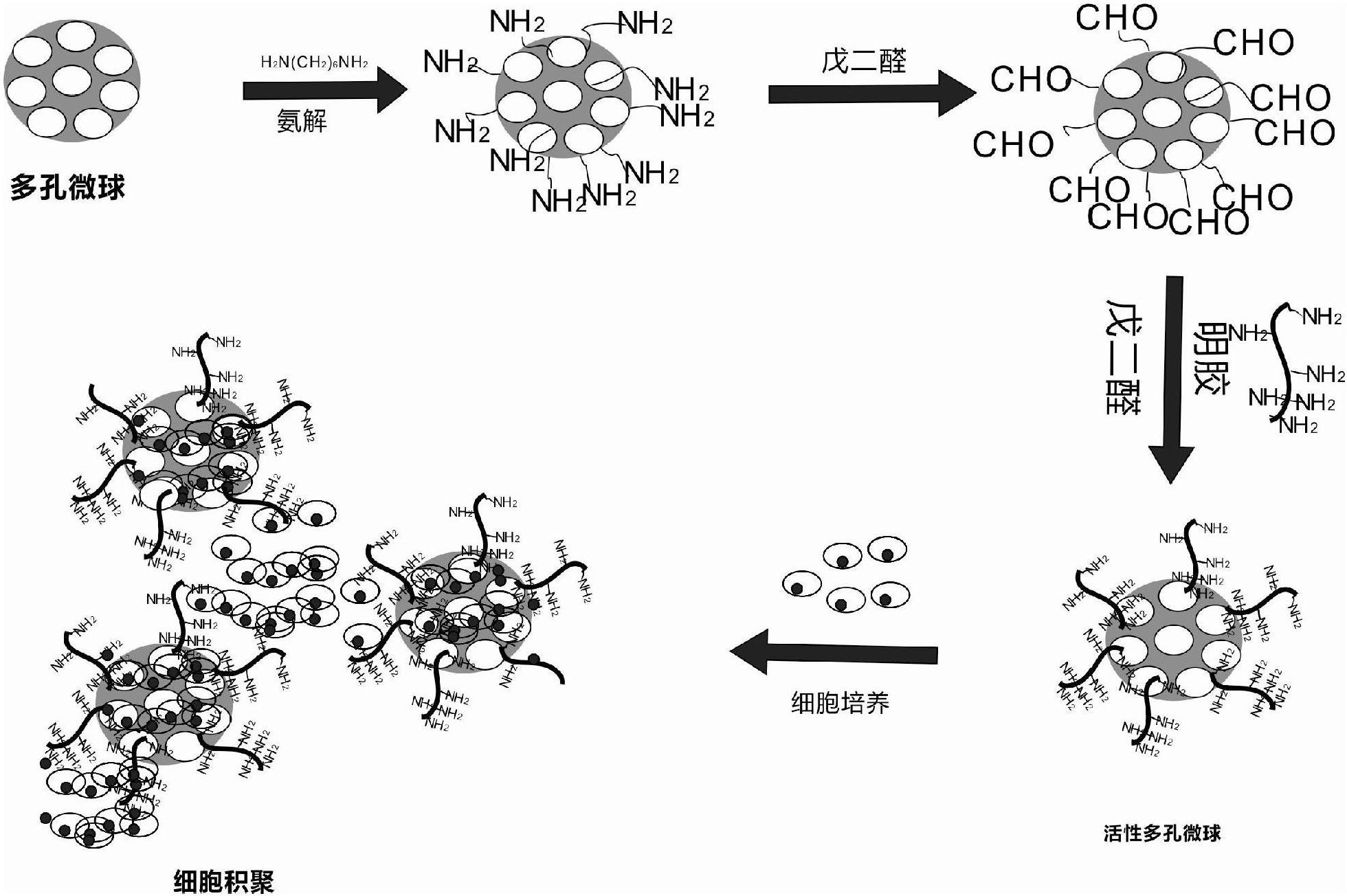
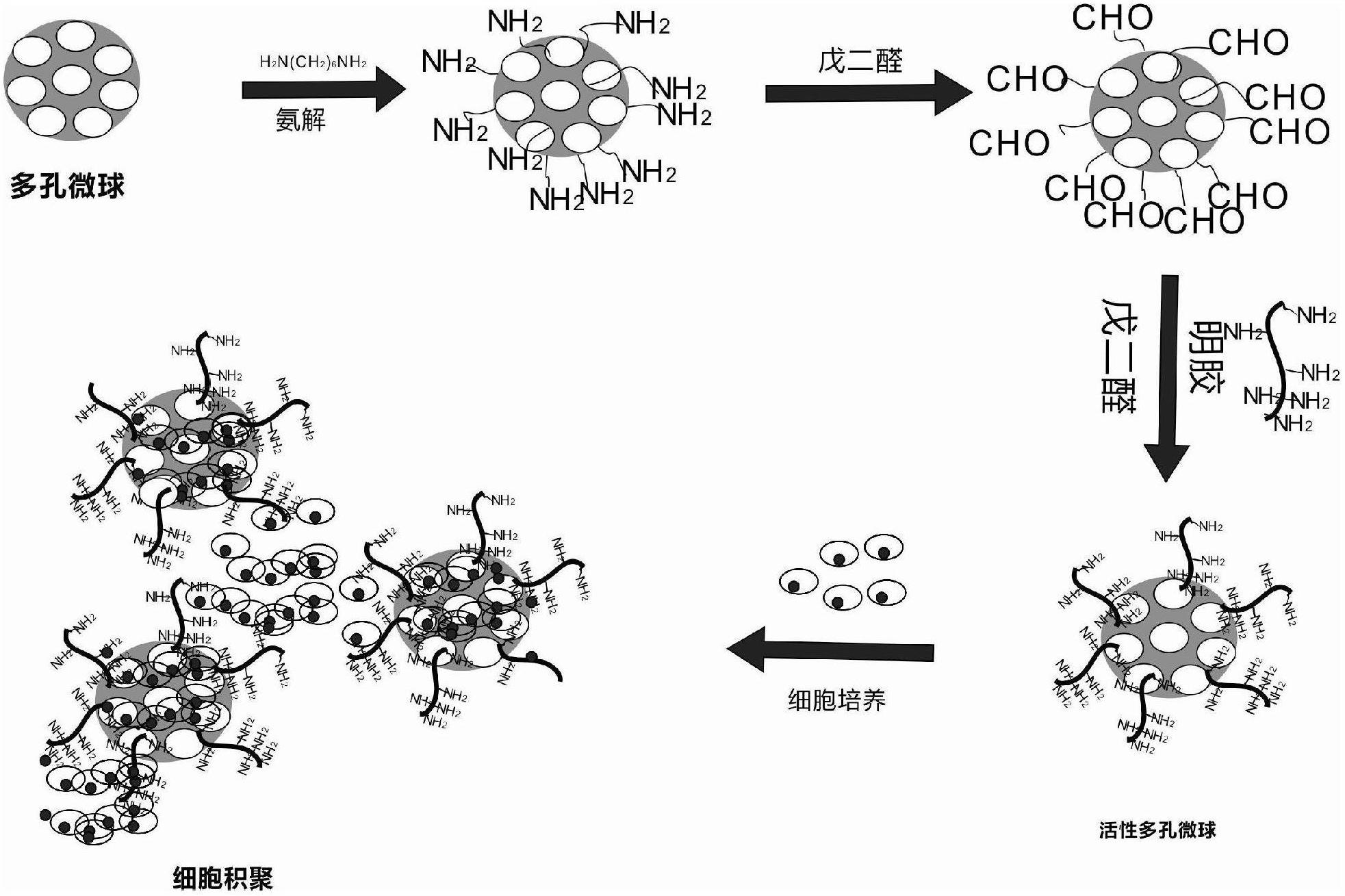
Active microspheres capable of directionally regulating and controlling chondrocyte accumulation and preparation method of active microspheres
A microsphere, bioactive technology, applied in the direction of bone/connective tissue cells, animal cells, vertebrate cells, etc., can solve the problem of lack of active regulatory cells and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] The preparation of embodiment 1 active porous microspheres:
[0017] (1) Preparation of porous polylactic acid polymer microspheres: 1.25ml of 5% NH 4 HCO 3 Solution (W 1 phase) was added to 4ml of polylactic acid polymer organic solution with a concentration of 3.13% (O phase), and then stirred at a high speed with a homogeneous mixer in an ice bath to obtain the primary emulsion (W 1 / O), quickly pour the resulting primary emulsion into 400ml 0.1% PVA aqueous solution (W 2 phase), mechanically stirred at room temperature to obtain a secondary emulsion (W 1 / O / W 2 ), the organic solvent volatilizes in the secondary emulsification process and finally obtains porous polylactic acid polymer microspheres, which are repeatedly washed with deionized water, and finally freeze-dried to obtain the desired microspheres; (2) chemical crosslinking: the porous polylactic acid polymer microspheres Soak the ball in 50ml ethanol / water (1 / 1, v / v) mixed solvent for 2-3 hours to rem...
Embodiment 2
[0018] The preparation of embodiment 2 active porous microspheres:
