Method for advanced treatment of coking wastewater
A coking wastewater and advanced treatment technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, multi-stage water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve problems such as poor results, failure to meet national discharge standards, high treatment costs, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of benefiting redox reaction, reducing COD and chroma, and strong coagulation adsorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
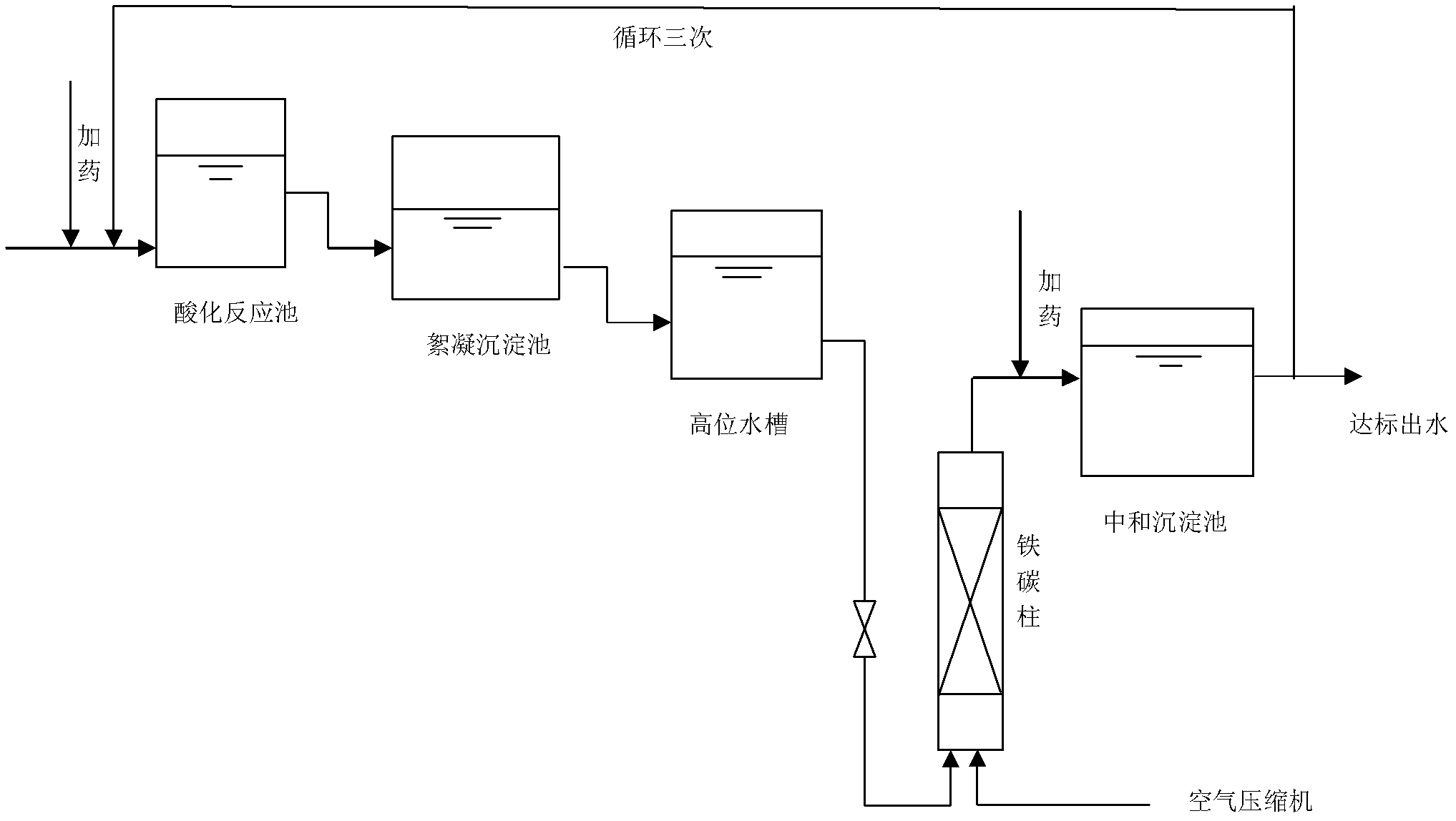
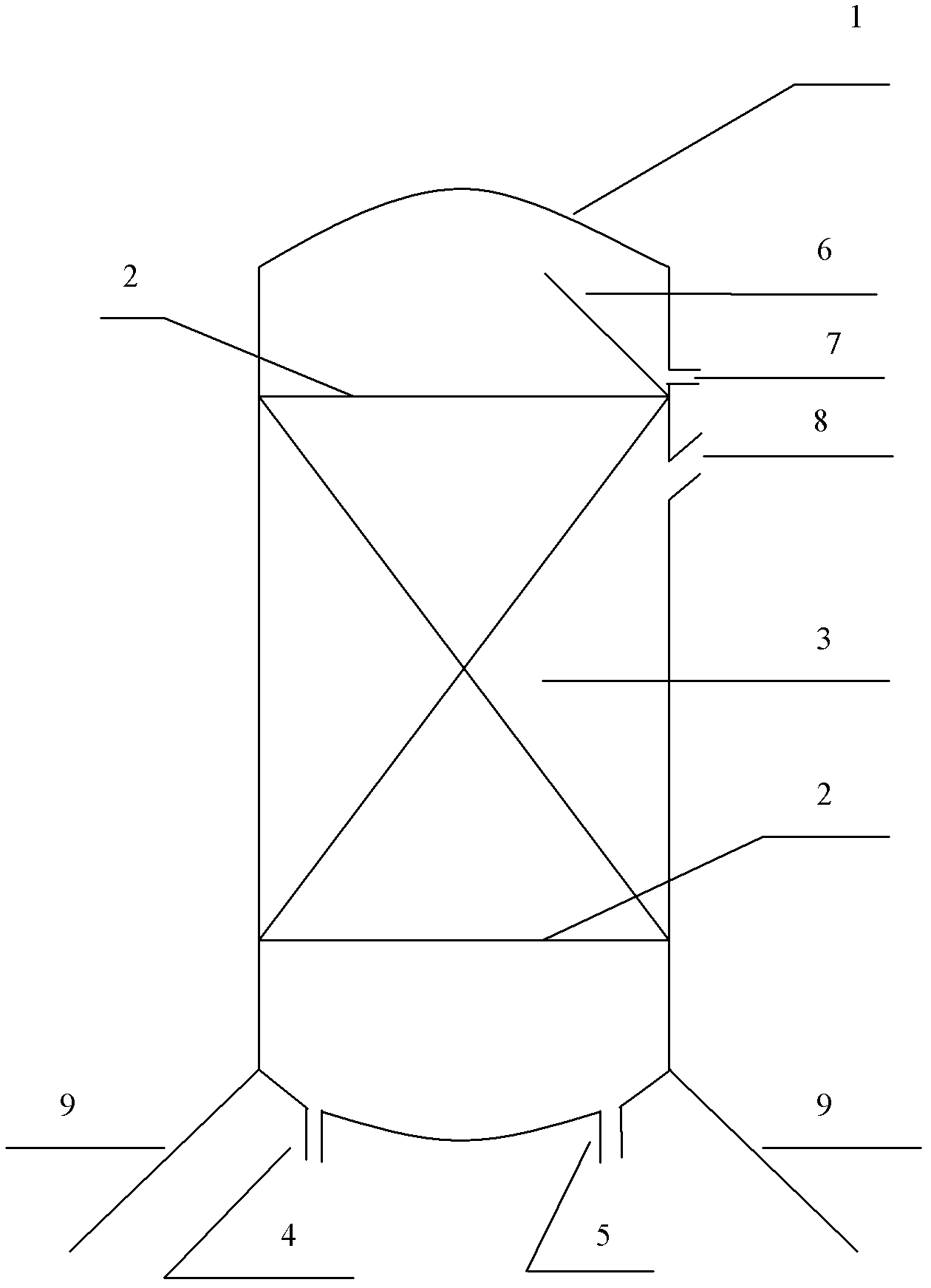
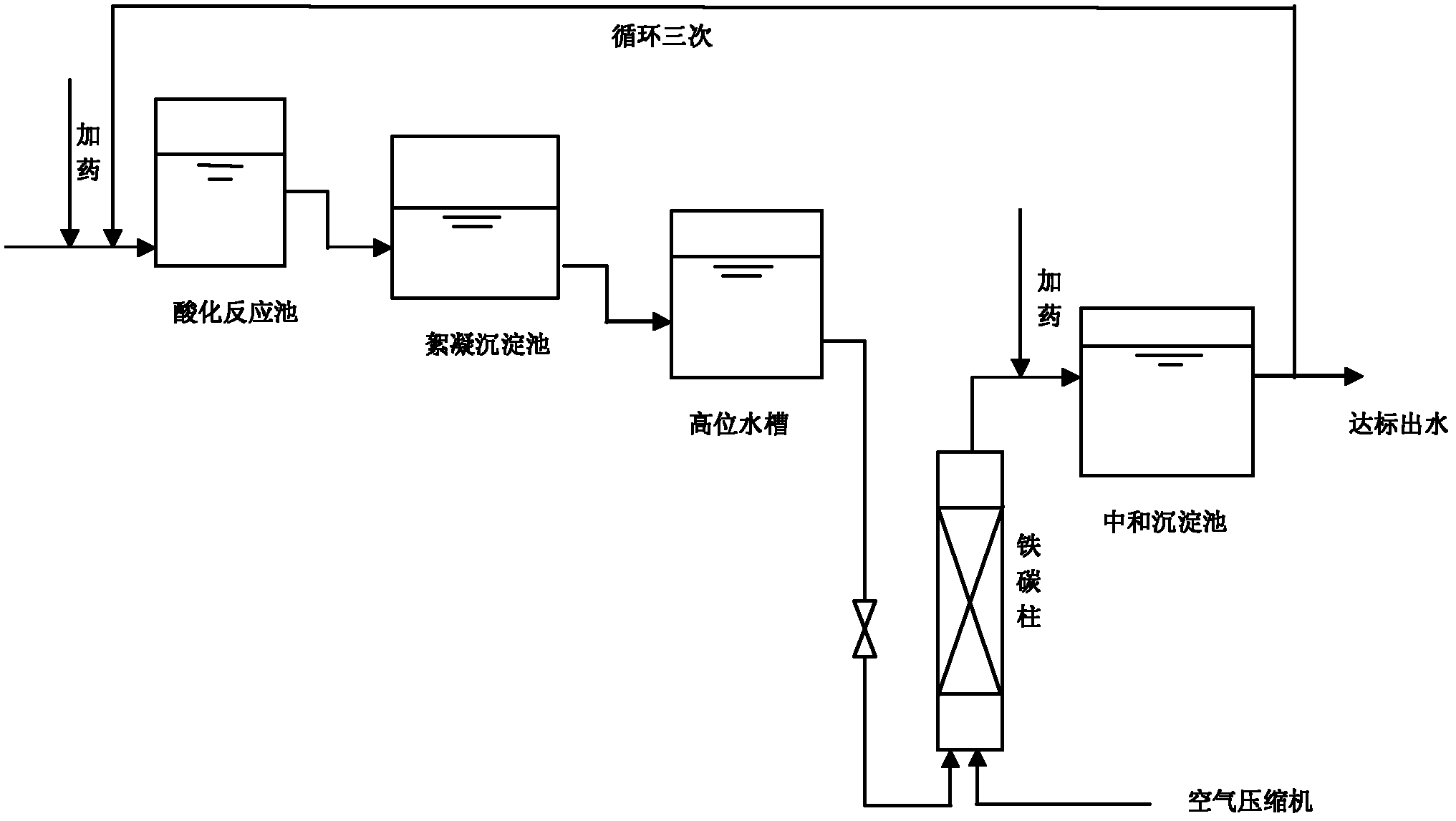
[0027] Example 1: Take some scrap iron filings, soak them with dilute sulfuric acid to remove oxides on their surfaces, then soak them in dilute NaOH solution to remove oil stains on their surfaces, and then fully wash the iron filings with clean water. Crush the coke into a particle size close to that of iron filings, take the processed iron filings, and then mix them evenly according to the ratio of iron filings and coke at a ratio of 10:1 (volume ratio), and pack them into a column. The coking wastewater after the secondary biochemical treatment enters the acidification treatment tank, where concentrated