Extraction method for chlorella vulgaris metallothioneins with whitening functions
A metallothionein and extraction method technology, which is applied in the field of chlorella metallothionein extraction, can solve the problems of difficulty in microbial culture and protein separation and extraction, high production cost, and non-compliance with animal protection requirements.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
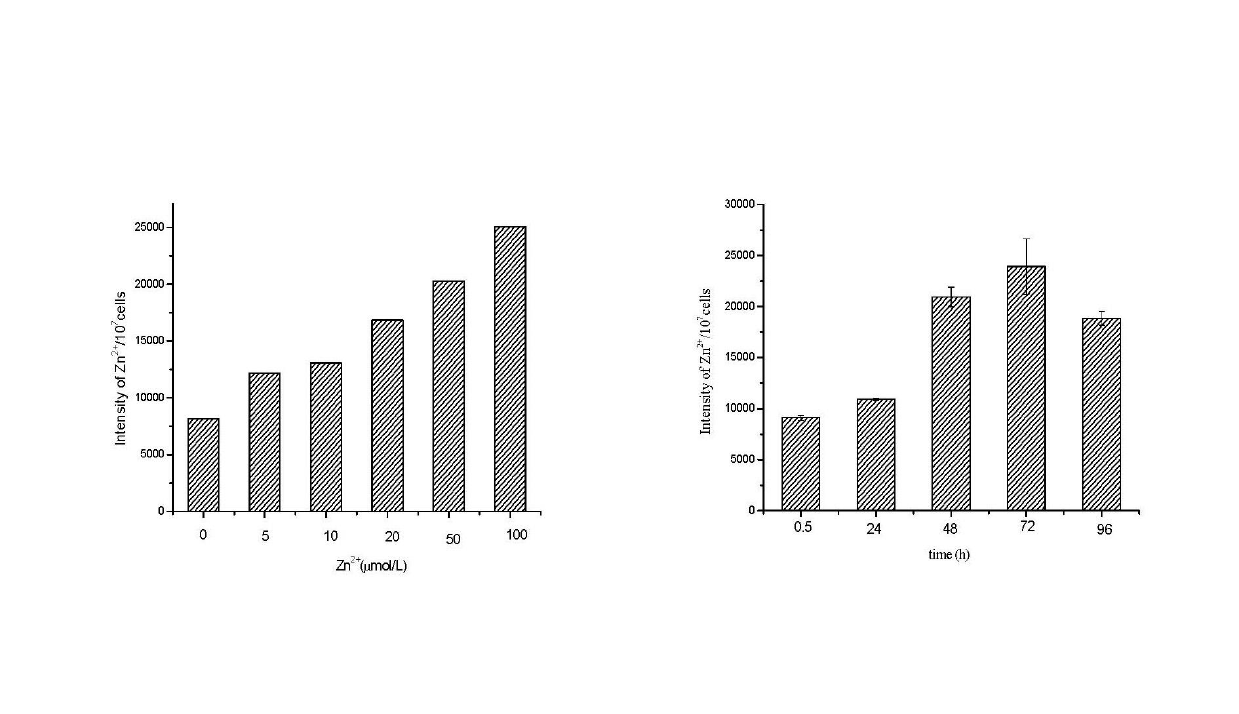
[0025] 1) Add 0.05 mol / L zinc chloride to the algae liquid of Chlorella in the logarithmic growth phase, control the final concentration of zinc in the algae liquid within the range of 5-100 μmol / L, and continue to cultivate Chlorella 24- 120 h, during the cultivation process, the flasks were manually shaken 5 times a day, each time for about 3 min. Take 100 mL of each chlorella liquid in the culture group, centrifuge at 10000 r / min, collect the algal cells, wash the algal cells twice with 5 mmol / L EDTA-2Na and ultrapure water respectively, add 10 mmol / L Tris-HCl With 5 mL of buffer solution, the algal cells were disrupted by ultrasonic wave in ice bath for 5 min, centrifuged at 12000 r / min for 10 min, and the supernatant was collected.
