Lithium ion battery
A lithium-ion battery and lithium-ion technology, which is applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of limited lithium ions, unsatisfactory discharge, storage capacity and acceleration that cannot be met, and achieve the effect of improving discharge efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1-making graphene layer
[0031] The graphene layer of this embodiment is produced by a solid-state growth method, and its general production method is as follows.
[0032] First, a high-purity graphite powder layer is coated on a quartz sheet, and the quartz sheet coated with the graphite powder layer is placed in a tubular boiler with a vacuum degree of about 10 -5 Thor.
[0033] Then, the quartz sheet coated with the graphite powder layer is heat-treated at 1200° C., so that the graphite powder layer forms a graphite film. After the boiler is cooled down slowly, the graphite film coated on the quartz sheet can be torn off from the cooled quartz sheet to obtain the stacked multi-layer graphene layer of this embodiment.
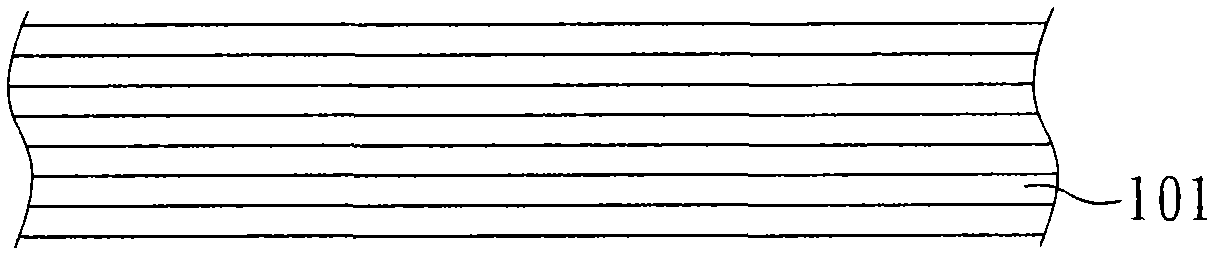
[0034] Through the above-mentioned process, the graphite film with graphene multilayer structure obtained in the present embodiment is as follows: Figure 1A As shown, it includes a plurality of graphene layers 101 .
Embodiment 2
[0035] Embodiment 2-making graphene layer
[0036] The graphene layer of this embodiment is produced by a solid-state growth method, and its general production method is as follows.
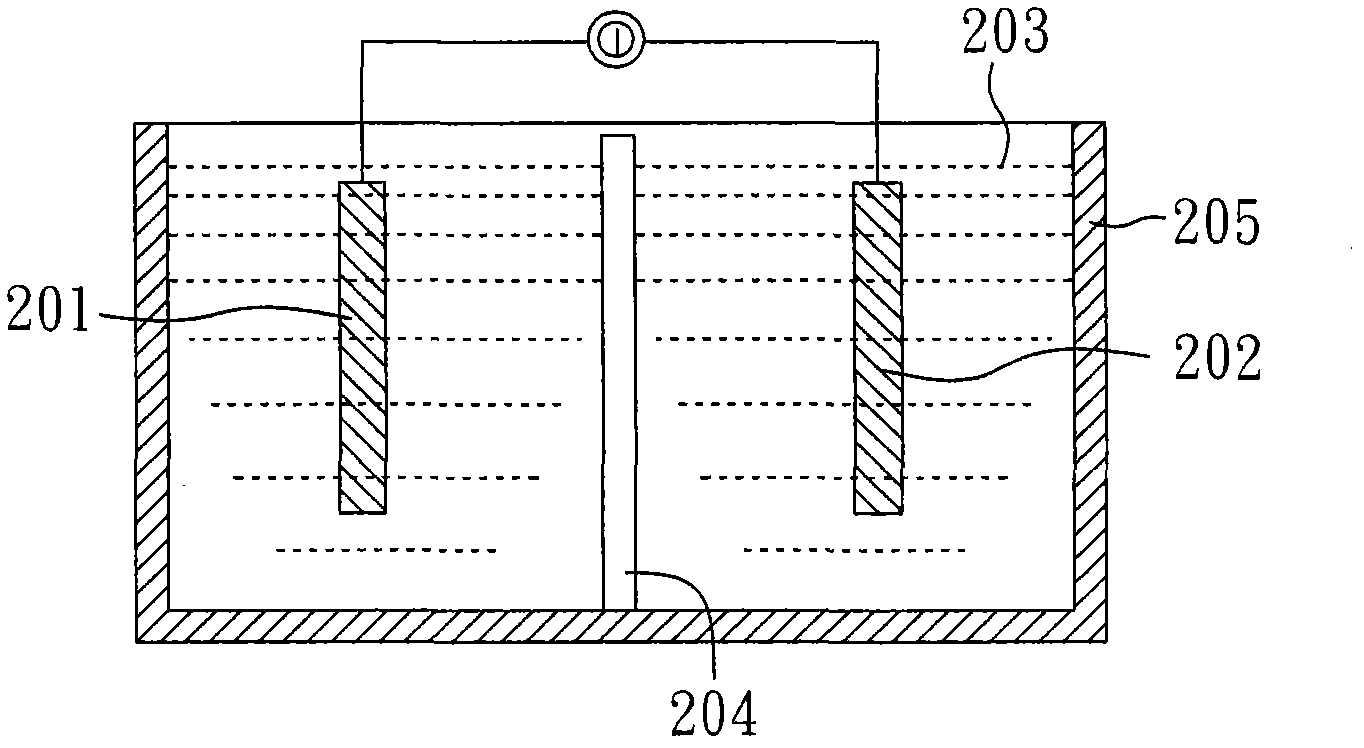
