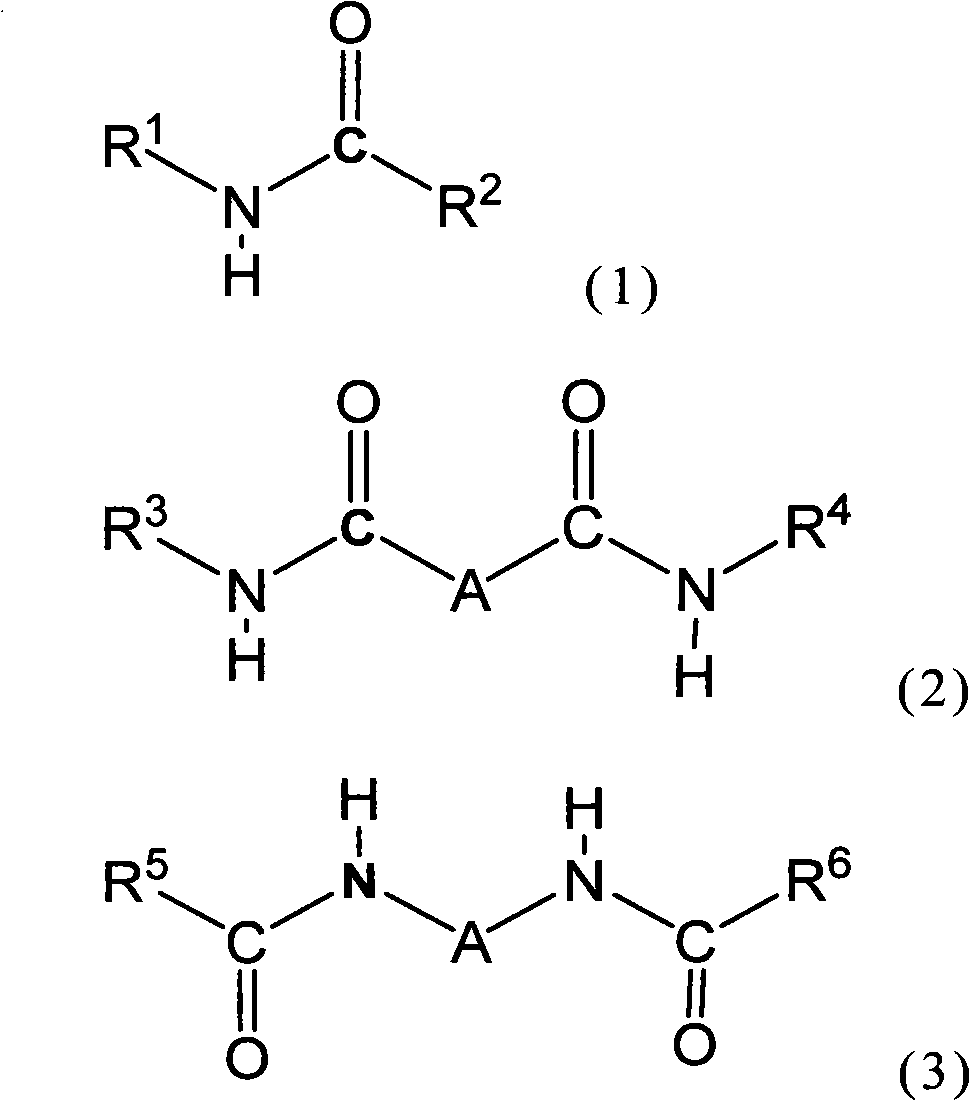
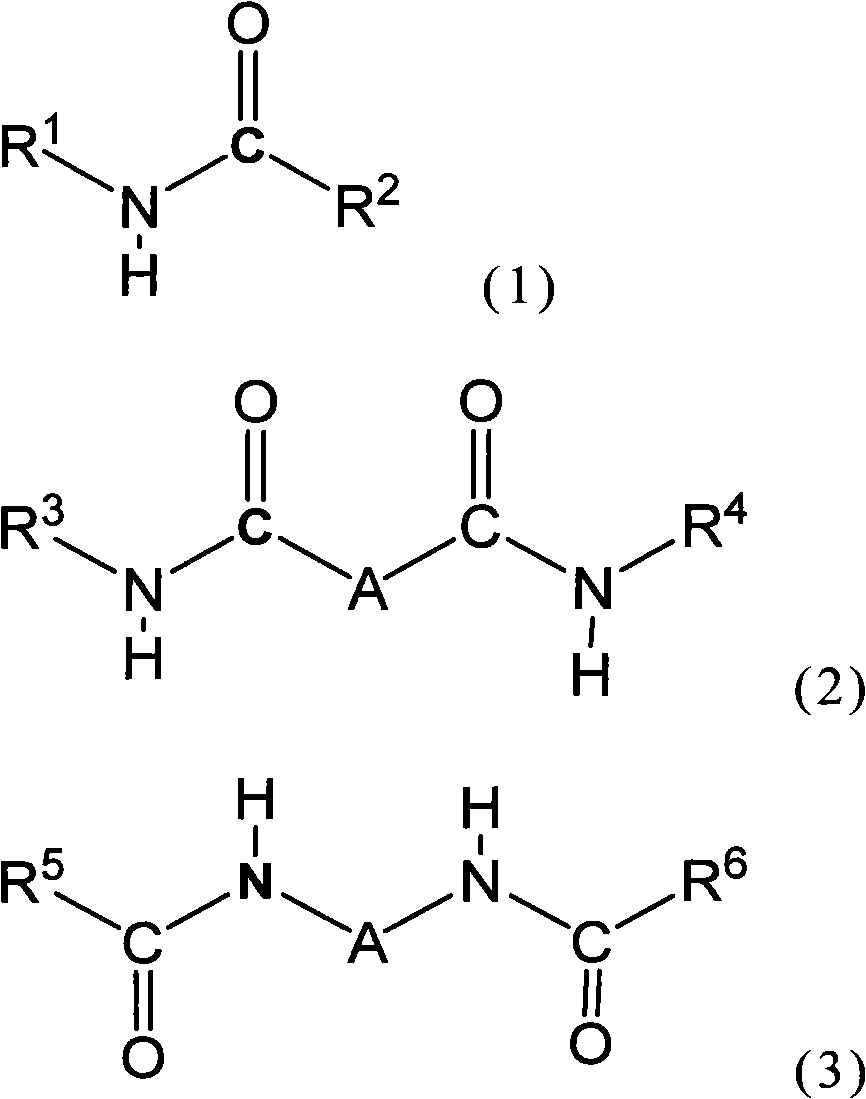
Radiation-sensitive resin composition, cured film, method for forming cured film, and display element
A technology of resin composition and radiation, which is applied in the fields of electrical components, nonlinear optics, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, etc., can solve the problems of reduced storage stability, and achieve excellent low-temperature firing, excellent storage stability, and heat-resistant linearity Excellent expansion effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0149]
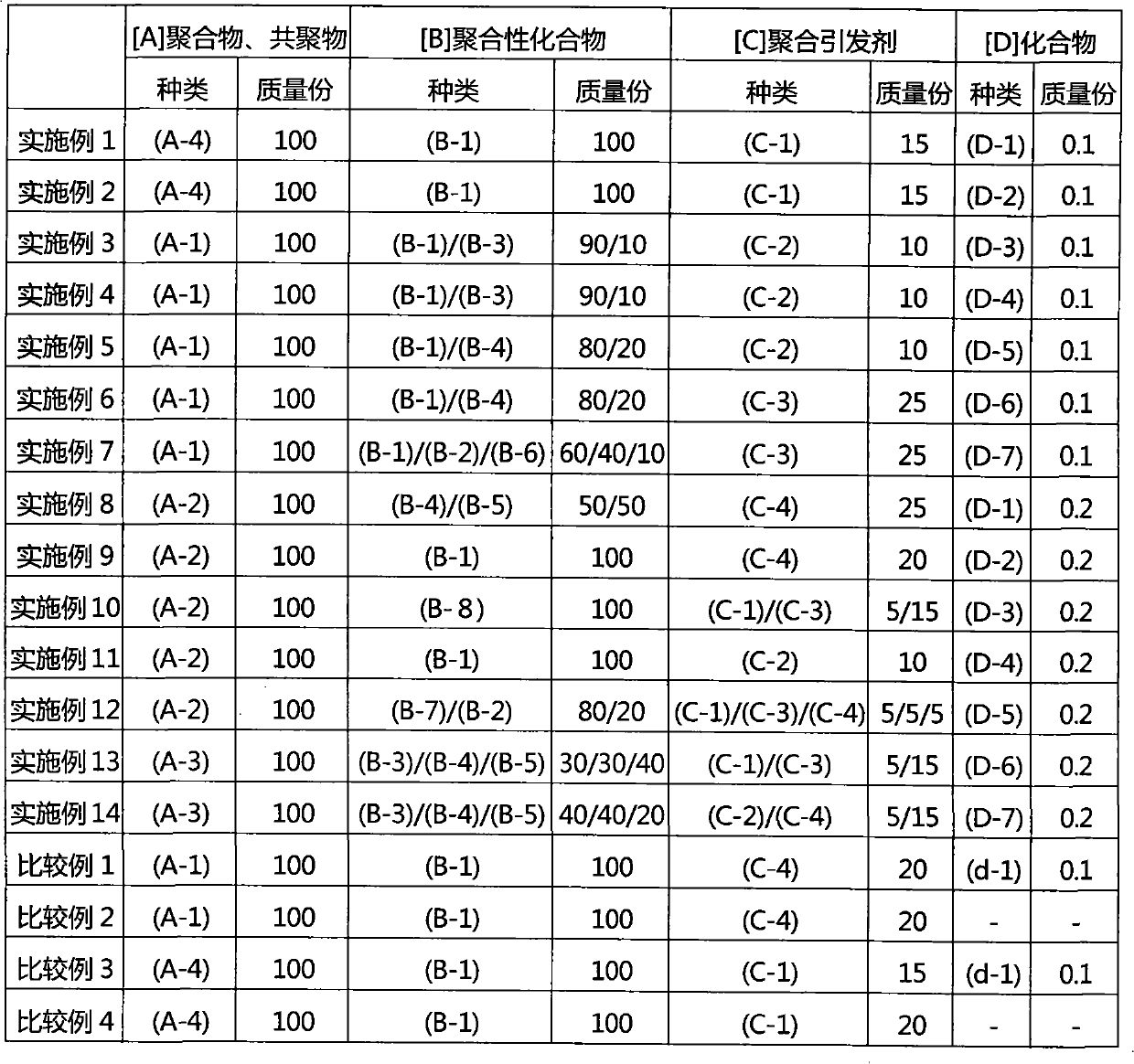
[0150] The radiation-sensitive resin composition of the present invention can be prepared by combining [A] polymer or [A] copolymer, [B] polymerizable compound, [C] polymerization initiator and [D] compound, and without damaging the desired Within the range of the effect, the optional ingredients added as needed are mixed and prepared in a prescribed ratio. This radiation-sensitive resin composition is preferably dissolved in an appropriate solvent and used in a solution state.