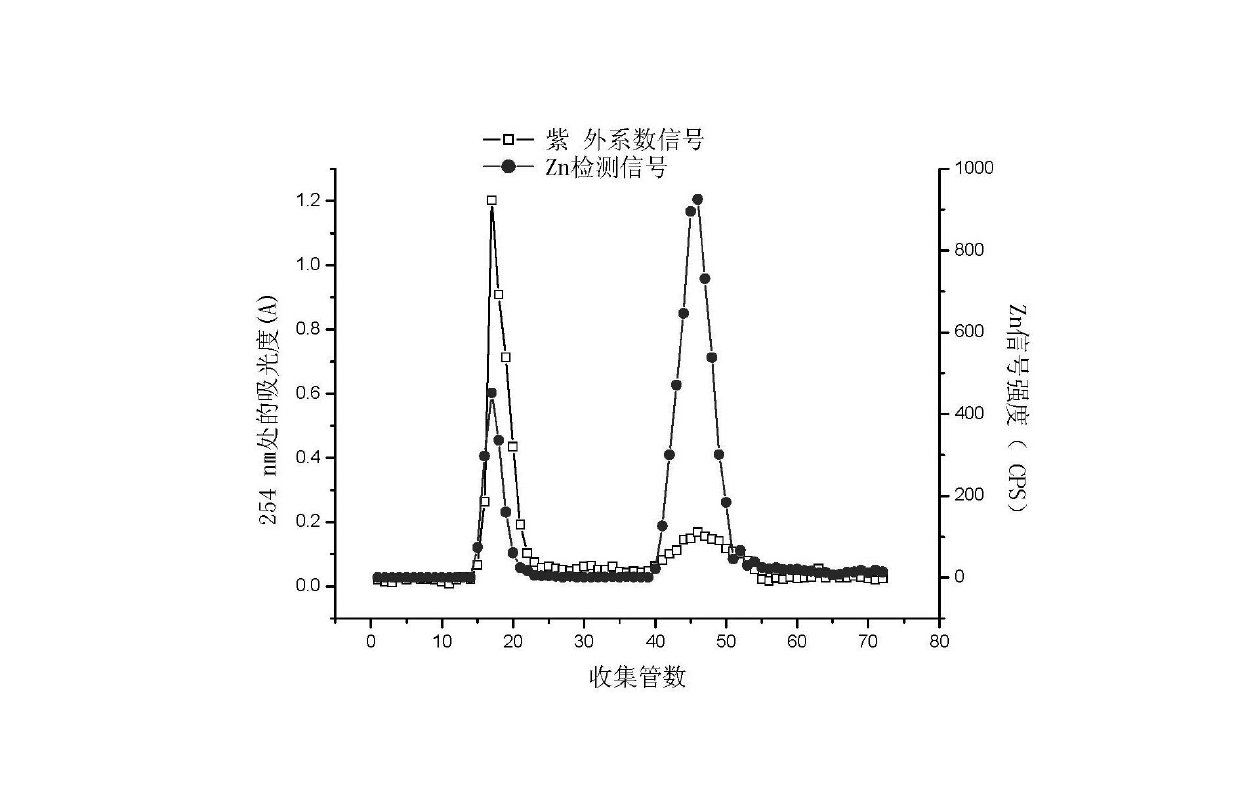
[0026] 2) Chromatographic separation was performed using a TSK-gel column (G3000PWxl, 7.8 mm i.d.×300 mm, 6 μm), with 10 mmol / L Tris-HCl buffer as the mobile phase, and the eluate was passed through inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometr...
Embodiment 2
[0032] 1) Add ZnCl to Chlorella in logarithmic growth phase 2 , so that the final concentration of zinc in the algae liquid reached 50 μmol / L, and aerated for 72 hours.
[0033] 2) Algae cells were collected by centrifugation. After repeated freezing and thawing for 5 times, the cells were disrupted by ultrasonic waves, and the supernatant was collected by centrifugation at 12000 r / min for 10 min.
