Chromium- and fluorine-free chemical conversion treatment solution for metal surfaces, metal surface treatment method, and metal surface coating method
A technology for chemical conversion treatment and metal surface treatment. It is used in devices for coating liquid on surfaces, metal material coating processes, and surface pretreatment. It can solve problems such as inability to remove fluorine components and achieve excellent corrosion resistance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
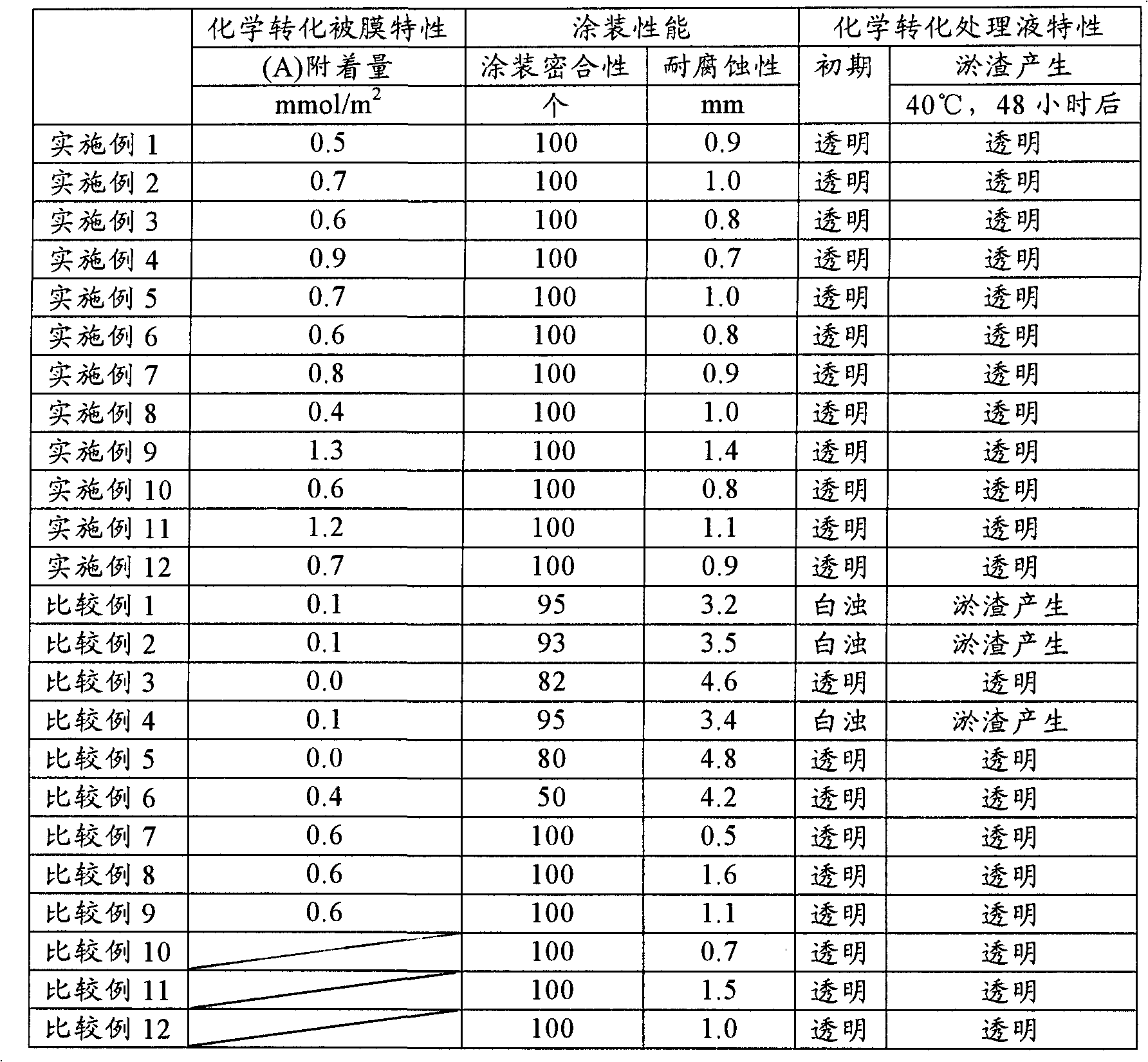
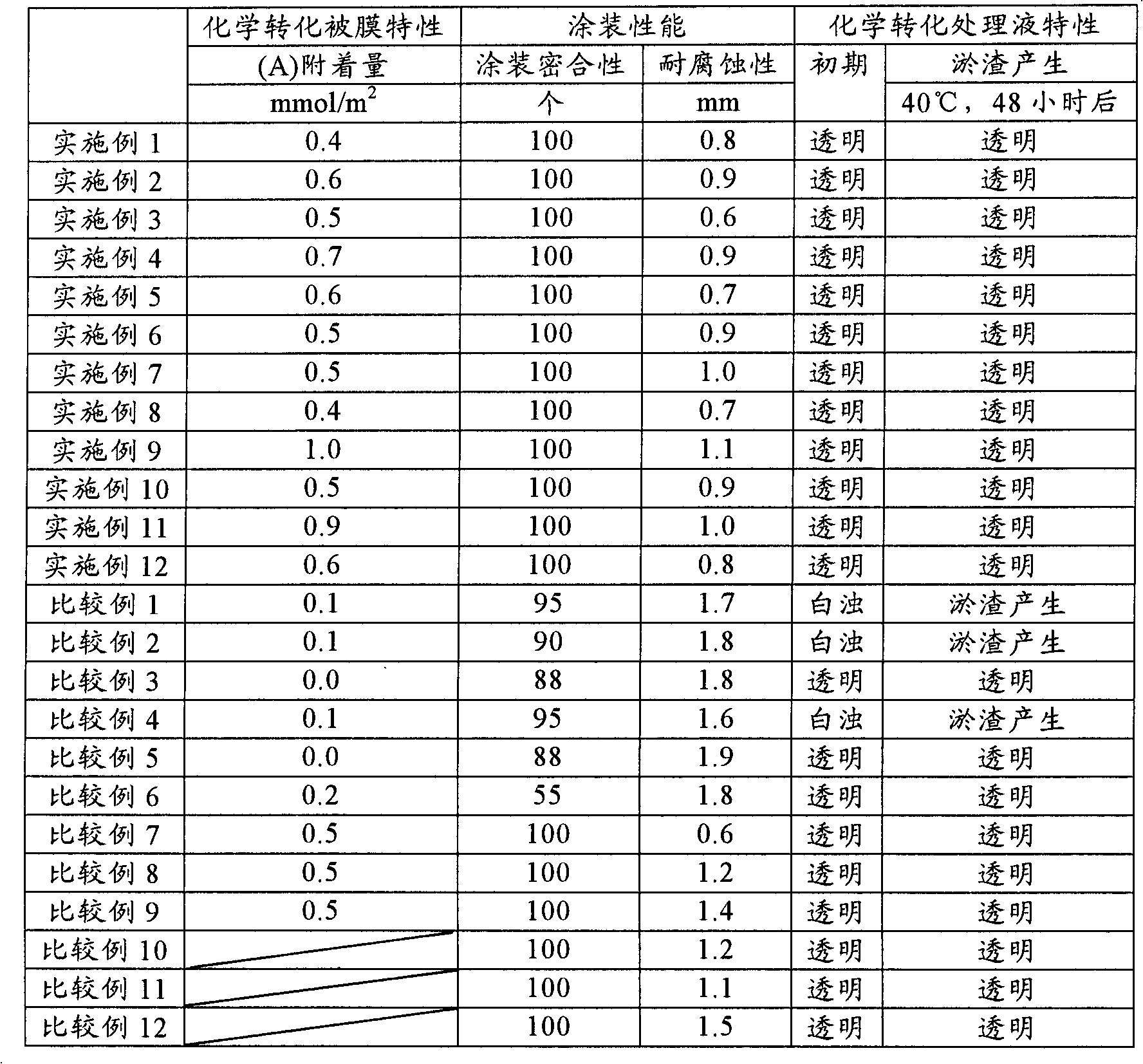
Examples
preparation example Construction
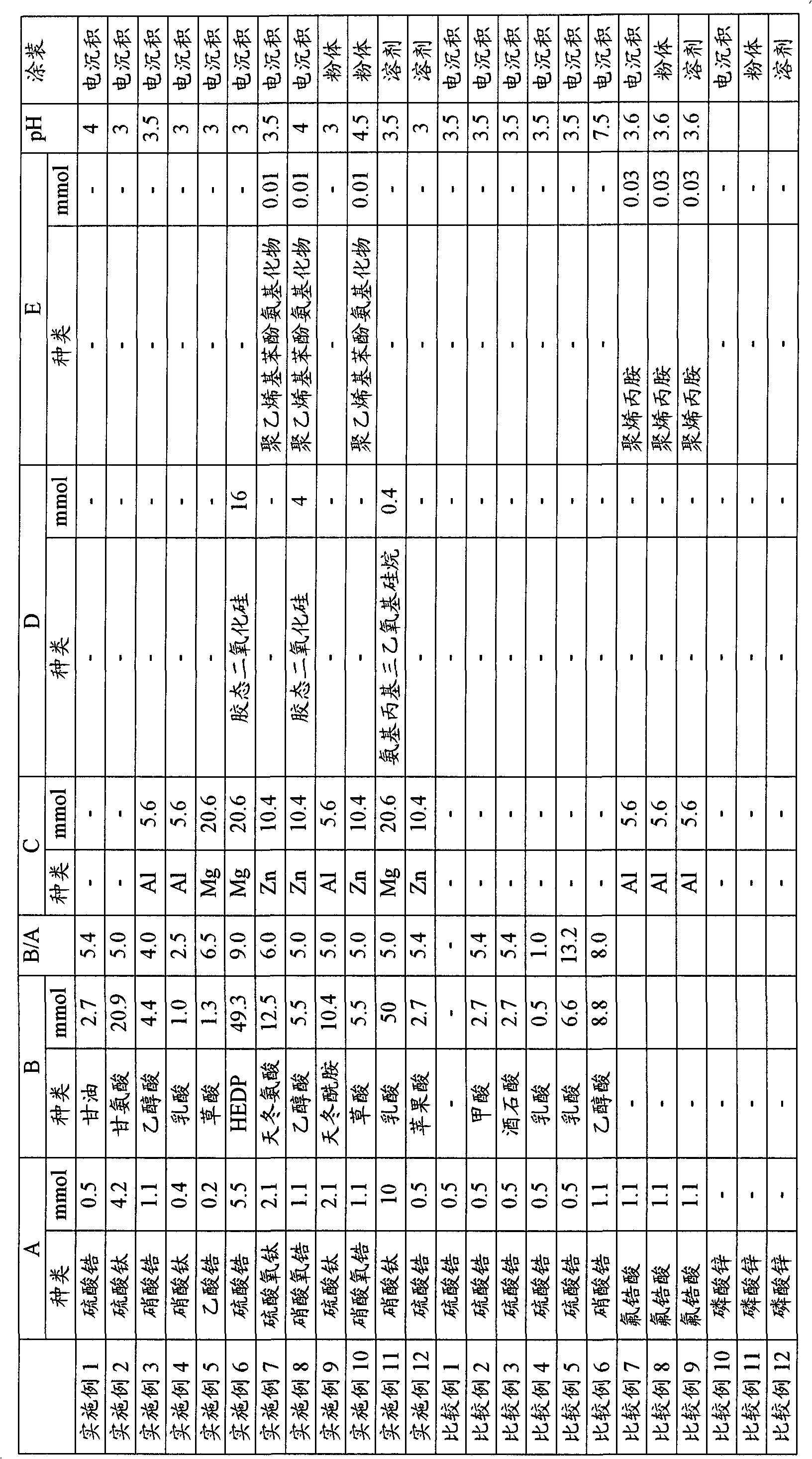
[0063] The method for preparing the chemical conversion treatment liquid of the present invention is not particularly limited, and it is prepared by adding essential components (A), (B) and optional components (C) to (D) to an aqueous solvent in any order. A preferable preparation method is, for example, a method of adding essential components and then optional components in an aqueous solvent, stirring and mixing at room temperature, and adjusting pH after heating.
