strain activation
[0031] Cordyceps militaris 1065 (preservation number: CGMCC 5.1973) was inoculated on potato solid medium (PDA) for activation, the culture temperature was 20° C., and the culture time was 10 days.
[0032] (2) Strain cultivation: use the mycelium of step (1) to inoculate in the potato liquid culture medium under aseptic conditions, the cultivation temperature is 20° C., and the cultivation method is to utilize a vortex shaker to cultivate, and the rotating speed is 150 rpm , cultivated to the logarithmic growth phase.
[0033] (3) Solid culture: insert the liquid seed activated in step (2) into the rice culture medium, and place it in an incubator for cultivation. First, culture at 18 DEG C in the dark for 10 days, then irradiate with natural light, culture at 18-25 DEG C for 40 days, and harvest the fruiting body of Cordyceps militaris t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com