Method for detecting residuals of sulfanilamides or fluoroquinolones drugs
A technology for fluoroquinolones and sulfonamides, which is applied in the field of analytical chemistry, can solve the problems of few types of sulfonamides in separation, cumbersome detection steps, etc., and achieves the effect of satisfying daily rapid quantitative detection, fast analysis speed, and reducing purification procedures.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
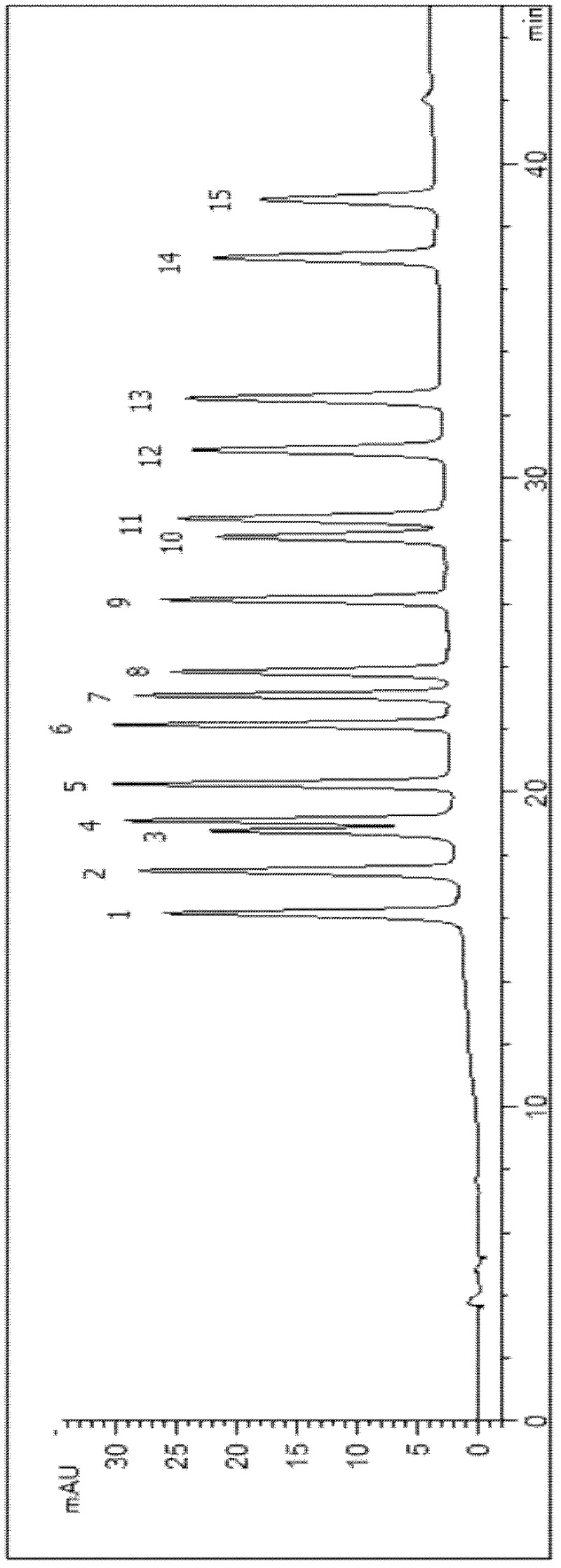
[0037] Specific Example 1: Separation and detection of sulfa antibiotic residues in pork
[0038] Take 5g of pork tissue, add 20mL of acetonitrile to homogenate, centrifuge at a centrifugal force of 10,000×g for 5min after homogenization, recover the supernatant, evaporate to dryness on a rotary evaporator, dissolve with 0.5mL of acetonitrile, wash repeatedly, and then purify the sample with nitrogen Blow dry, and finally dissolve the sample with 1 mL of acetonitrile (other well-known organic solvents can also be used to make up the volume), filter through a 0.45 μm filter membrane, and carry out chromatographic analysis and quantification.