[0037] First, coat high-purity graphite powder on a thin nickel sheet, and place the thin nickel sheet coated with graphite powder in a tubular boiler with a vacuum of about 10 -5 Thor. Here, thin nickel flakes act as a catalyst for converting graphite powder into graphene.
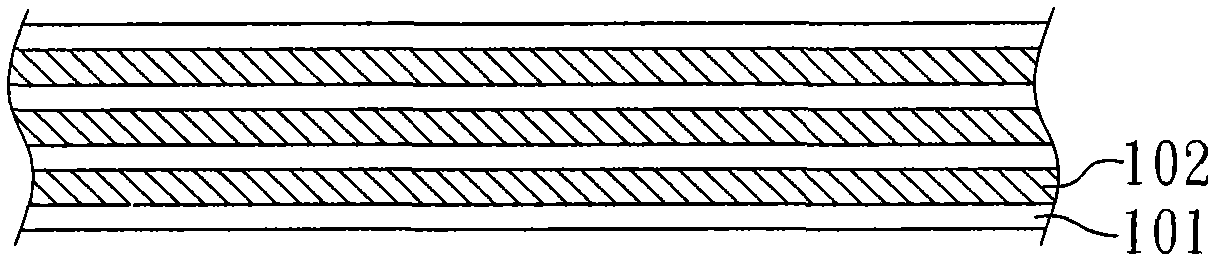
[0038] Then, at a temperature of 1200°C, the graphite powder is catalyzed by the nickel sheet to recombine into a graphene layer with a nearly continuous lattice, which is coated on both sides of the nickel sheet, and a graphite film is formed on both sides of the nickel sheet. After the boiler cools down slowly, the graphite film coated on both sides of the nickel sheet can be torn off from the cooled nickel sheet. However, in this embodiment, graphene and nickel layers are overlapped, so the graphite film with graphene ...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Embodiment 3-making graphene layer
[0041] The manufacturing method of the graphite film with graphene multilayer structure in this embodiment is the same as that in Embodiment 2, except that after the graphite film is formed, the process of removing the nickel layer is also carried out.
[0042] Here, the graphite film with nickel layers and graphene layers interlaced in Example 2 is immersed in acid (such as sulfuric acid, nitric acid, or hydrochloric acid) to dissolve the metal catalyst. After cleaning, then obtain the graphite film of the tool graphene multilayer structure of present embodiment, its structure is the graphite film structure that makes with embodiment 1 similar, also comprises a plurality of graphene layers 101, as Figure 1A shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com