Application of snake venom-sourced cytotoxin-CTX1 to preparation of acute leukemia resisting medicine
A-CTX1, the technology of acute leukemia, applied in the application field of cytotoxin-CTX1 in the preparation of anti-acute leukemia drugs, to achieve the effects of being conducive to large-scale production, low toxicity and drug resistance, and a single component
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0026] The preparation and analysis of CTX1 has applied for related patents (cytotoxin derived from snake venom-CTX1 application in the preparation of detoxification drugs, application number: 200910215378.2)
[0027] The resulting amino acid sequence of CTX1 is:
[0028] LKCNKLIPIA SKTCPAGKNL CYKMFMMSDL TIPVKRGCID VCPKNSLLVKYVCCNTDRCN.
Embodiment 1
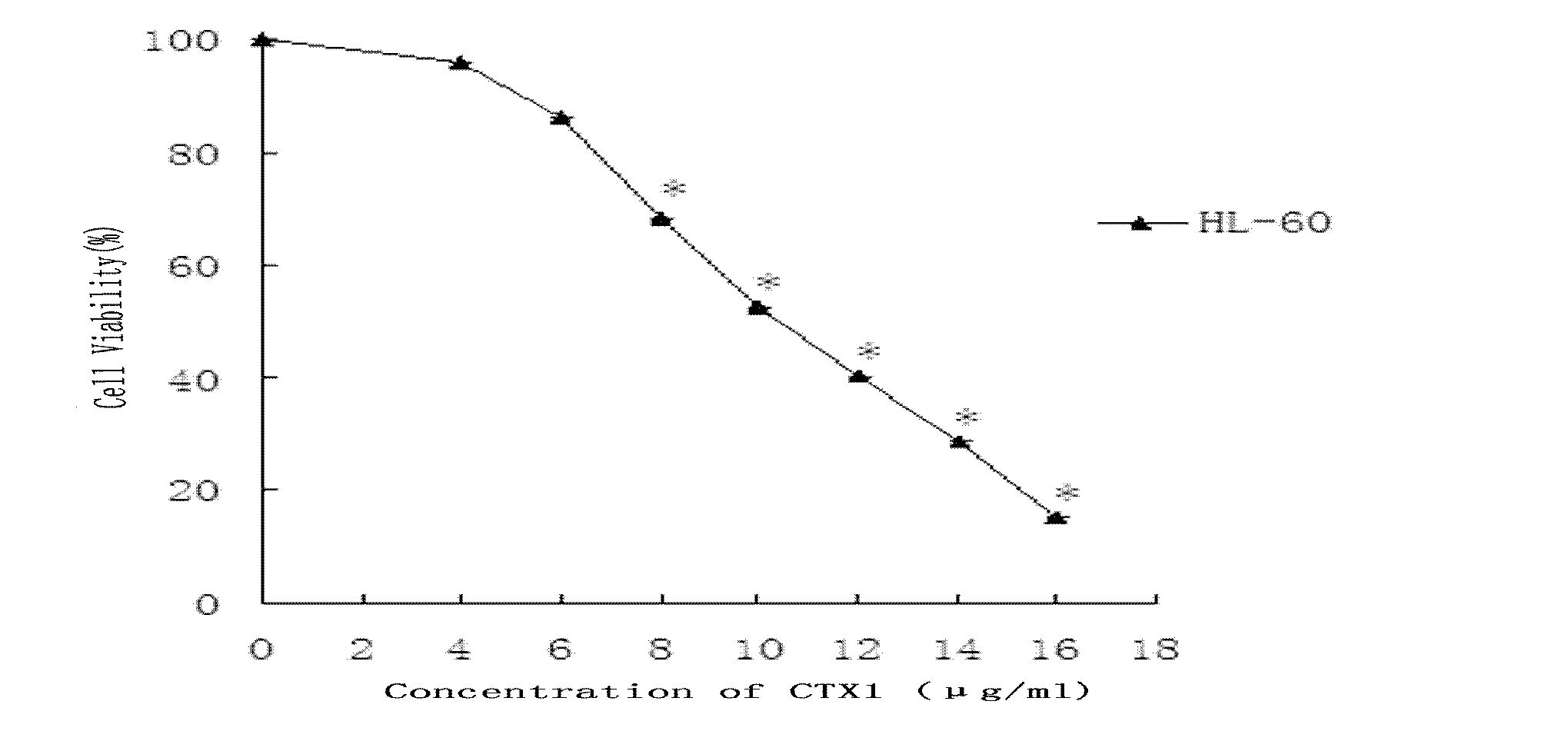
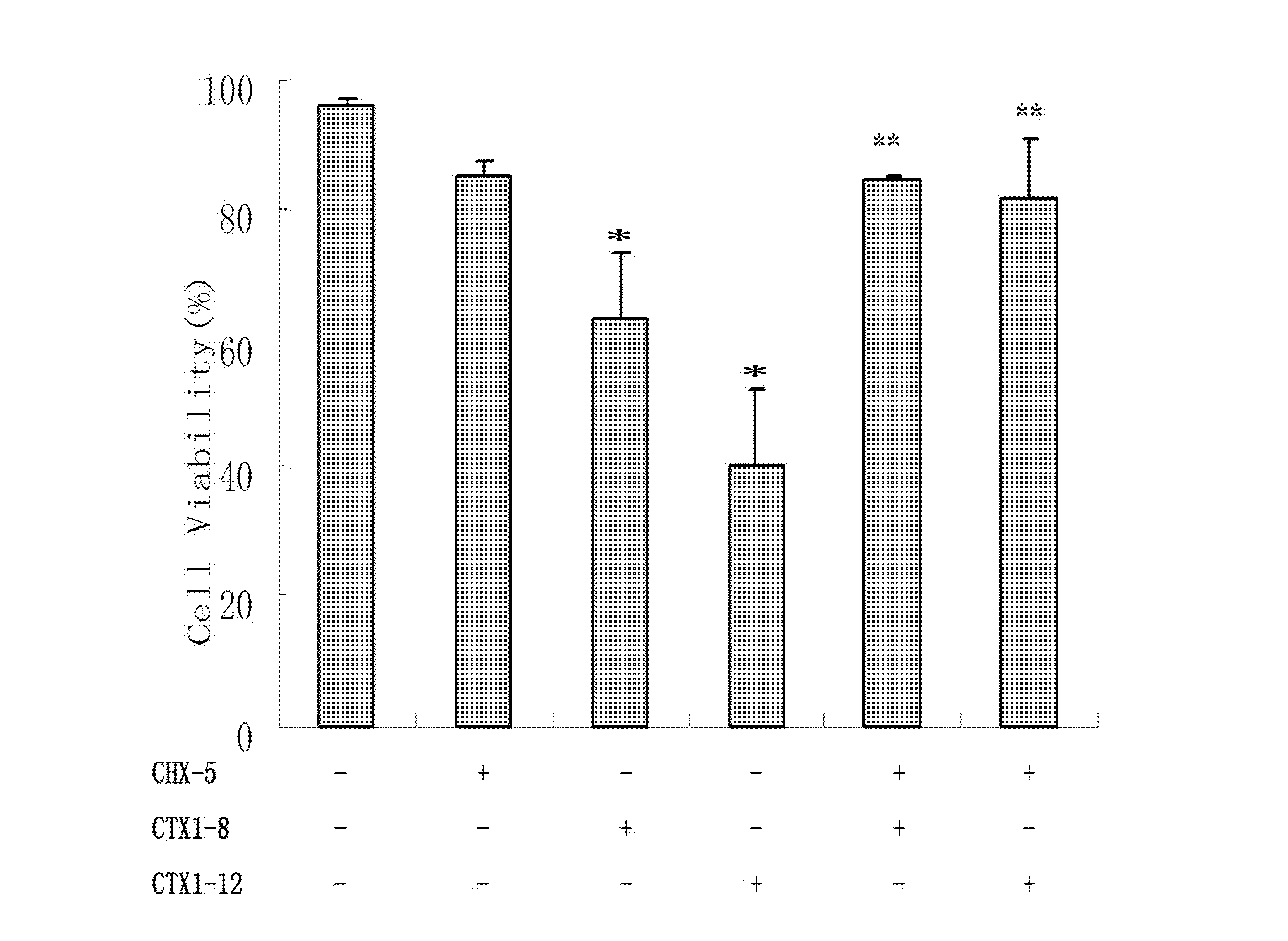
[0029] Example 1: MTS method detects the influence of CTX1 on the relative viability of HL-60 cells