[0039] Chromatographic separation conditions: high performance liquid chromatography; reversed-phase chromatographic column (4.6mm I.D.×250mm); flow rate: 0.8mL / min; temperature: room temperature; eluent: A: 0.1% formic acid solution; B: acetonitrile; C: 0.01mol / L ammonium acetate solution; detection wavelength is 270nm (adopted the maxim...
specific Embodiment 2
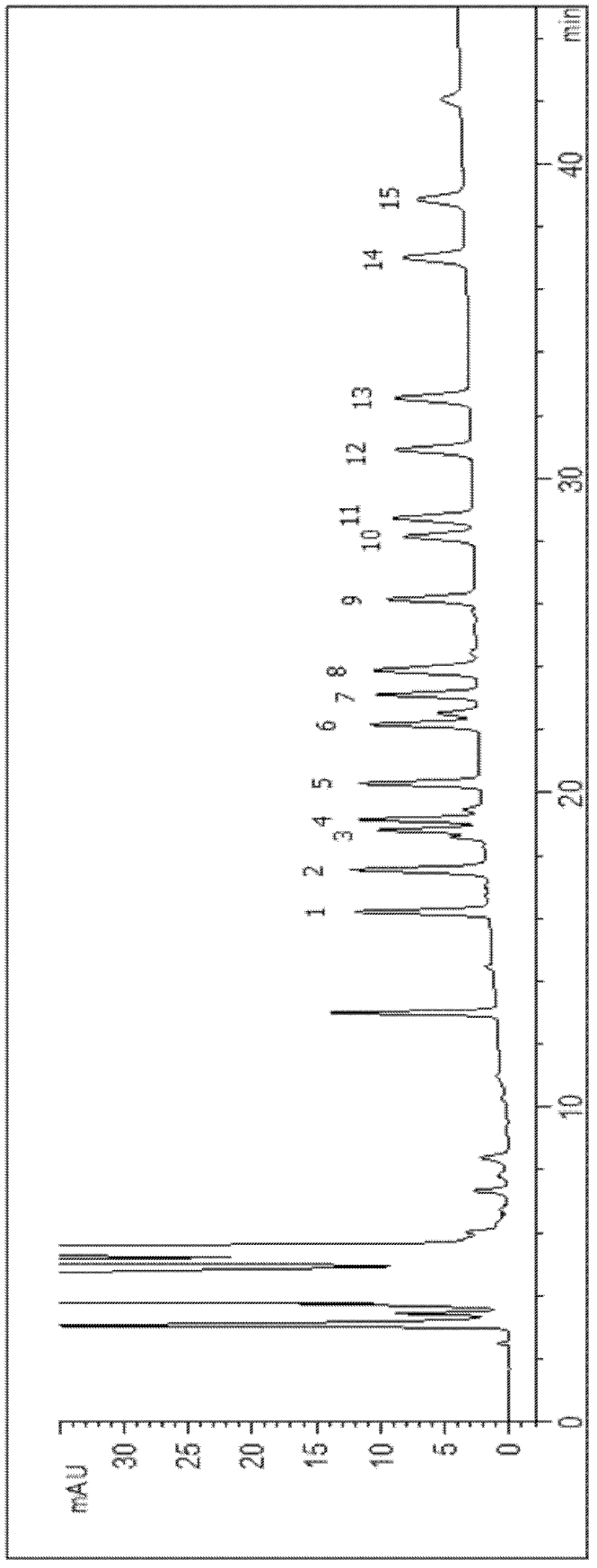
[0043] Specific Example 2: Separation and detection of sulfonamide antibiotic residues in milk
[0044] Take 0.45mL of milk, add 0.5mL of trichloroacetic acid (1g / mL) to precipitate the protein in it, then centrifuge at 10,000×g for 5min, recover the supernatant, and re-dilute to 5mL with acetonitrile (other known organic solvents can also be used to dilute to 5mL). Volume), 0.45μm membrane filtration, chromatographic analysis and quantification.