[0034] 3) Same as steps (4) and (5) in Example 1
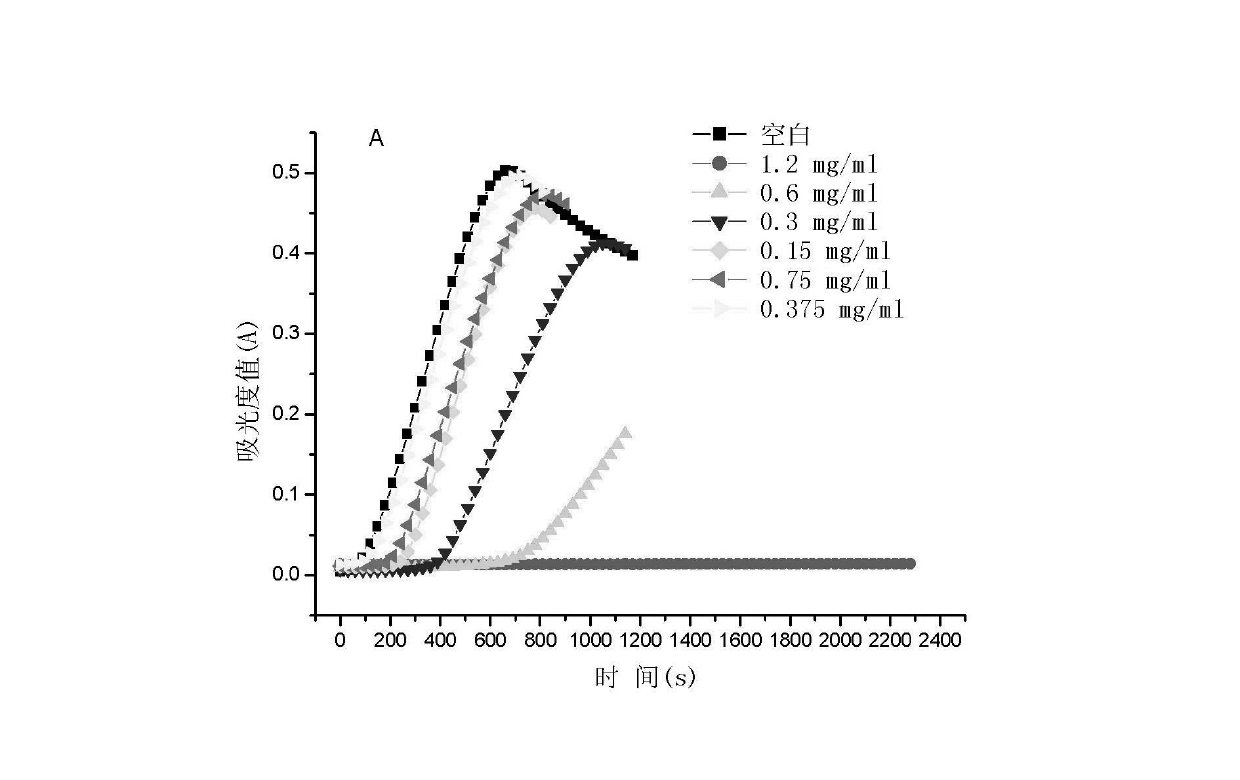
[0035]4) Through the test of inhibition of tyrosinase activity, it was proved that when the concentration of chlorella metallothionein was 1.2 mg / mL, the activity of monophenolase could not be displayed within 2300 s, and the activity of diphenolase could be reduced by 87%. , indicating that the protein has a strong whitening effect.
Embodiment 3
[0037] 1) Add ZnCl to Chlorella in logarithmic growth phase 2 , so that the final concentration of zinc in the algal fluid reached 5 μmol / L, and aerated for 120 hours.
[0038] 2) Algae cells were collected by centrifugation, and the cells were disrupted by ultrasonic waves in an ice bath (540 w, 1.2 s on and 3 s off each time), and observed with a microscope until the cells were completely disrupted. The supernatant was collected by centrifugation at 12000 r / min for 10 min.
[0039] 3) Same as steps (4) and (5) in Example 1
[0040] 4) Through the test of inhibition of tyrosinase activity, the half-inhibition concentration of metallothionein on monophenolase activity is 0.5 mg / mL, and the half-inhibition concentration of diphenolase activity is 0.7 mg / mL, indicating that the protein Has whitening function.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com