Proinsulin containing protecting lysine and preparation method for insulin by utilizing proinsulin
A technology of proinsulin and insulin lispro, which is applied in the field of insulin and its preparation, can solve problems such as difficult separation, difficult control of reaction conditions, and adverse effects on insulin quality, so as to avoid by-products, pure production costs, simplify enzymatic hydrolysis and follow-up The effect of the purifying operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0055] In the method for preparing proinsulin with protected lysine at position 29 of the present invention or insulin with protected lysine at position B29, for translation in a translation system, the translation system can be Any known translation system that can be used to translate proinsulin or insulin may be an in vitro translation system, or may be a prokaryotic or eukaryotic expression system. Those skilled in the art can understand that such a system includes a suitable buffer system and enzymes related to protein synthesis. For example, Escherichia coli or yeast expression systems commonly used in the art can be used in the method of the present invention. For example, expression systems that can be used to express proinsulin or insulin of the present invention include, but are not limited to, Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, baker's yeast, Pichia pastoris, insect cells and animal cells.
[0056] In a specific embodiment, the human proinsulin gene sequence with...
Embodiment 1
[0073] 1. Experimental materials:
[0074] The biological carrier-Escherichia coli mutant strain BL21 (DE3) used to express proinsulin and the deoxynucleic acid polymerase Platinum Pfx used for DNA amplification were purchased from Invitrogen;
[0075] The endodeoxynuclease-NdeI and SacI used for plasmid construction, calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase-CIP, deoxynucleic acid ligase-T4 DNA ligase, deoxynucleic acid molecular ruler, and protein molecular ruler were purchased from NEB Biolabs;
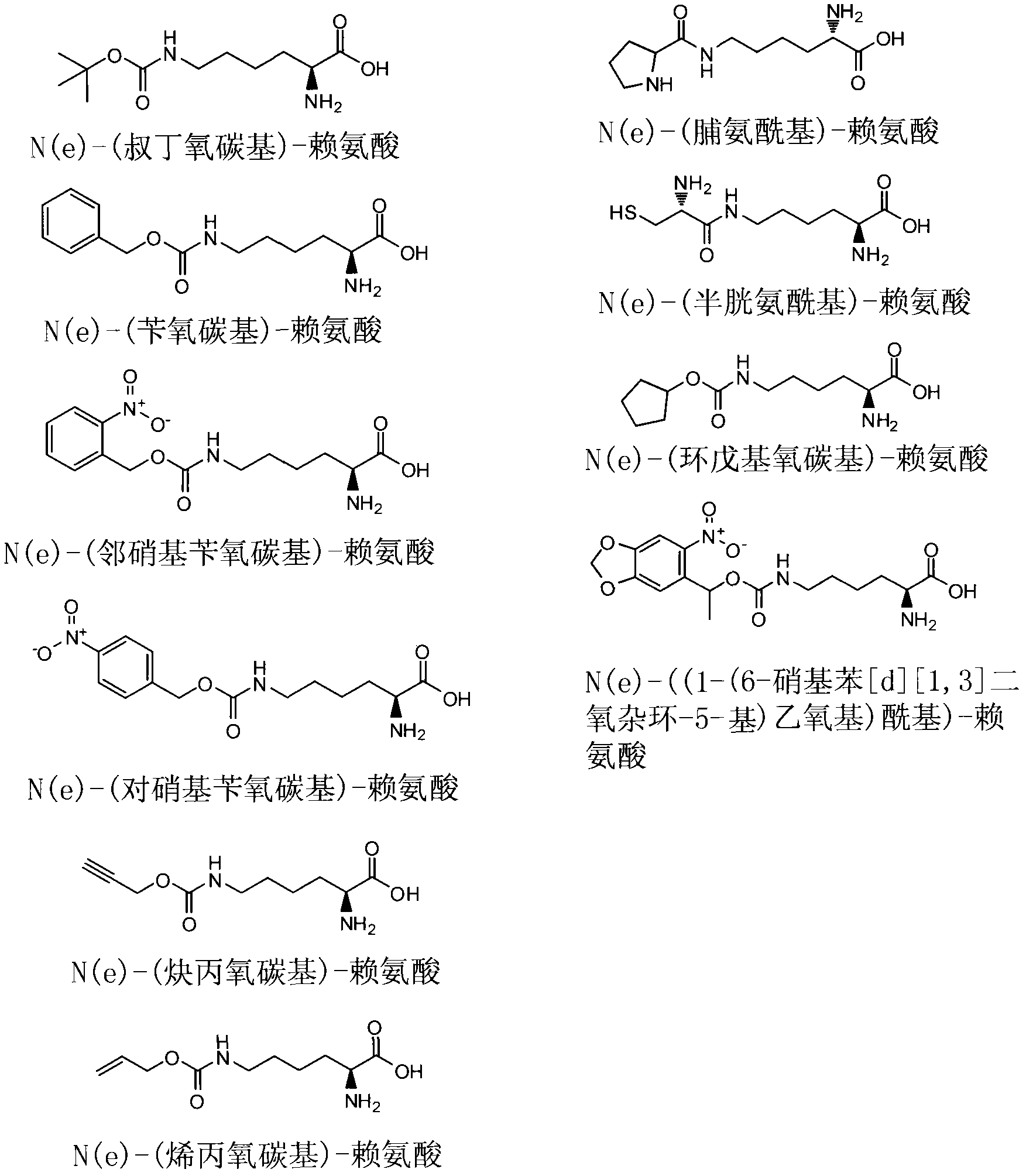
[0076] LB medium and Nε-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-lysine were purchased from Sigma;
[0077] Kits for plasmid mini-extraction were purchased from Qiagen.
