Method for biologically treating sewage through cation exchange, adsorption and filtering by using rice hull carbon
A cation exchange and biological treatment technology, which is applied in the field of constructed wetland water treatment, can solve the problem that the cation exchange capacity of wetland soil is not particularly obvious, and achieve the effect of significant diversity of microbial communities, improvement of cation exchange level, and promotion of plant growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
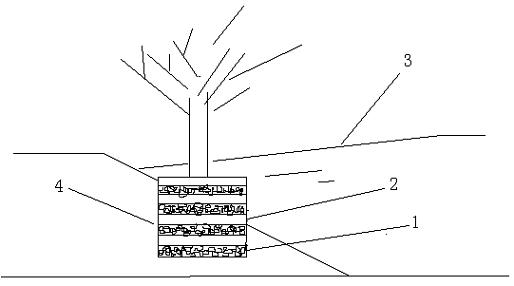
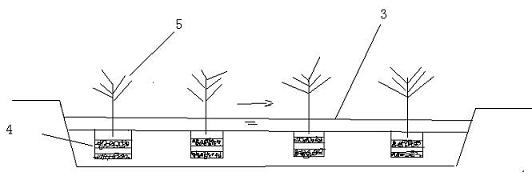
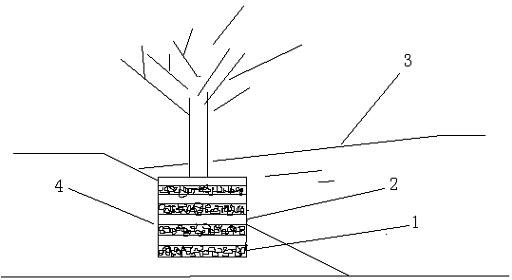
[0013] On one side of a field ditch with a width of 5m and a length of 500m, dig a piece of earth with a length, width and height of 1.5m*1.5m*1.5m every five meters (such as figure 2 shown). After backfilling the earthwork, spread rice husk charcoal with a particle size of about 2.5mm and the original soil every 5cm in the earthwork, and plant a bald cedar (such as figure 1 ). Utilizing the water level drop of the natural water body, the water flows through the interlayer of artificial carbon soil to make the water body fully contact with the carbon material, so that filtration, adsorption, and ion exchange reactions occur, forming a sewage treatment system to absorb and remove pollutants such as nitrogen and phosphorus. At the same time, the soil improved by rice husk charcoal, due to the enhanced cation exchange capacity, improves the surrounding soil environment, enhances soil fertility, and better promotes the growth of crops.
[0014] Rice husk charcoal is used to imp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com