[0151] As a solvent for preparing the composition, it is possible to use a solvent capable of uniformly dissolving or dispersing [A] polymer or [A] copolymer, [B] polymerizable compound, [C] polymerization initiator, [D] compound and any Select components, and solvents that do not react with each component. Examples of such solvents include the same ones as those exemplified as solvents that can be used to synthesize the above [A] copolymer, and preferably contain at least one solvent sele...
Synthetic example 1
[0193] In a flask with a condenser and a stirrer, 5 parts by mass of 2,2'-azobis(2,4-dimethylvaleronitrile) and 220 parts by mass of diethylene glycol ethyl methyl ether were added. Next, add 20 parts by mass of styrene, 12 parts by mass of methacrylic acid, 28 parts by mass of dicyclopentanyl methacrylate and 40 parts by mass of glycidyl methacrylate, replace with nitrogen, and slowly stir while raising the temperature of the solution. Up to 70°C, the temperature was maintained for 5 hours to carry out polymerization to obtain a solution containing the copolymer (A-1). The solid content concentration of the obtained copolymer solution was 31.3%, and Mw of the copolymer (A-1) was 12,000. In addition, the solid content concentration refers to the ratio of the copolymer mass to the total mass of the copolymer solution.
Synthetic example 2
[0195] In a flask with a condenser and a stirrer, 5 parts by mass of 2,2'-azobis(2,4-dimethylvaleronitrile) and 220 parts by mass of diethylene glycol methyl ethyl ether were added. Then, add 10 parts by mass of styrene, 12 parts by mass of methacrylic acid, 23 parts by mass of tricyclic dicyclopentanyl methacrylate and 20 parts by mass of glycidyl methacrylate, 20 parts by mass of 2-methyl shrinkage methacrylate Glyceride, 10 parts by mass of tetrahydrofurfuryl methacrylate, after nitrogen replacement, further add 5 parts by mass of 1,3-butadiene, and slowly stir while raising the temperature of the solution to 70°C, and keep the temperature After 5 hours, polymerization proceeded to obtain a solution containing a copolymer (A-2). The solid content concentration of the obtained copolymer solution was 31.5%, and the Mw of the copolymer (A-2) was 10,100.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com