[0078] Other reagents not identified were from VWR.
[0079] 2. Experimental method:
[0080] 1. Plasmid construction
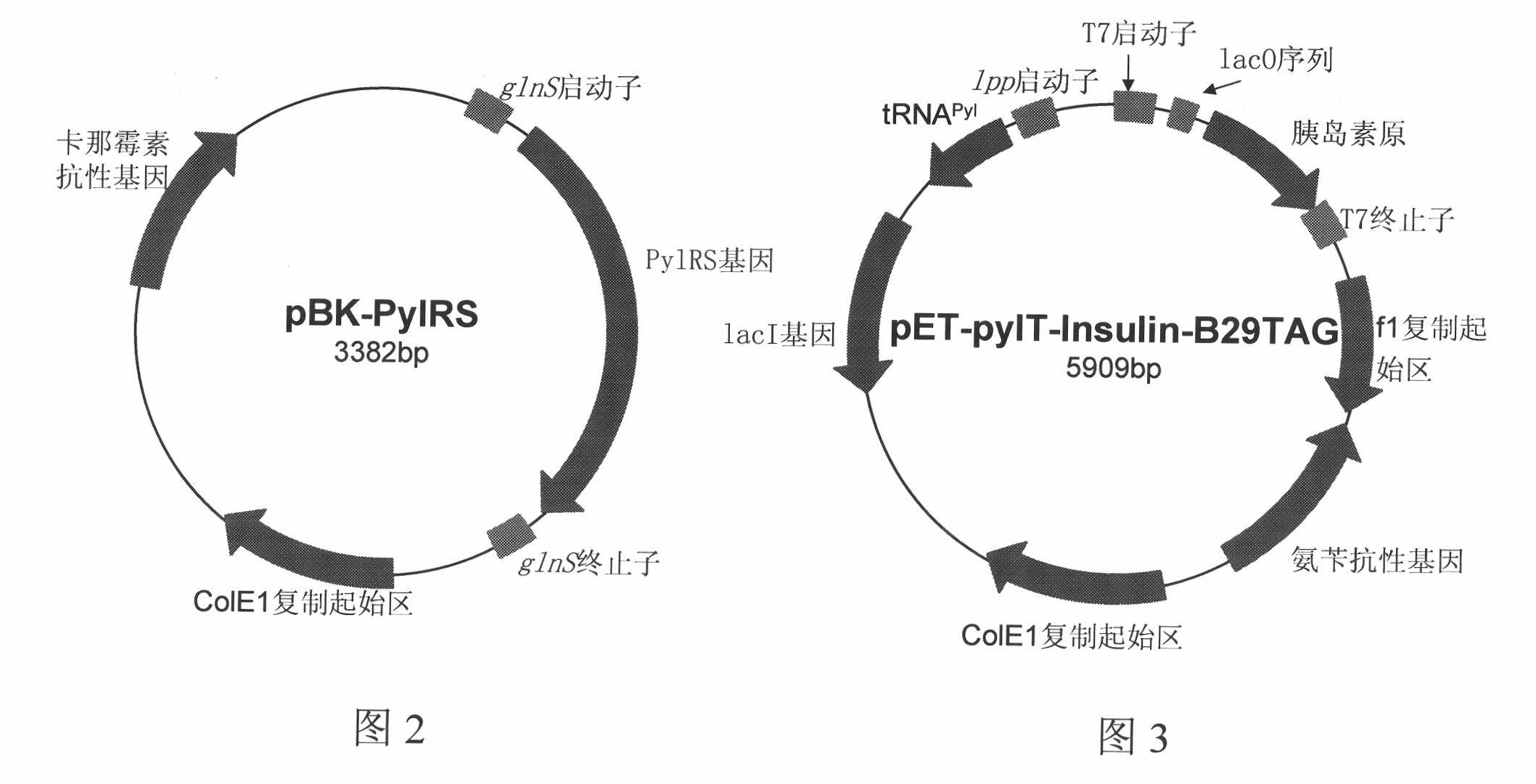
[0081] Two plasmids for expressing human proinsulin with Nε-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-lysine at position 29 of proinsulin in Escherichia coli variant BL21(DE3) are as follows: figure 2 and image 3 As shown (the cons...
