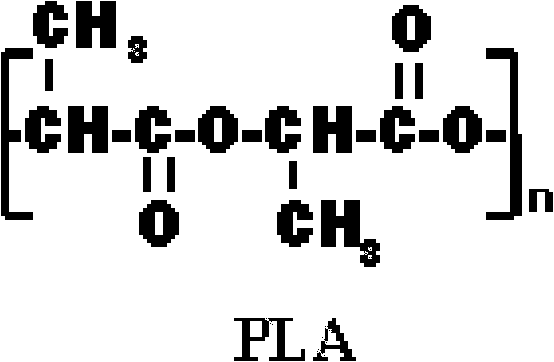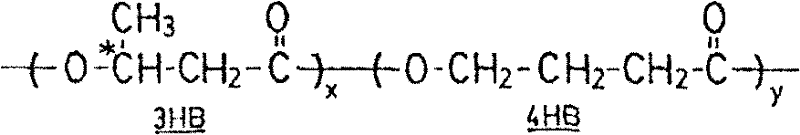Biological degradable film and laminated material
A technology for degrading films and laminates, used in layered products, synthetic resin layered products, non-woven fabrics, etc., can solve the problem of slow degradation rate and achieve the effect of improving mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0061] Although poly-3-hydroxybutyrate and poly-4-hydroxybutyrate polyester (P(3HB-co-4HB)) products are easily degraded in soil, sludge and seawater, the degradation rate in water lacking microorganisms Very slowly (Saito, Yuji, Shigeo Nakamura, Masaya Hiramitsu and Yoshiharu Doi, "Microbial Synthesis and Properties of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-4-Hydroxybutyrate)", International Polymer 39 (1996), 169- 174). Therefore, P(3HB-co-4HB) products have a very long shelf life in a clean environment, such as dry storage in a sealed package or storage in a wet wipe cleaning solution. However, discarded P(3HB-co-4HB) fabrics, films and packaging materials are very Easily degradable. It should be noted that polylactic acid (PLA) is not easily degraded in the above-mentioned dirty environment, but is easily corroded. The heat and moisture in the humus first break down the PLA polymer into shorter polymer chains and eventually into lactic acid. The humus and soil microbes then consume th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com