H 2 SO 4 Adjust the pH of the solution to about 3, let it settle, and the supernatant enters the flocculation tank, and add flocculant FeCl at 3g / L 3, let it settle down, and the supernatant enters the high-level water tank in a countercurrent manner, that is, water enters from the bottom of the column, and the water exits from the upper part, and adjust the flow rate of t...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2: Take some scrap iron filings, soak them with dilute sulfuric acid to remove oxides on their surfaces, then soak them in dilute NaOH solution to remove oil stains on their surfaces, and then fully wash the iron filings with clean water. Crush the coke into a particle size close to that of iron filings, take the processed iron filings, and then mix them evenly according to the ratio of iron filings and coke at a ratio of 10:1 (volume ratio), and pack them into a column. The coking wastewater after the secondary biochemical treatment enters the acidification treatment tank, where concentrated H 2 SO 4 Adjust the pH of the solution to about 2, let it settle, and the supernatant enters the flocculation tank, and add flocculant FeCl at 2.5g / L 3 , set aside to settle, and the supernatant enters the high-level water tank in a countercurrent manner, that is, the water enters from the bottom of the column and the water exits from the upper part, and the flow rate of t...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Example 3: Take some scrap iron filings, soak them with dilute sulfuric acid to remove oxides on their surfaces, then soak them in dilute NaOH solution to remove oil stains on their surfaces, and then fully wash the iron filings with clean water. Crush the coke into a particle size close to that of iron filings, take the processed iron filings, and then mix them evenly according to the ratio of iron filings and coke at a ratio of 10:1 (volume ratio), and pack them into a column. The coking wastewater after the secondary biochemical treatment enters the acidification treatment tank, where concentrated H 2 SO 4 Adjust the pH of the solution to about 3.5, let it settle, and the supernatant enters the flocculation tank, and add flocculant FeCl at 5g / L 3 , set aside to settle, and the supernatant enters the high-level water tank in a counter-current manner, that is, water enters from the bottom of the column, and the water exits from the upper part, and the flow rate of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com