Embodiment 2
[0101] In this example, the steps of Example 1 were repeated with the same operation, except that the amber codon UAG in Example 1 was replaced with ocher codon UAA; UUA Instead of tRNA in Example 1 CUA ; Replace Nε-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-lysine in Example 1 with Nε-(benzyloxycarbonyl)-lysine; replace SEQ ID NO.5 with SEQ ID NO.9; replace SEQ ID NO.5 with SEQ ID NO.11 replaces SEQ ID NO.4; And the steps of removing Nε-(benzyloxycarbyl)-lysine from insulin are as follows: 0.1 M bromic acid (purchased from VWR) was added to the acid insulin solution, and ammonium bicarbonate was added after 2 hours to terminate the reaction.
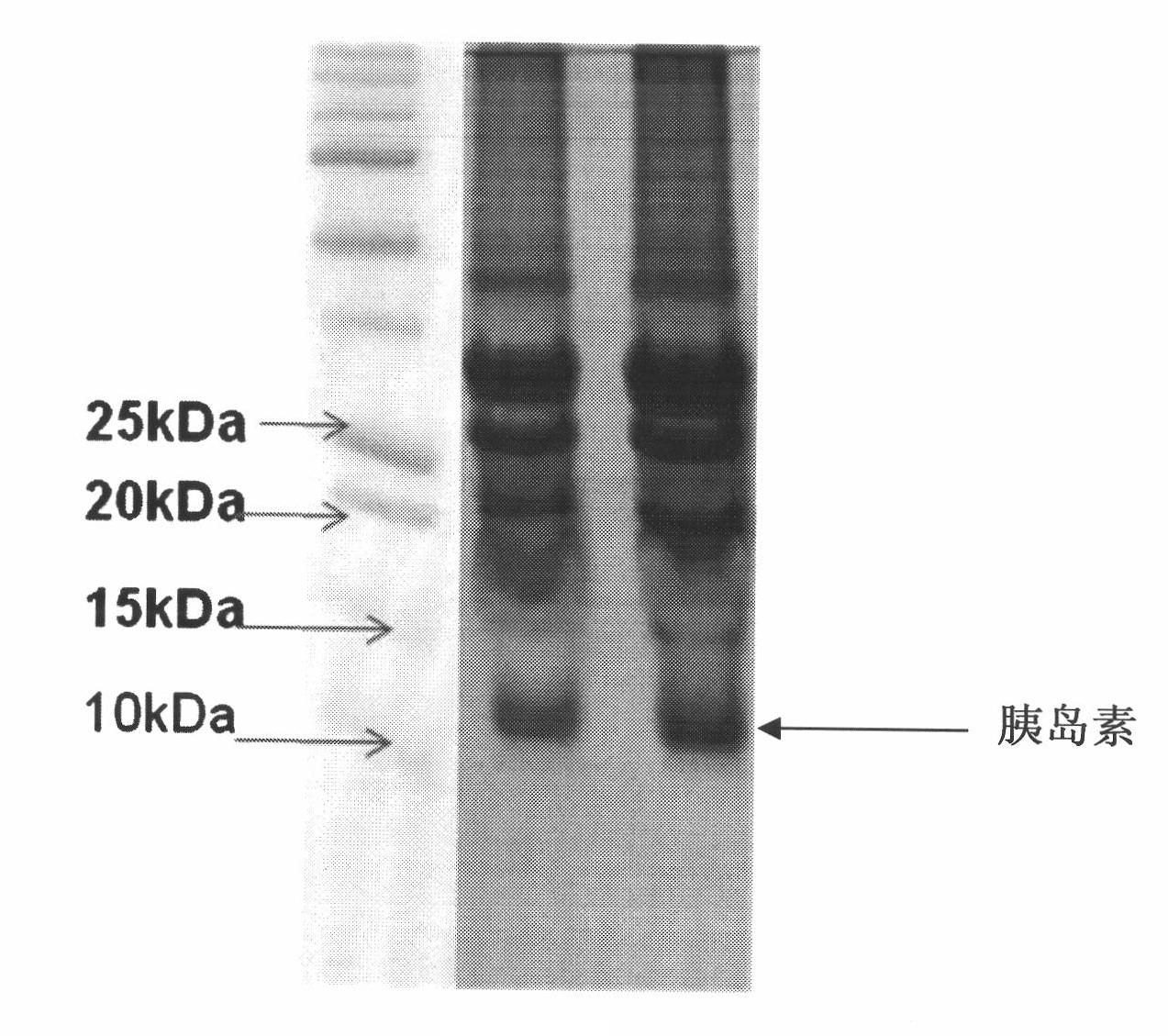
[0102] The results of this example were similar to those of Example 1. According to SDS-PAGE analysis and subsequent mass spectrometric analysis, the purity of the finally produced insulin reached 97%. The expression level of proinsulin measured by BCA protein concentration analysis of mature human insulin was 48 mg / L.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com