Self-expandable segment tectorial asymmetric areolate stent
A self-expanding, non-symmetrical technology, applied in the direction of the stent, can solve the problems of acute thrombosis risk, poor release of the wall, shrinkage of the covering membrane, etc., to increase metal coverage, reduce acute thrombosis, reduce shrunken and angulated effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
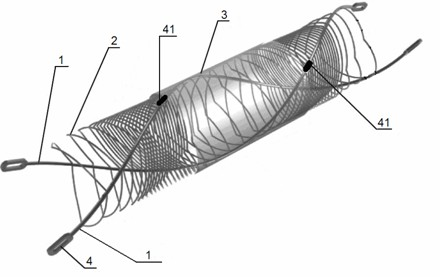
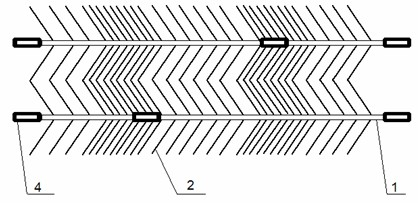
[0027] Such as figure 1 with figure 2 As shown, the self-expanding section-coated non-uniform interstitial stent of the present invention is composed of a stent skeleton and an outer covering membrane material 3 coated on the outside of the stent skeleton; wherein, the stent skeleton is a network tubular hollow structure, consisting of two The main support rod 1 is connected with several connecting rings 2; the connecting rings 2 connecting two main supporting frames 1 are V-shaped and arranged non-uniformly; the external film material 3 is only coated on the outside of the frame.
[0028] The stent skeletons are all processed by laser engraving, cutting and electrochemical polishing. The main support rod 1 and the connecting rod 2 of the stent skeleton are metal alloy wires of the same material that meet medical implantability standards, such as nickel-titanium shape memory alloy , nickel-titanium alloy superelastic alloy, 316 medical stainless steel and cobalt-chromium-nic...
Embodiment 2
[0033] On the basis of Example 1, the main support rods 1 are arranged in a double-helix symmetrical structure, and the apex of the V-shaped structure of the connecting ring 2 is also arranged in a spiral shape to form a secondary support shaft, which is spatially symmetrical with the helical structure of the main support rods form a quadruple helix structure.
[0034] The design of the helical structure can avoid damage to the vessel wall caused by the angulation of the stent during the release of the segmental stent in the curved section of the vessel.
Embodiment 3
[0036] On the basis of Examples 1 and 2, such as figure 2 As shown, 3 outer coating materials of the non-uniform mesh stent of the present invention are only coated on the middle section of the stent skeleton, and the two ends of the stent skeleton and the middle film covering area are loosely arranged parts of the connecting ring, and the two ends are loosely arranged. The part between the middle section and the middle section is the densely arranged part of connecting rings.
[0037] Specifically: the main struts of the loosely arranged part of the connecting rings at both ends of the stent are connected by 2 to 4 connecting rings, the closely arranged part of the second proximal end is connected by 20~30 connecting rings, and the loosely arranged part of the middle part of the stent is connected by 4~5 connecting rings. The metal coverage rate of the densely arranged part is 25%-30%, and the metal coverage rate of the loosely arranged part is 6%-8%.
[0038] The outer coa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com