[0030] HL-60 cells are grown in suspension, routinely cultured in RPMI1640 medium (penicillin 100U / ml, streptomycin 100U / ml) containing 10% fetal bovine serum, placed at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultured in a constant temperature incubator, subcultured every other day, and the cells in the logarithmic growth phase were used for experiments. Adjust the cell concentration, inoculate 95 μL of cell suspension in a 96-well plate according to 5000 cells per well, set different concentrations of CTX1 dose groups within the range of 4-16 μg / ml CTX1 concentration, add 5 μL of NS, 5 μL of different Concentration of CTX1, three parallel wells were set up for each group. After a certain period of drug action, 20 μL of MTS was added to each well, and incubated in an incubator in the dark for 4 hours, and the absorbance value of each group was measured with an automatic microplate reader at a detecti...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2: Detection of CTX1-induced HL-60 cell death by flow cytometry
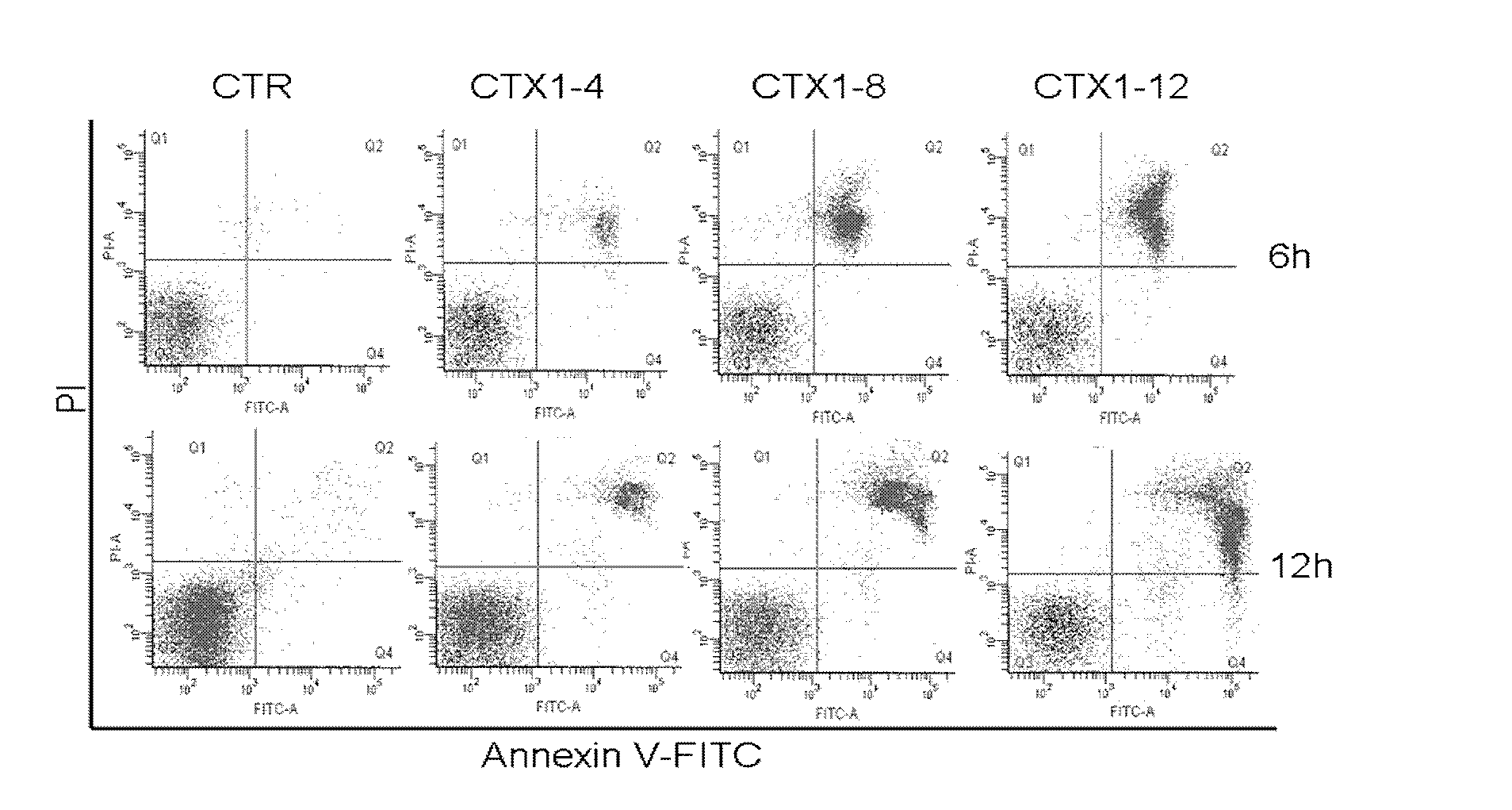
[0032] Take HL-60 cells in good logarithmic growth phase, adjust the cell concentration, inoculate the cell suspension in a 96-well plate (5000 cells / well) and add CTX1 (concentrations are 4 μg / ml, 8 μg / ml, 12 μg / ml). Collect the HL-60 cells treated with drugs for 6h and 12h respectively and centrifuge (1000rpm / 5min), wash the cells twice with PBS, discard the supernatant, and keep the cell pellet (1~5×10 5 ) cells, add 500 μL Binding buffer to resuspend the cells, add 5 μL Annexin V-FITC and mix well, then add 5 μL PI and mix well, react at room temperature in the dark for 5-15 minutes, and use flow cytometry to detect cell death within 1 hour.
[0033] Such as figure 2As shown, with the increase of CTX1 concentration and the prolongation of the action time, the cell death gradually increased, showing a dose-dependent and time-dependent relationship, and the dead cells were concentrated in th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com