[0064] The pH of the chemical conversion treatment solution of the present invention is extremely important, and must be controlled within the range of 2.0 to 6.5. If the pH is less than 2.0, the dissolved amount of the metal base material will increase and sludge will increase, which is not preferable. If the pH exceeds 6.5, the ability to remove the oxide film on the surface of the metal base material is poor, and corrosion resistance and coating film adhesion may be reduced, which is not preferable. A more pr...
Embodiment 1
[0099] The following components (A) to (B) were sequentially added to water at the following concentrations, and stirred at room temperature for 20 minutes. Next, the temperature was raised to 45° C., and the pH was adjusted to 4.0 with aqueous ammonia to prepare a chemical conversion treatment solution 1 . Using the chemical conversion treatment solution 1, the surface treatment of the cleaned metal substrate was performed under the surface treatment condition 1 to form a chemical conversion treatment film. Then, the surface of the metal substrate was washed with water or deionized water, but without drying, electrodeposition coating was performed to form a coating film.
[0100] (A): Zirconium sulfate: 0.5mmol / L
[0101] (B): Glycerin: 2.7mmol / L
[0102] (C)(D)(E): None
Embodiment 2
[0104] The following components (A) to (B) were sequentially added to water at the following concentrations, and stirred at room temperature for 20 minutes. Next, the temperature was raised to 50° C., and the pH was adjusted to 3.0 with aqueous ammonia to prepare a chemical conversion treatment liquid 2 . Using the chemical conversion treatment solution 2, the surface treatment of the cleaned metal base material was performed under the surface treatment condition 3 to form a chemical conversion treatment film. Then, the surface of the metal substrate was washed with water or deionized water, but without drying, electrodeposition coating was performed to form a coating film.
[0105] (A): Titanium sulfate: 4.2mmol / L
[0106] (B): Glycerin: 20.9mmol / L
[0107] (C)(D)(E): None
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| coating thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| coating thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com