Microporous metal-organic framework material as well as preparation method and application thereof
An organic framework and metal technology, applied in the field of microporous metal-organic framework materials and their preparation, can solve the problems of reducing application value and structural stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
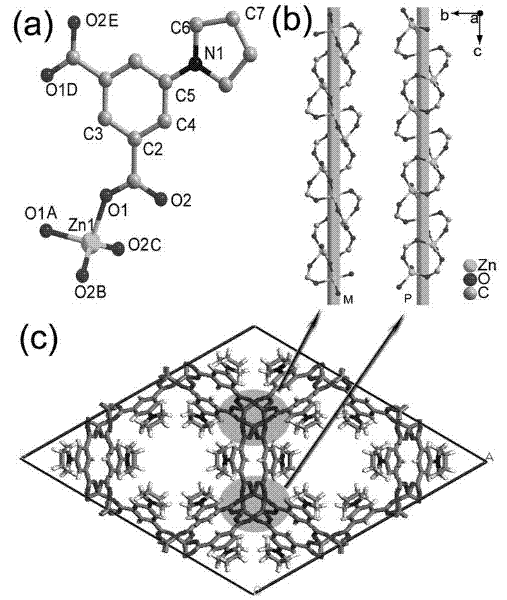
[0017] Example 1 Preparation of Zn(pybdc) microporous metal-organic framework material.
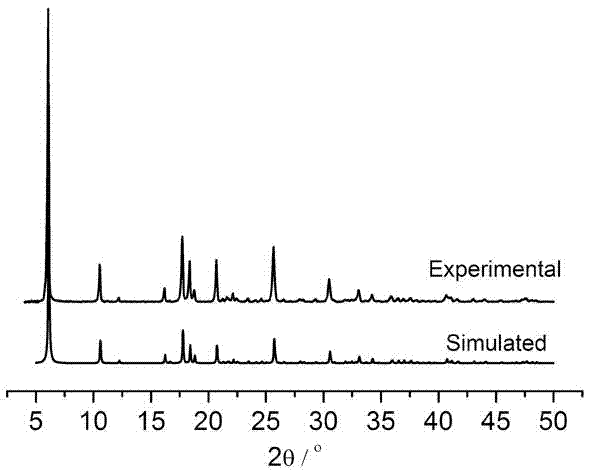
[0018] Weigh Zn(AcO) 2 2H 2 O 0.025 g (0.1 mmol), H 2 pybdc 0.02 g (0.1 mmol), dissolved in 8 mL of deionized water and 2 mL of absolute ethanol, stirred at room temperature for 2 hours, and transferred the suspension to a 15 mL stainless steel reactor with a Teflon liner , crystallized at 140° for 72 hours, cooled to room temperature, brown transparent needle-like crystal Zn (pybdc) was precipitated, filtered, washed, and dried to obtain 25 mg. Yield 55.5%. The X-ray diffraction pattern of the product and the simulated X-ray diffraction pattern of a single crystal are shown in figure 2 .
Embodiment 2
[0019] Example 2 Structural characterization of Zn(pybdc) microporous metal-organic framework materials.
[0020] The single crystal X-ray diffraction data were measured on Bruker's SMART APEX CCD single crystal diffractometer, and the diffraction data were collected by Mo / Ka rays (λ= 0.71073 ?) and ω scanning. The unit cell parameters and orientation matrix are corrected by the least square method, and the crystal structure is analyzed by the direct method or the Patterson method to obtain the initial structure, and then the coordinates of all non-hydrogen atoms and organic groups are obtained by least square correction and difference Fourier method. The hydrogen atoms on the water were obtained by theoretical hydrogenation, and the hydrogen atoms on the water were determined by the difference Fourier method. And corrected by full-matrix least [84] squares, all non-hydrogen atoms were refined using anisotropic thermal parameters. Using the corrected precise atomic coordinate...
Embodiment 3
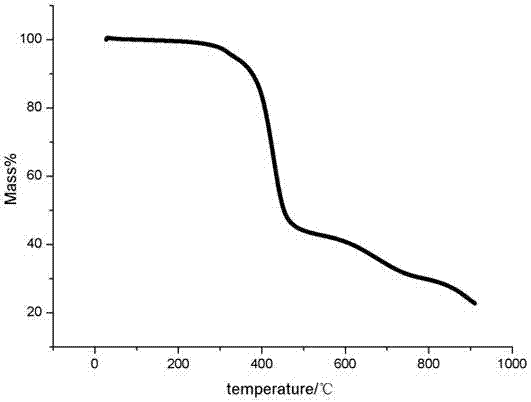
[0023] Example 3 The thermal stability of the microporous metal-organic framework material Zn(pybdc) obtained in Example 1 was characterized.
[0024] The thermal stability of the microporous metal-organic framework material Zn(pybdc) is analyzed by thermogravimetry, and the thermogravimetric curve is shown in image 3 .
[0025] Example 4 Characterization of gas adsorption properties of the microporous metal-organic framework material obtained in Example 1.
[0026] We carried out hydrogen adsorption at 77 K and CO adsorption at 273 K using samples of Zn(pybdc) 2 Adsorption studies. At 77K, the adsorption amount of hydrogen on the Zn(pybdc) sample showed a rapid increase in the low pressure region, and then increased linearly with the increase of pressure, and the adsorption amount reached 17 cm at 800 mmHg pressure. 3 / g. And at 273K, CO 2 The adsorption amount on the Zn(pybdc) sample showed a linear increase in the whole pressure range. Its adsorption isotherm diagram...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com