[0019] (1) Preparation of porous polylactic acid polymer microspheres: 1.25ml of 5% NH 4 HCO 3 Solution (W 1 phase) was added to 4ml of polylactic acid polymer organic solution with a concentration of 3.13% (O phase), and then stirred at a high speed with a homogeneous mixer in an ice bath to obtain the primary emulsion (W 1 / O), quickly pour the obtained primary emulsion into 400ml of 0.1% PVA aqueous solution (W 2 phase), mechanically stirred at room temperature to obtain a secondary emulsion (W 1 / O / W 2), the organic solvent volatilizes in the secondary emulsification process and finally obtains porous polylactic acid polymer microspheres, which are repeatedly washed with deionized water, and finally freeze-dried to obtain the desired microspheres; (2) chemical crosslinking: the porous polylactic acid polymer microspheres Soak the ball in 50ml ethanol / water (1 / 1, v / v) mixed solvent for 2-3 hours to re...
Embodiment 3
[0020] The preparation of embodiment 3 active porous microspheres:
[0021] (1) Preparation of porous polylactic acid polymer microspheres: 1.25ml of 5% NH 4 HCO 3 Solution (W 1 phase) was added to 4ml of polylactic acid polymer organic solution with a concentration of 3.13% (O phase), and then stirred at a high speed with a homogeneous mixer in an ice bath to obtain the primary emulsion (W 1 / O), quickly pour the resulting primary emulsion into 400ml 0.1% PVA aqueous solution (W 2 phase), mechanically stirred at room temperature to obtain a secondary emulsion (W 1 / O / W 2 ), the organic solvent volatilizes in the secondary emulsification process and finally obtains porous polylactic acid polymer microspheres, which are repeatedly washed with deionized water, and finally freeze-dried to obtain the desired microspheres; (2) chemical crosslinking: the porous polylactic acid polymer microspheres Soak the ball in 50ml ethanol / water (1 / 1, v / v) mixed solvent for 2-3 hours to rem...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com