New strains K05 and K03 of lentinus edodes and breeding method for strains
A new strain and strain technology, applied in the field of edible fungus breeding, can solve the problems of unstable transformants, over-density, and long-term use, and achieve obvious mutagenesis effects, improved production traits, and enhanced adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] 1. Materials and methods
[0029] 1.1 Materials
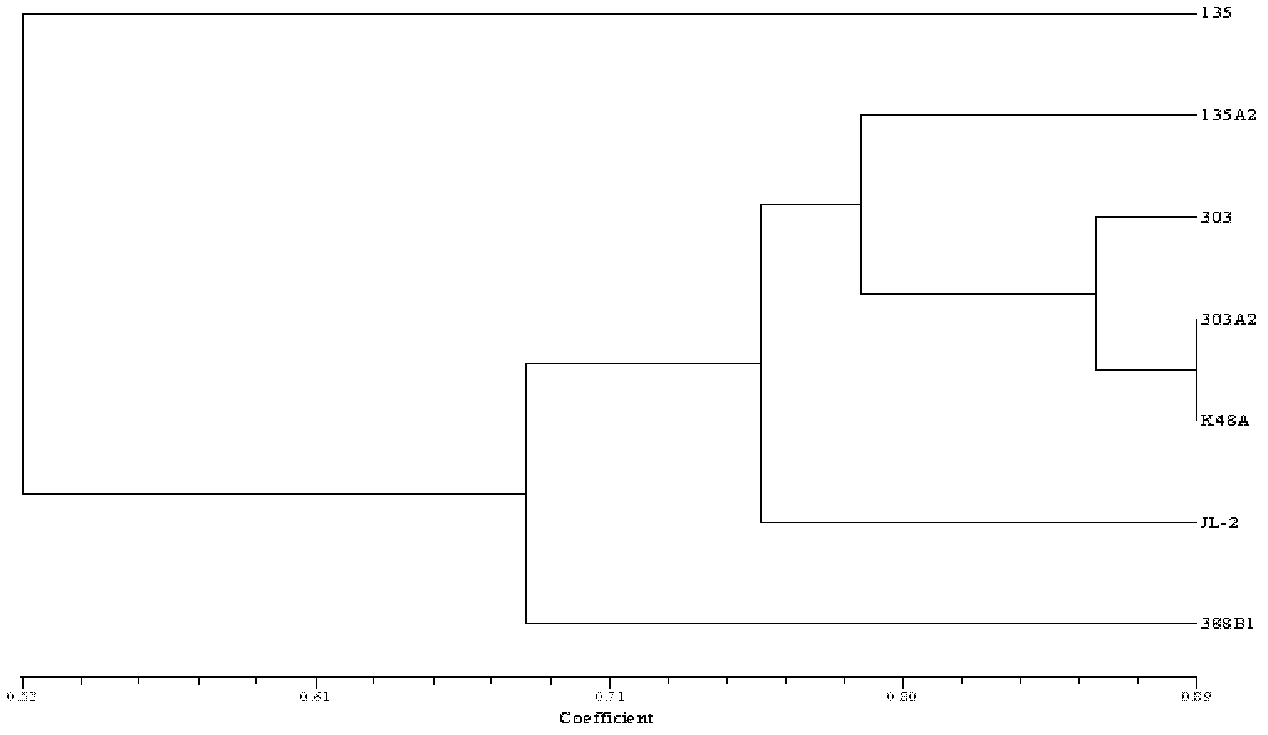
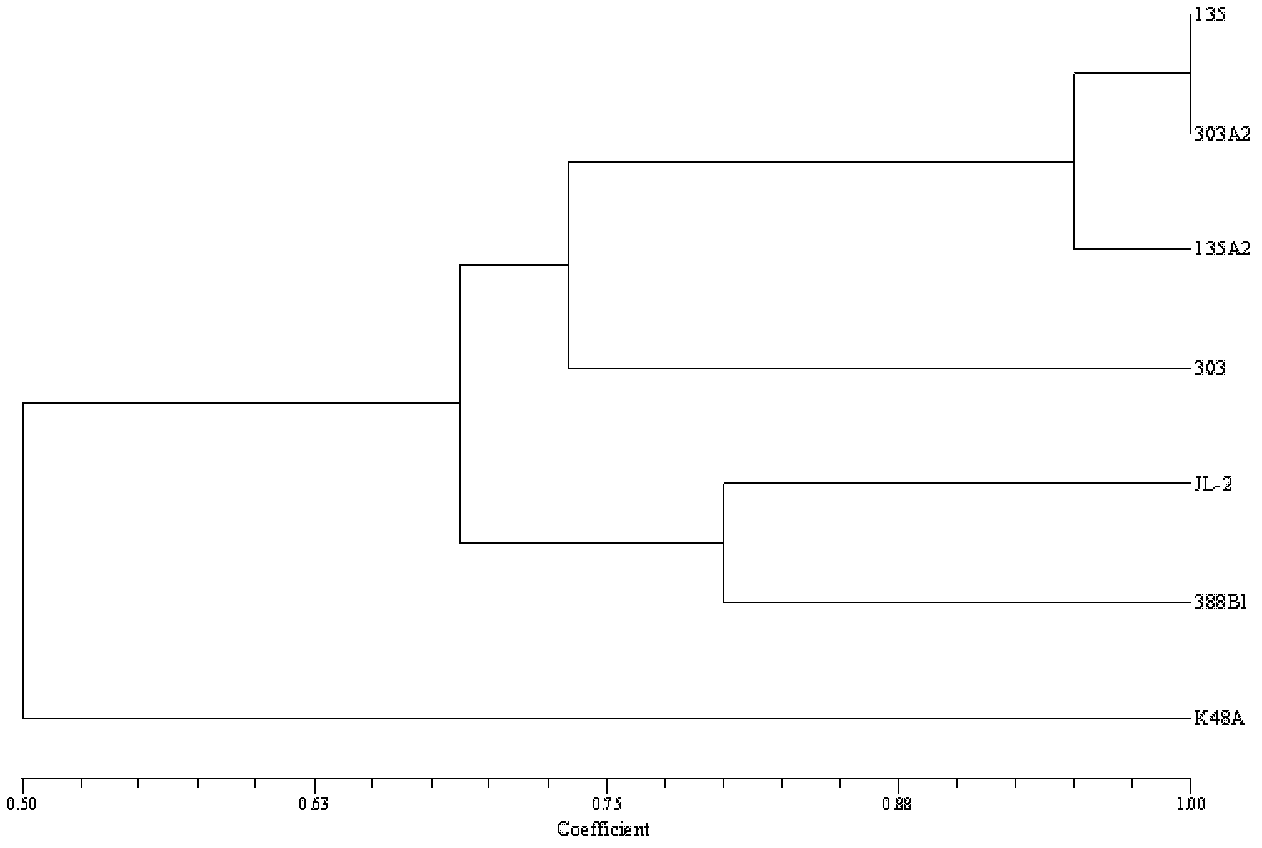
[0030] 1.1.1 Parental strains
[0031] Shiitake 135 (introduced by Sanming Institute of Fungi), Shiitake 303 (crossbreeding by our company).
[0032] 1.1.2 Medium
[0033] Test medium: PDA+20% fungus chaff boiled juice.
[0034] Mutation medium: PDA+0.1% colchicine.
[0035] Cultivation medium: miscellaneous sawdust 83%, bran 15%, sugar 1%, gypsum 1%.
[0036] 1.1.3 Main reagents
[0037] Colchicine (C22H25NO 5 ): 98% content, analytically pure, imported by Shanghai Huishi Biochemical Reagent Company.
[0038] Fluorescent dye: Hoechst33258 (trade name), bisbenzimidazole (C 25 h 24 N 5 o 13 HCL) chemical name, imported from Switzerland.
[0039] 1.2 Method
[0040] 1.2.1 Mutagenesis treatment of dikaryon strains
[0041] Dikaryon strains of Lentinus edodes 135 and 303 were respectively inoculated on slant medium containing 0.1% colchicine, cultured in a constant temperature incubator at 25°C, and each strain...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com