[0045] Chromatographic separation conditions: high performance liquid chromatography; reversed-phase chromatographic column (4.6mm I.D. × 250mm); flow rate: 0.8mL / min; temperature: room temperature; eluent: A: 0.06% acetic acid solution; B: acetonitrile; C: 0.015mol / L sodium acetate solution; the detection wavelength is 270nm, and the gradient ratio during separation is shown in the table below:
[0046] Chromatographic gradient ratio when table 2 separates sulfonamides
[0047]
[0048]
[0049] After the separation is comp...
specific Embodiment 3
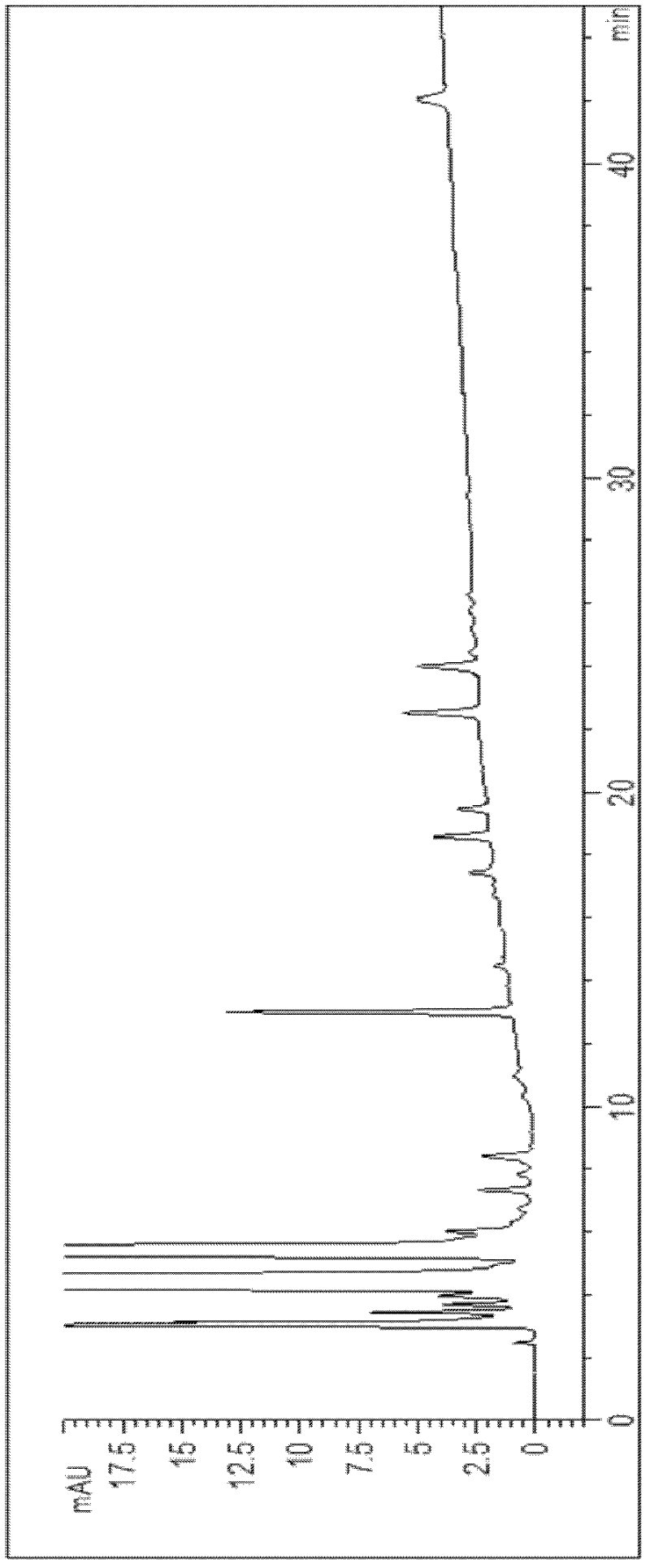
[0050] Specific Example 3: Separation and detection of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in beef
[0051] Take 2g of beef tissue, add 10mL 50mmol / L phosphate for homogenization, centrifuge at 10,000×g for 5min after homogenization, recover the supernatant, evaporate to dryness on a rotary evaporator, and use 0.05mol / L phosphoric acid solution / triethylamine- Acetonitrile (82:18, volume ratio) was dissolved, and the volume was adjusted to 1 mL, and chromatographic analysis and quantification were carried out after filtration with a 0.45 μm filter membrane.
[0052] Chromatographic gradient ratio when table 3 separates sulfonamides
[0053]
[0054] After the separation is completed, the area of the separated residual sulfonamide antibiotics is integrated, and quantitative calculation is performed based on the standard curve prepared by the standard to obtain the residual content. The standard curve made of the standard substance mentioned here should also adopt the same chromato...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com